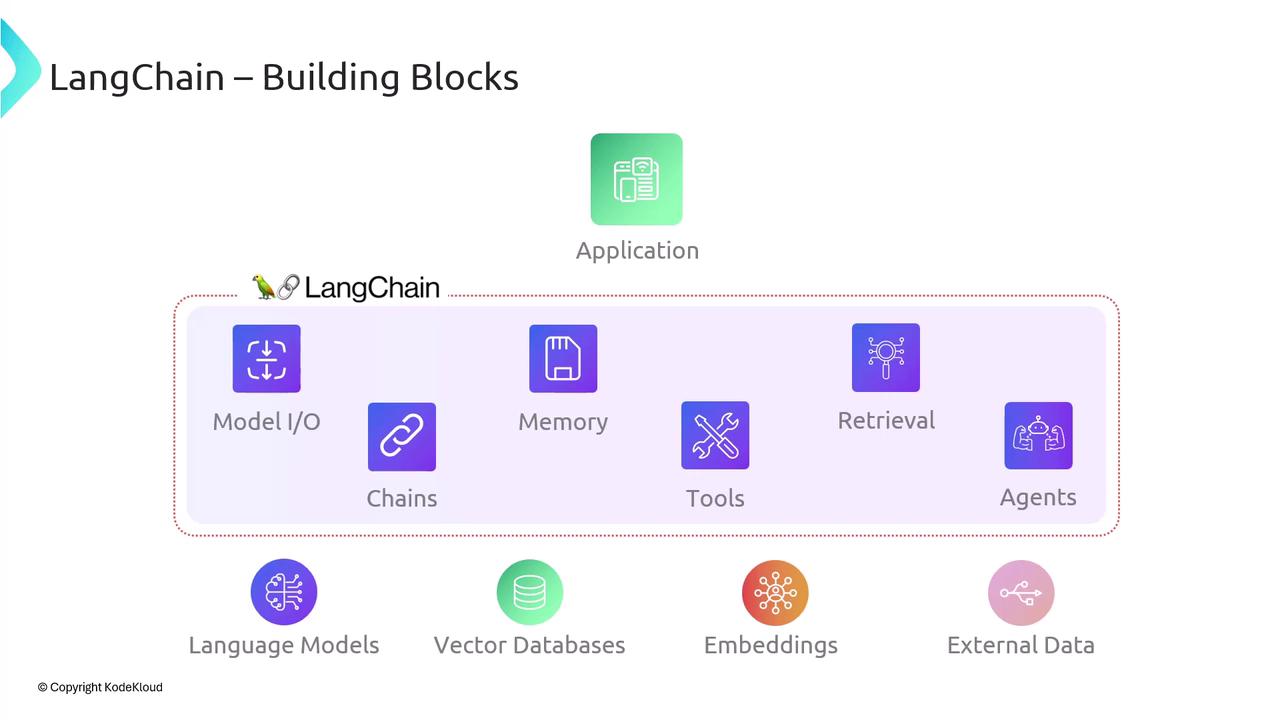
| Component | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Model I/O | Manages prompt formatting, response parsing, and streaming | OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face |
| Memory | Persists conversational context or state | Redis, in-memory cache |
| Retrieval | Retrieves relevant documents or embeddings | Pinecone, FAISS, Weaviate |
| Agents | Orchestrates decision-making across tools and APIs | Custom toolkits, action chains |
| Embeddings | Converts text into vectors for similarity search | OpenAI Embeddings, Cohere |
| External Data | Integrates external knowledge sources (databases, APIs) | SQL/NoSQL, RESTful APIs |