Exposed Docker ports (2375) allow unauthenticated remote container management. Always restrict access or enable TLS authentication.
Threat Management and Response
All three major cloud platforms offer managed SIEM/SOAR-style tools for continuous threat monitoring and automated response.| Provider | Service | Description | Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure | Azure Sentinel | Integrated SIEM + SOAR for threat detection, hunting, and automated playbooks. | https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/sentinel |
| AWS | Amazon GuardDuty | ML-driven threat detection for AWS accounts and workloads, no rule authoring required. | https://aws.amazon.com/guardduty |
| GCP | Security Command Center (SCC) | Centralized dashboard for asset inventory, vulnerability scanning, and threat insights. | https://cloud.google.com/security-command-center |

Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
To defend against OWASP Top 10 attacks and DDoS, each provider offers a native WAF solution.| Provider | Service | Key Features | Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure | Azure WAF | Integrated with Application Gateway, OWASP rule sets, custom rules. | https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/web-application-firewall |
| AWS | AWS WAF | Custom rule creation, integration with CloudFront & ALB, real-time metrics. | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/waf |
| GCP | Cloud Armor | DDoS protection, geo-based access controls, custom security policies. | https://cloud.google.com/armor |
Container Security
Container orchestration platforms combine built-in controls with ecosystem tools to enforce runtime and image compliance.| Provider | Service | Security Features | Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Control-plane hardening, Azure Policy integration, image scanning. | https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/aks |
| AWS | Amazon EKS + Bottlerocket | Bottlerocket OS, kube-bench CIS checks, IAM roles for service accounts. | https://aws.amazon.com/eks https://aws.amazon.com/bottlerocket |
| GCP | Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Private clusters, Anthos policy enforcement with OPA, binary authorization. | https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine https://www.openpolicyagent.org/ |
Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security is a partnership: the provider secures the cloud infrastructure, and you secure your workloads in the cloud.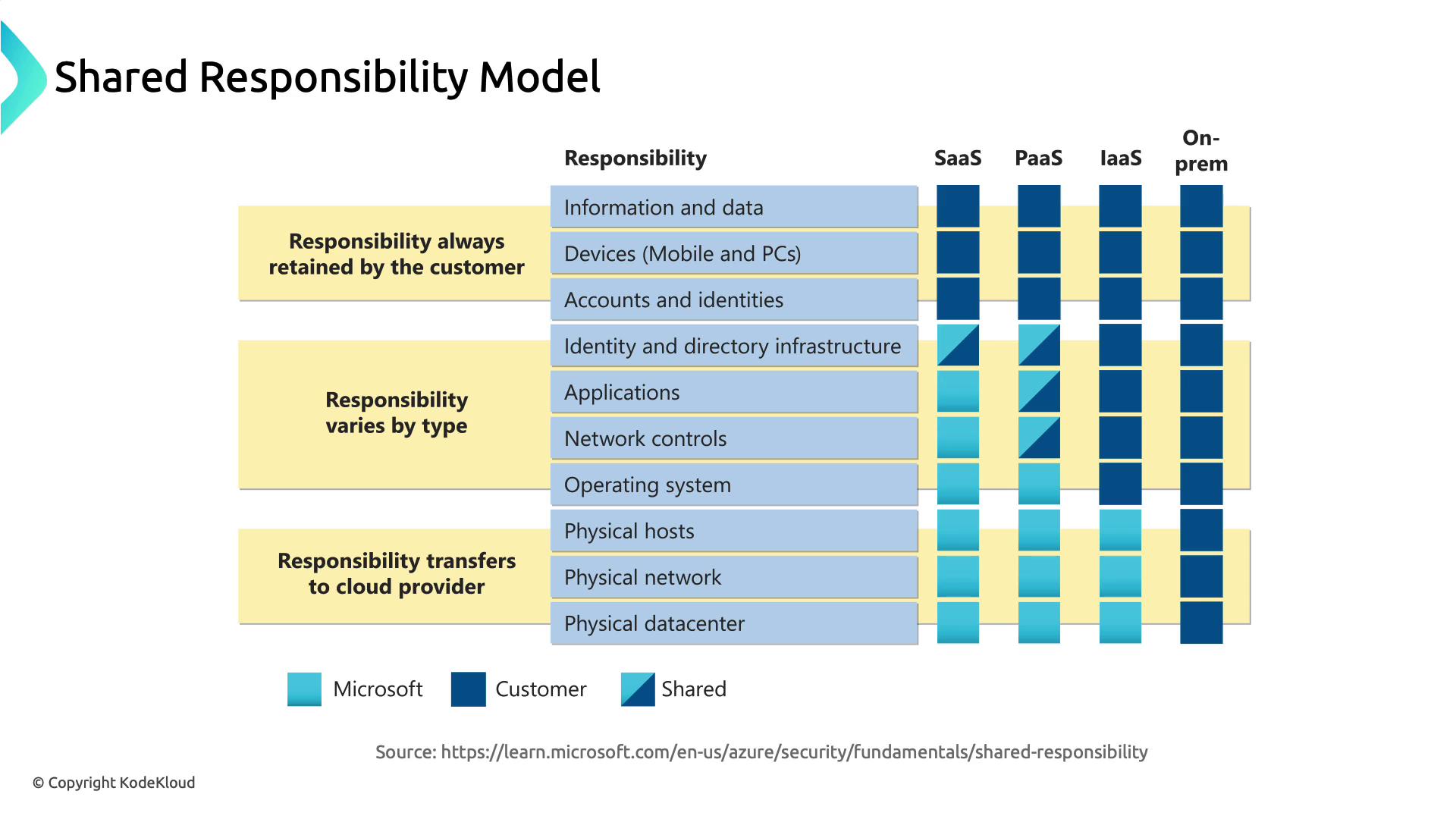
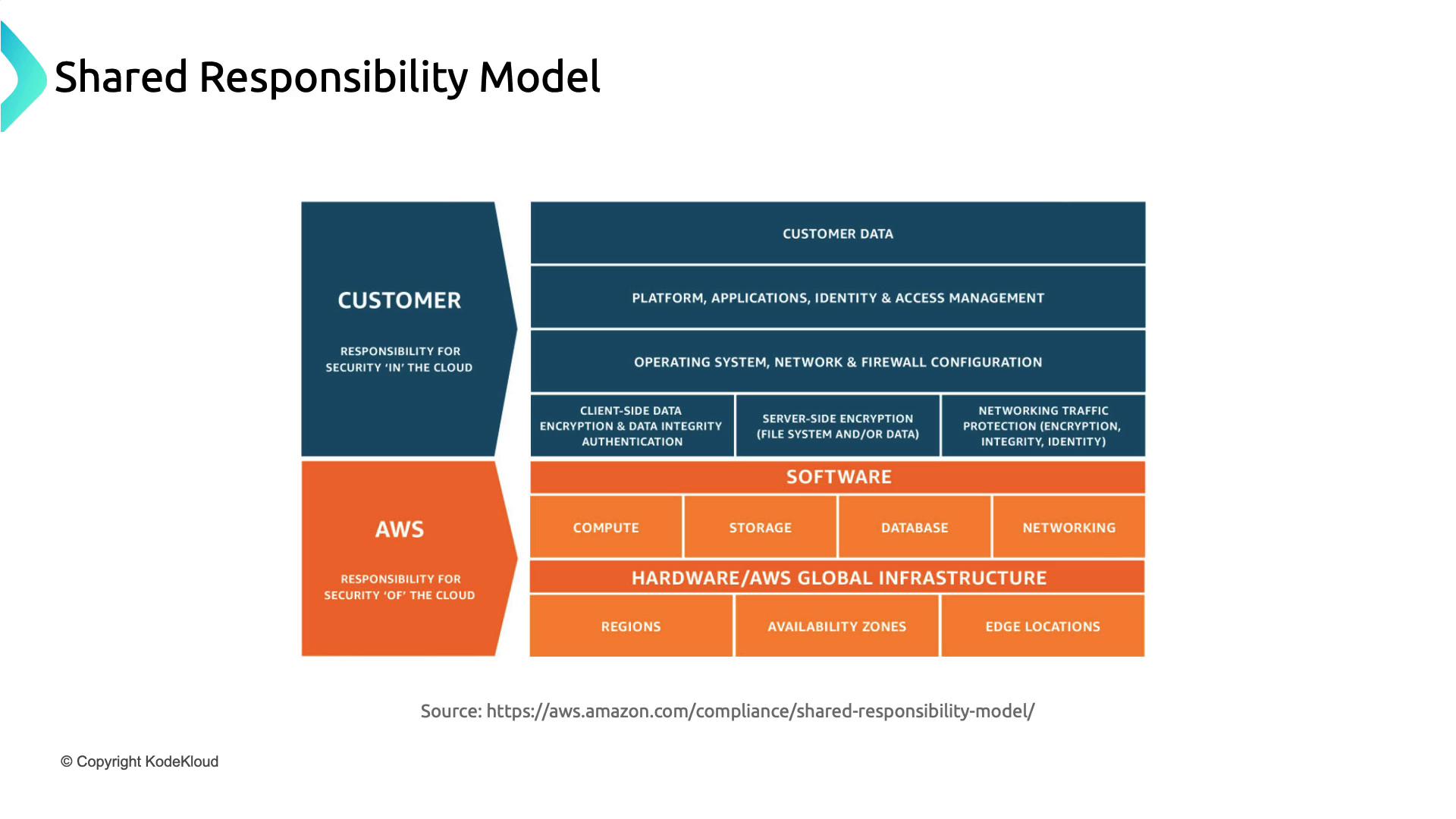
Review the shared responsibility matrix for each cloud provider to ensure you cover all security controls—from networking rules to application hardening.
In this article, we examined how Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud approach:
- Threat Management & Response
- Web Application Firewalls
- Container Security
- The Shared Responsibility Model