Containerization Benefits
Team A selected containerization for their CRM application to achieve:- Portability
- Scalability
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Enhanced security
Risk of Untrusted Base Images
In the rush to deploy, Team A used alatest-tagged base image from Docker Hub without verifying its origin or maintenance status. While the container spun up successfully, the CRM soon experienced performance degradation and instability.
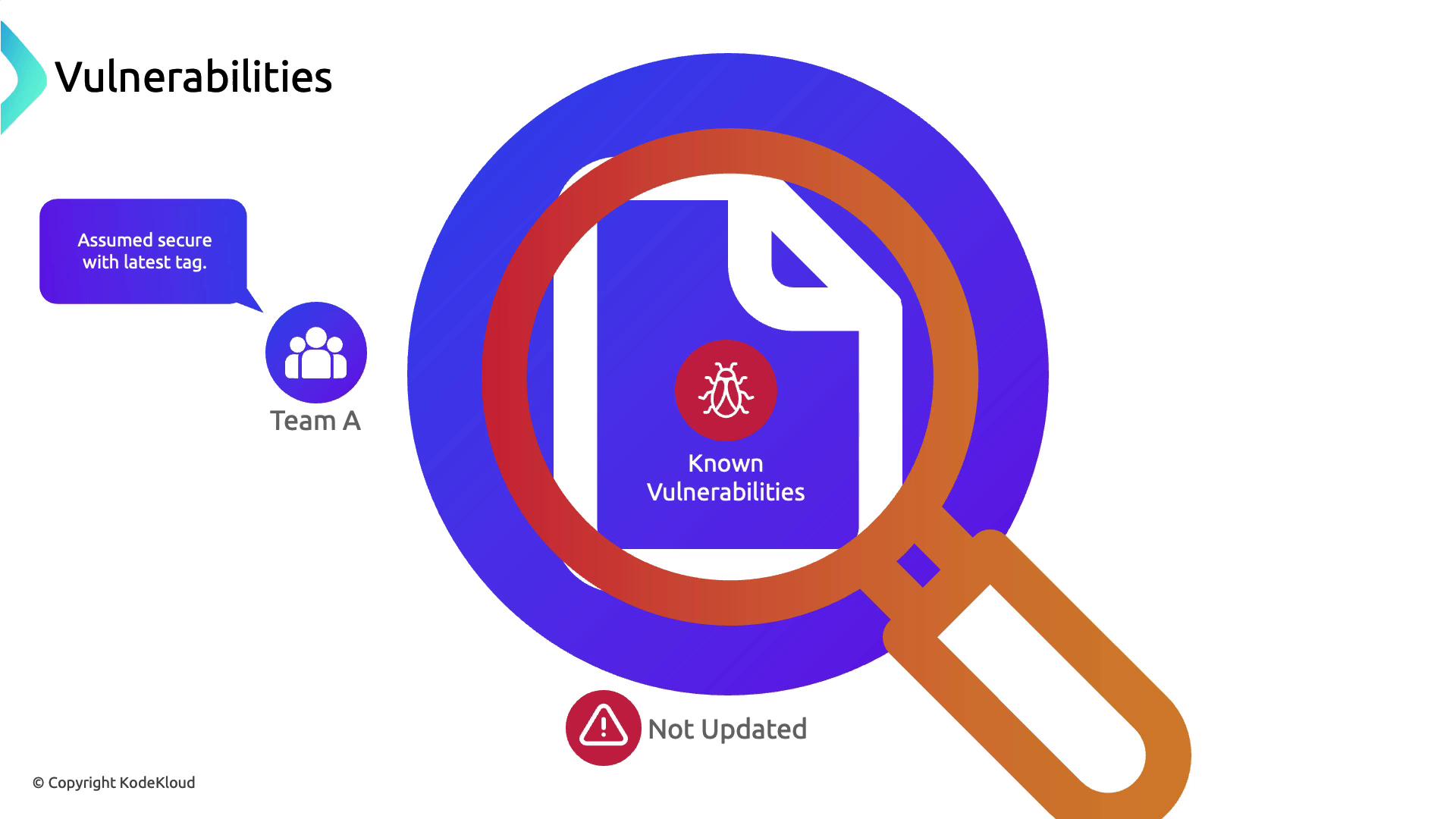
latest image, which attackers exploited to compromise data integrity and leak customer information.

Relying on the
latest tag does not ensure up-to-date security patches. Image maintainers can assign it arbitrarily, leaving you exposed to risks.Integrating Vulnerability Scanning
To prevent future incidents, Team A added automated scanning tools into their CI/CD pipeline:
| Scanner | Description | Command Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trivy | Lightweight, fast vulnerability scanner | trivy image <image> |
| Clair | Static analysis of vulnerabilities in images | clair-scanner --ip <host-ip> <image> |
Adopting Minimal Official Base Images
After remediating all discovered flaws, Team A switched to an officially maintained minimal image (Ubuntu or Alpine). This approach reduces the attack surface and ensures timely security updates.
Understanding Build Artifacts
Any output from your build process—compiled binaries, JAR/WAR files, logs, reports, and especially container images—counts as a build artifact.
Storing Container Images
While Docker Hub is popular for hosting images, it has limited access controls and no built-in vulnerability scanning.
| Repository | Access Control | Scanning | Image Signing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docker Hub | Basic | No | No |
| Nexus Repository | Fine-grained | Via add-on | Limited |
| GitHub Packages | Fine-grained | Yes | Yes |
| JFrog Artifactory | Fine-grained | Yes | Yes |
Advanced Artifact Repositories
For stricter compliance, consider:- Nexus Repository (https://www.sonatype.com/nexus-repository-oss)
- GitHub Packages (https://github.com/features/packages)
- JFrog Artifactory (https://jfrog.com/artifactory/)

JFrog Artifactory Security
JFrog Artifactory continuously scans stored images, integrates with vulnerability tools, and can enforce digital signatures to guarantee image authenticity.
Digital signatures on images detect unauthorized modifications and improve supply chain security.

Next Steps
- Integrate automated scans in your CI/CD pipeline.
- Standardize on minimal, official base images.
- Use a robust artifact repository with access controls and signing.
- Continuously monitor and update images to address new vulnerabilities.