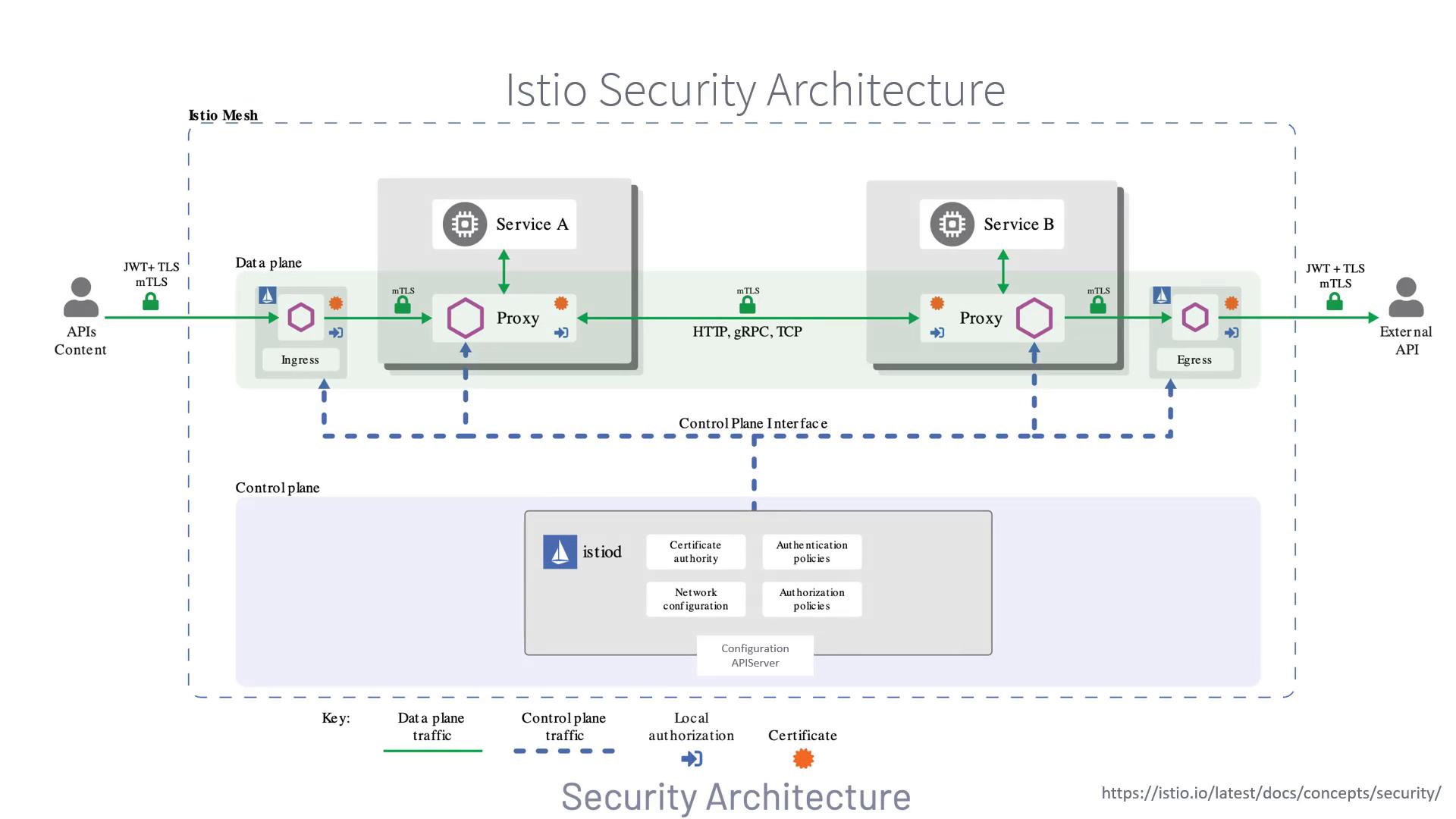
The following diagram illustrates Istio’s security architecture. It shows secure service-to-service communication via Envoy sidecars, how ingress and egress gateways handle external traffic, and how the istiod control plane manages certificates and policies.
1. istiod Control Plane as Certificate Authority
At the heart of Istio security, the istiod component serves as a built-in certificate authority (CA). It:- Issues, rotates, and revokes workload certificates and private keys
- Manages SPIFFE-based identities for workloads
- Provides a configuration API server for distributing security policies
How Certificate Issuance Works
- When a new workload starts, its Envoy sidecar contacts the local Istio agent.
- The agent requests a signed certificate and private key from istiod.
- Istiod signs the CSR (Certificate Signing Request) and returns credentials.
- The proxy establishes mTLS connections to other services using these certs.
2. Authentication, Authorization, and Secure Naming
Istio’s configuration API server (part of istiod) pushes the following policies to each Envoy proxy:- Authentication Policies: Define which workloads require mTLS or JWT verification.
- Authorization Policies: Control access based on attributes like
source.principalorrequest.headers. - Secure Naming: Ensures that only services with valid SPIFFE identities can communicate.
3. Data Plane Proxies: Sidecars, Ingress, and Egress Gateways
All traffic—both internal and external—flows through Envoy proxies:| Component | Role | Example Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Sidecar Proxy | Intercepts and secures pod-to-pod traffic | sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true" |
| Ingress Gateway | Terminates external traffic, applies edge policies | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 ingress specs |
| Egress Gateway | Controls and monitors external egress, policy checks | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 egress specs |
Traffic Flow
- Internal: Service A → its Envoy sidecar (mTLS) → Service B’s sidecar → Service B
- Ingress: External client → Ingress Gateway → Destination sidecar
- Egress: Service sidecar → Egress Gateway → External service
4. Mutual TLS Handshake
- Sidecar A presents its certificate to Sidecar B.
- Sidecar B verifies the certificate against Istio’s root CA.
- Both proxies agree on encryption keys.
- Secure channel established—data is encrypted, authenticated, and authorized.