What Is a CVE?
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is the industry-standard database for public security flaws. Each vulnerability gets a unique identifier, helping you avoid duplicates and streamline research.Visit the CVE Database to search for published vulnerabilities and track remediation status.

- Unauthorized access bypasses (e.g., confidential data exposure)
- Denial-of-service or performance degradation bugs
Understanding CVSS Severity Ratings
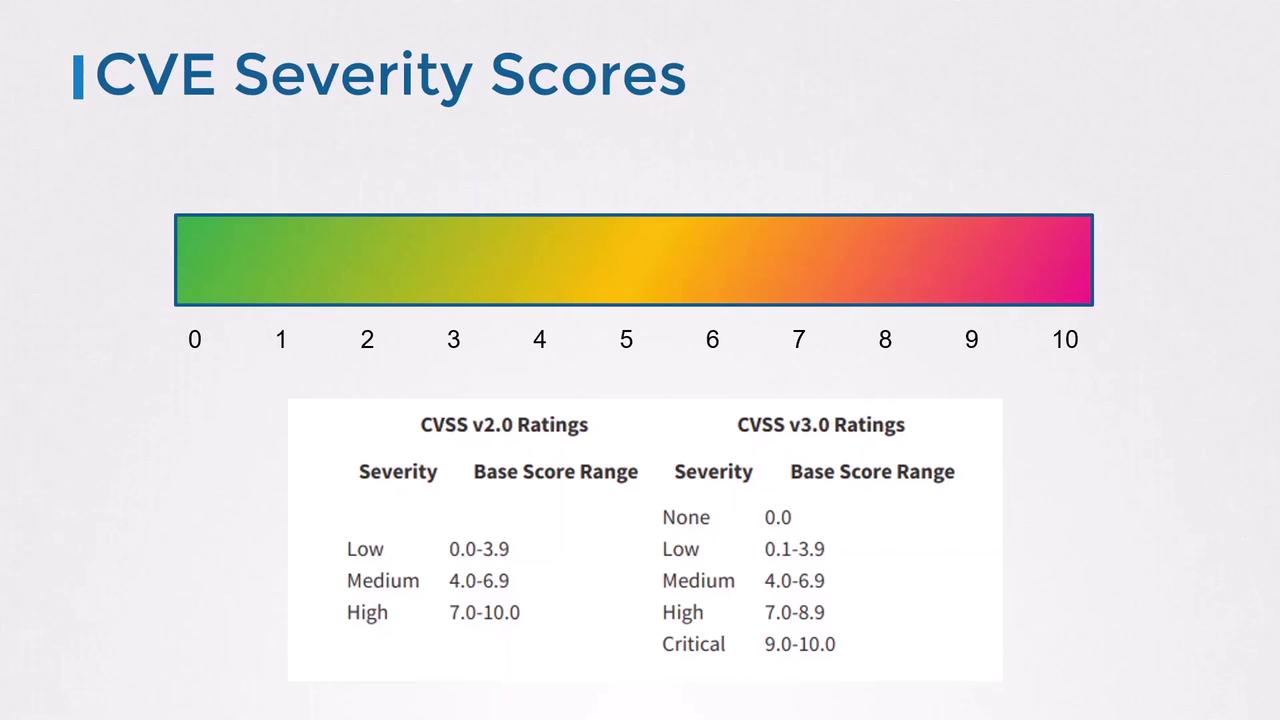
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides both a numeric score (0–10) and a qualitative severity label. Use the table below to interpret scores:| Severity | CVSS Score Range |
|---|---|
| None | 0.0 |
| Low | 0.1 – 3.9 |
| Medium | 4.0 – 6.9 |
| High | 7.0 – 8.9 |
| Critical | 9.0 – 10.0 |
Example: CVE-2020-5911
CVE-2020-5911 affects the NGINX Ingress Controller installer on Debian/Ubuntu by downloading packages over HTTP instead of HTTPS. Its CVSS base score is 7.3 (High), indicating a serious risk.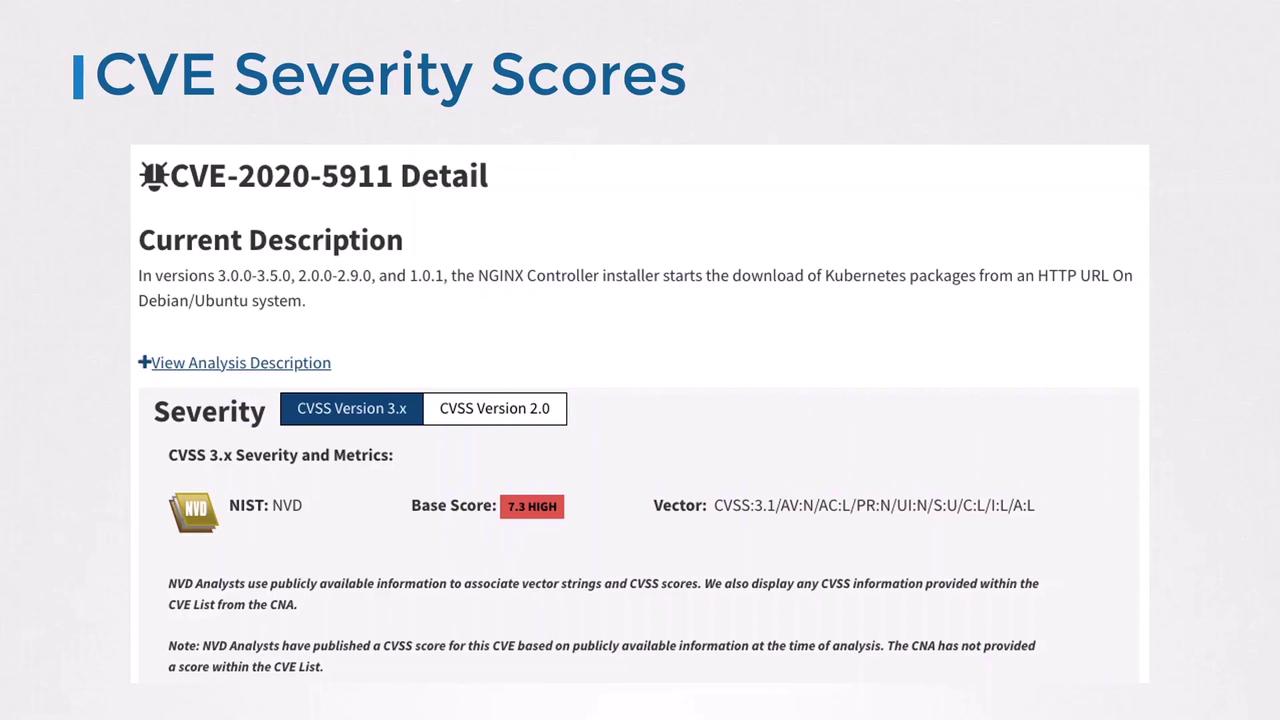
Why Scan Container Images?
Containers often bundle multiple libraries and OS packages, each a potential vector for attacks. Automated scanners help you:- Identify and upgrade vulnerable packages
- Apply patches or workarounds
- Remove unused components to reduce risk
Container Vulnerability Scanner: Trivy
Trivy by Aqua Security is a fast, user-friendly scanner that integrates easily into Docker workflows and CI/CD pipelines.Installing Trivy on Debian/Ubuntu
Running a Basic Scan
Filtering and Advanced Options
Using
--ignore-unfixed can hide critical risks if no patch is available. Always review the full report before deployment.Reduce Your Image’s Attack Surface
Smaller base images generally contain fewer vulnerabilities. Compare these scan results:| Image | Total CVEs |
|---|---|
| nginx:1.18.0 (debian) | 155 |
| nginx:1.18.0-alpine | 0 |

Image Scanning Best Practices
- Continuously re-scan images to catch newly disclosed CVEs
- Enforce admission controls to block or quarantine unscanned or unsafe images
- Maintain an internal registry of pre-scanned, approved images for rapid rollouts
- Integrate scanning into CI/CD pipelines so that every build is audited at source