Linux System Administration for Beginners
Essential Commands
Create Delete Copy and Move Files and Directories
Managing files and directories is a foundational skill for any Linux user or administrator. In this guide, you’ll learn how to list, create, copy, move (or rename), and delete files and directories using core commands like ls, touch, mkdir, cp, mv, and rm.
Listing Files and Directories with ls
The ls (list) command displays directory contents. By default, hidden files (those beginning with .) are not shown.
Common ls Usage
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| (none) | Show non-hidden items | ls |
-a | Include all entries, including . files | ls -a |
-l | Long format (permissions, owner, size) | ls -l /var/log |
-h | Human-readable sizes (use with -l) | ls -lh |
-alh | Combine all flags | ls -alh |
Basic Listing
$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Videos
Including Hidden Files
$ ls -a
. .. .bashrc .ssh Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Videos
Detailed, Human-Readable Output
$ ls -alh
total 76K
drwx------. 16 aaron aaron 4.0K Nov 1 17:57 .
drwxr-xr-x. 7 root root 4.0K Oct 26 16:54 ..
-rw------- 1 aaron aaron 5.0K Nov 1 17:56 .bash_history
...
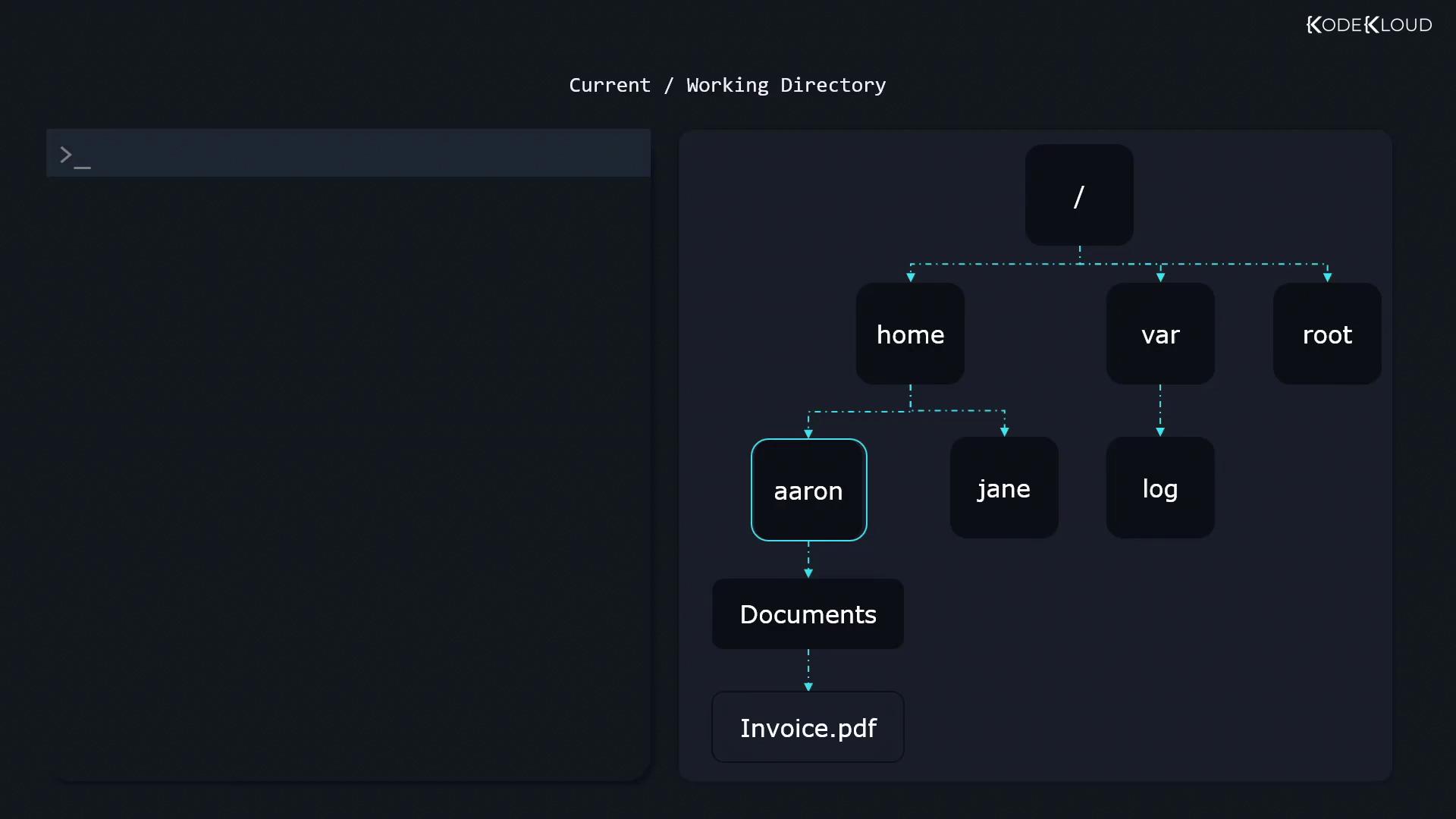
Understanding the Linux File System Tree
Linux files and directories form an inverted tree with / as the root. Every path you use is either absolute (from /) or relative (from your current directory).
//home/home/aaron/home/aaron/Documents/home/aaron/Downloads
/var/etc
Absolute vs. Relative Paths
Absolute paths start with / and always refer to the same location.
Relative paths begin from your current directory (check with pwd).
Absolute Path
/home/aaron/Documents/invoice.pdf
Relative Path
$ pwd
/home/aaron
# From /home/aaron, this goes to invoice.pdf inside Documents
$ cd Documents
$ ls invoice.pdf
To move up one level:
$ cd ..
Jump to your home directory:
$ cd
$ pwd
/home/aaron
Creating Files and Directories
- Create an empty file:
$ touch receipt.pdf - Create a directory:
$ mkdir receipts
Both commands accept absolute or relative paths:
$ mkdir /home/aaron/new_folder
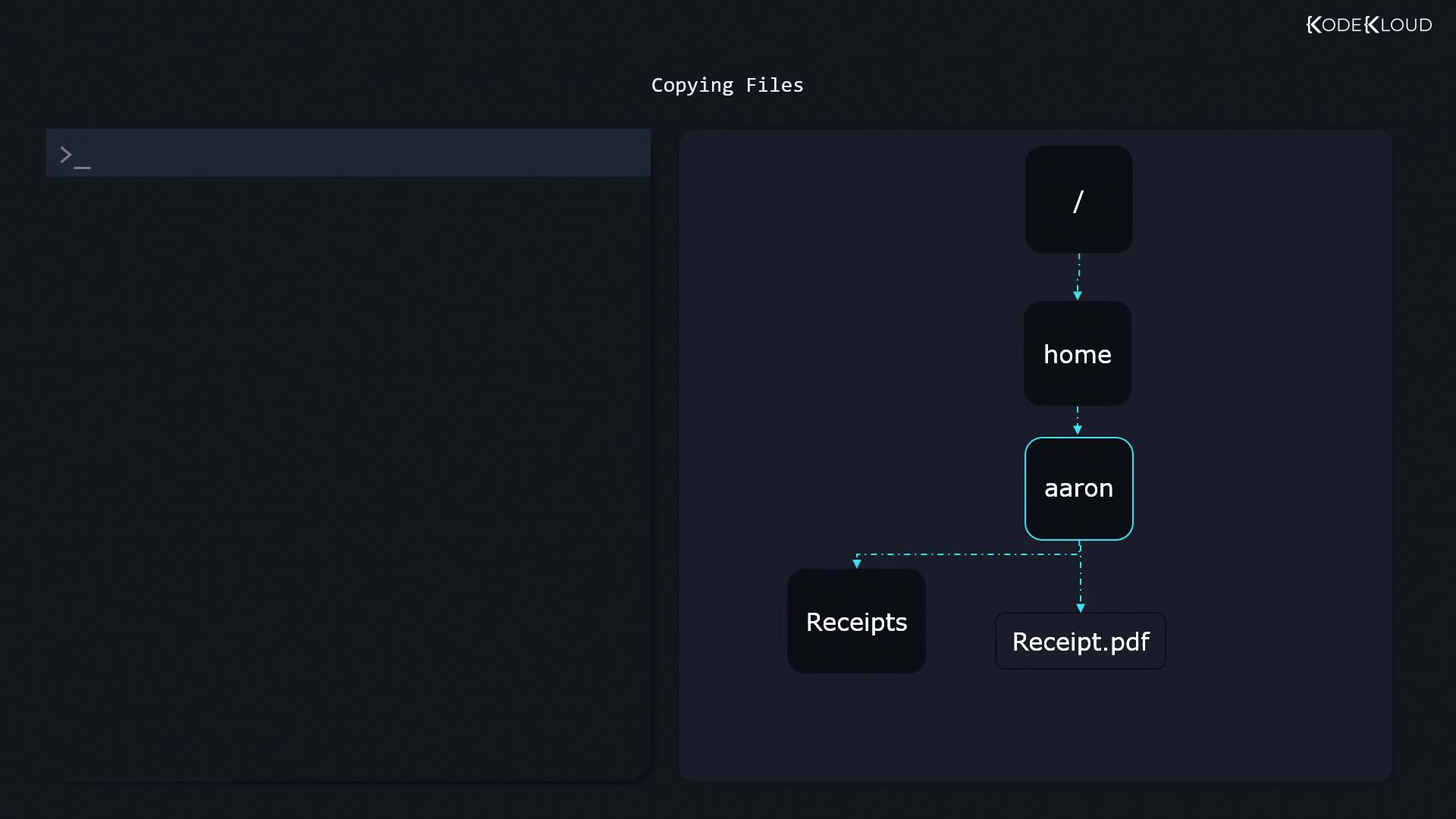
Copying Files and Directories with cp
Use cp to duplicate files and directories.
Copying a Single File
$ cp receipt.pdf receipts/
To copy and rename at the same time:
$ cp receipt.pdf receipts/receipt_backup.pdf
Copying Directories Recursively
$ cp -r Receipts/ BackupOfReceipts/
This duplicates the entire Receipts folder and its contents into BackupOfReceipts. Ensure the destination name does not already exist to avoid nesting.
Moving and Renaming with mv
The mv command handles both moving and renaming:
- Move a file:
$ mv receipt.pdf receipts/ - Rename a file:
$ mv receipt.pdf old_receipt.pdf - Rename or move a directory:
$ mv receipts/ old_receipts/
No recursive flag is needed for directories; mv automatically moves contents.
Deleting Files and Directories with rm
Use caution when removing files and directories:
- Remove a file:
$ rm invoice.pdf - Remove a non-empty directory:
$ rm -r invoices/
Warning
The rm -r command permanently deletes directories and their contents. Always double-check the path before pressing Enter!
References
Watch Video
Watch video content