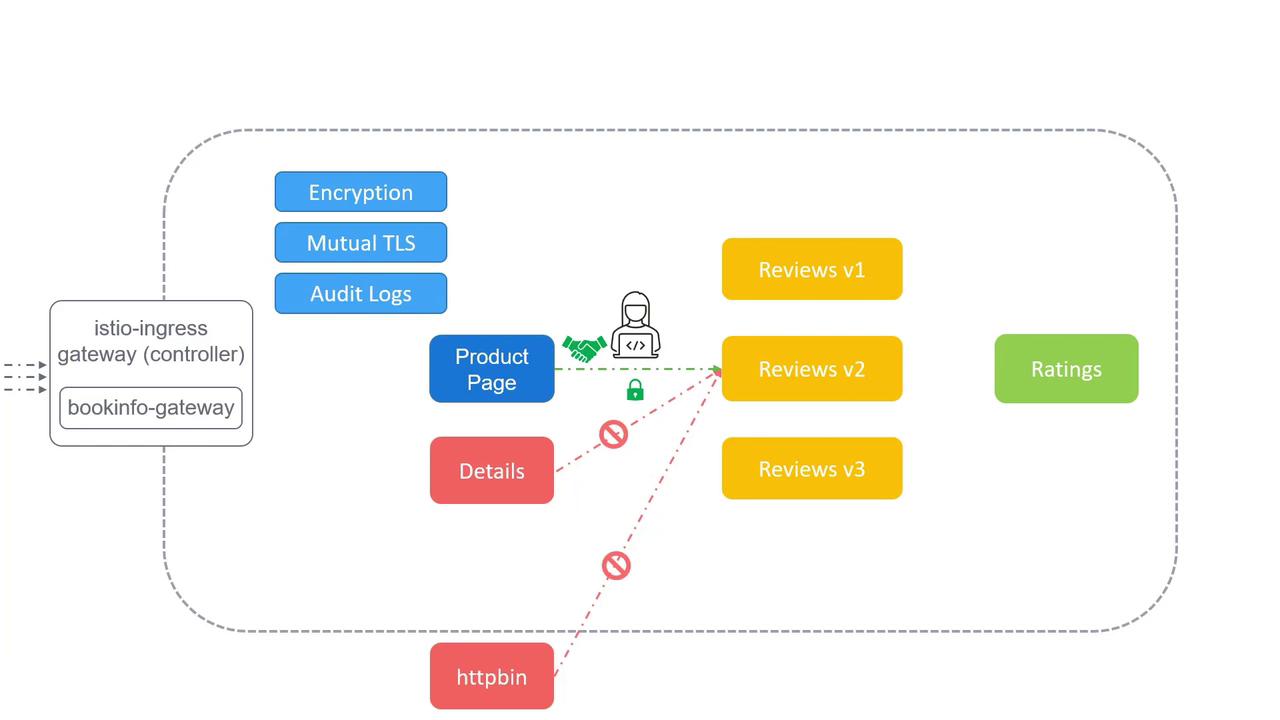
- Encryption of service-to-service traffic to prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
- Fine-grained access control to restrict which services can communicate.
- Audit logging to capture who accessed which service and when.
- How to enable and configure mTLS in Istio
- Defining access control policies with
AuthorizationPolicy - Collecting and analyzing audit logs for compliance and forensics
1. Mutual TLS (mTLS)
Istio’s mTLS ensures that both client and server authenticate each other and encrypt all data in transit. This prevents eavesdropping and tampering by default.Enabling mTLS
- Namespace-wide PeerAuthentication
- DestinationRule for TLS settings
Strict mTLS mode requires that all workloads have the Istio sidecar injected. Use
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled if sidecars are missing.2. Access Control Policies
Istio’sAuthorizationPolicy CRD lets you define which services can talk to each other. You can permit or deny traffic based on namespaces, principals, ports, and even request attributes.
Sample AuthorizationPolicy
productpage service account to call reviews, blocking all other callers.
Common Policy Patterns
| Use Case | Resource | Key Field |
|---|---|---|
| Allow only one service as caller | AuthorizationPolicy | source.principals |
| Block traffic from unknown sources | AuthorizationPolicy | no from entry |
| Port-based access control | AuthorizationPolicy | to.ports |
Misconfigured policies can inadvertently block legitimate traffic. Always test changes in a staging environment before promoting to production.
3. Audit Logging
Istio captures detailed telemetry and access logs, which you can export to backends like Prometheus, Elasticsearch, or Stackdriver.Enabling Access Logging
- MeshConfig with accessLogFile:
- EnvoyFilter for custom log format: