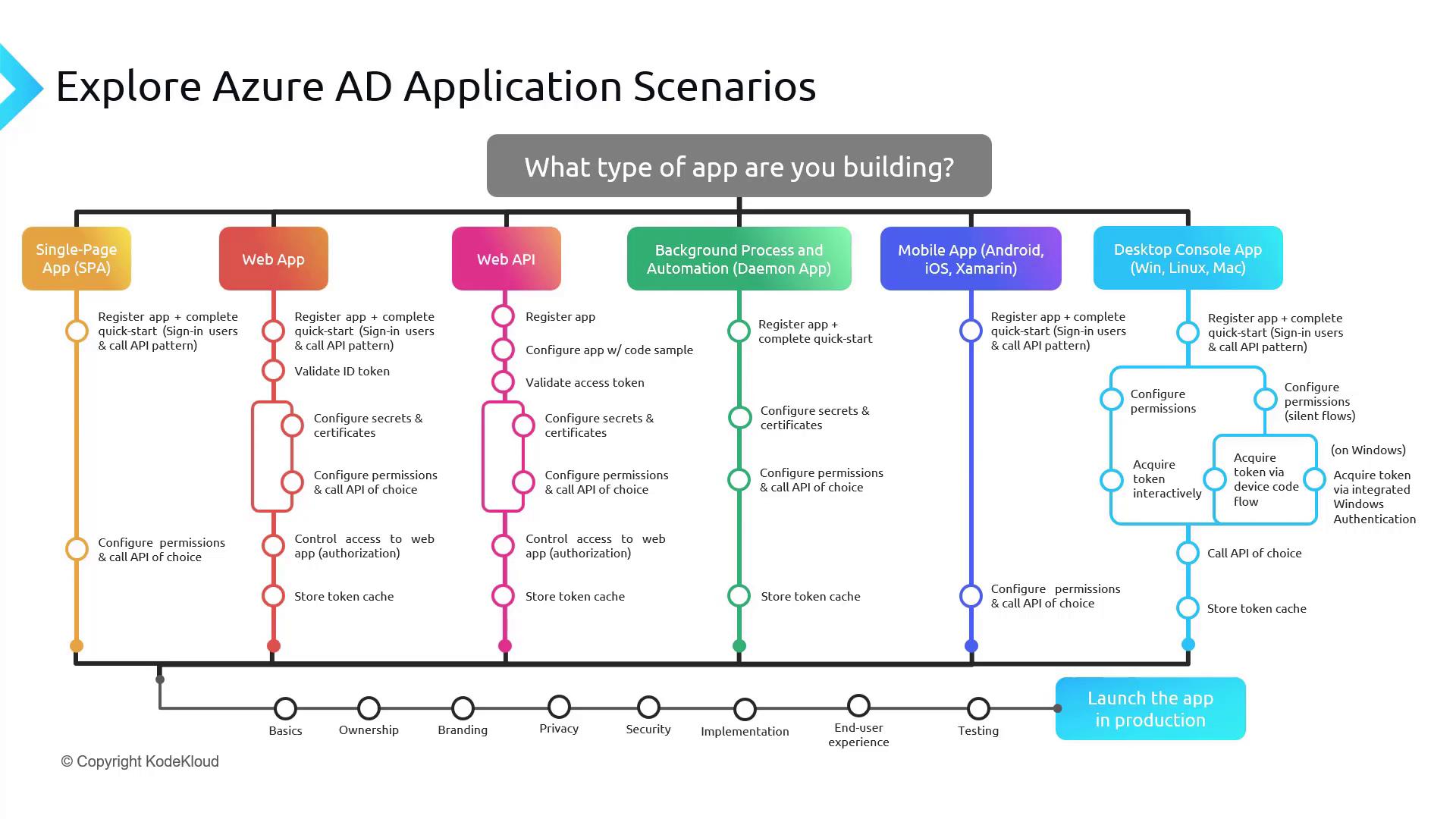
Single-Page Applications (SPA)
For instance, consider a lightweight React application used as an internal company dashboard. A typical SPA integration workflow involves:-
App Registration and Kickstart
Register the SPA with Azure AD and configure the authentication flows to get started. -
Authentication Flow Implementation
Implement the OAuth2/OpenID Connect flow so that users can sign in and obtain tokens. These tokens are usually stored in local or session storage, with the storage strategy selected based on token expiration and security considerations. -
API Permissions
Grant the SPA the necessary permissions to access APIs such as the Microsoft Graph API for retrieving user profile data for the dashboard.
Web Applications
Consider a .NET Core web application designed for a cloud-based document management system. The process includes:-
Registration and Setup
Register the web application in Azure AD and integrate with OpenID Connect middleware to support user sign-in. -
Token Validation
Upon successful authentication, validate the received ID token to ensure its integrity. -
Secrets, Certificates, and API Permissions
- Secure any secrets and certificates using services like Azure Key Vault.
- Configure API permissions (for instance, granting access to the SharePoint API).
-
Access Control
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) within the application to manage user privileges. -
Token Storage
Cache tokens using session stores or distributed caches to enhance application scalability.
Web APIs
For a RESTful API built with Node.js serving data to a mobile application, the Azure AD integration process is as follows:-
App Registration
Register the API with Azure AD to ensure proper identification. -
Integration Code
Use sample code from Azure documentation as a foundation for implementing token-based authentication. -
Access Token Validation
Validate access tokens provided by API consumers before processing any data, ensuring only authorized requests are served. -
Secrets and Certificates
Store required secrets securely (e.g., in Azure Key Vault) and configure necessary API permissions such as for Microsoft Graph API. -
Authorization
Utilize RBAC or similar mechanisms to protect sensitive endpoints. -
Token Storage
Cache validated tokens as needed for efficiency in subsequent requests.
Background Processes and Automation (Daemons)
For background processes, such as a Python script scheduled to sync data between an on-premises and a cloud database, follow these integration steps:-
App Registration
Begin by registering the background process with Azure AD. -
Authentication Configuration
Configure your Python script using the appropriate authentication flow. Azure documentation provides sample code to simplify this setup. -
Secrets and Certificates Management
Use Azure Key Vault or a similar solution to manage secrets and certificates securely. -
API Permissions
Configure the necessary permissions to allow your process to access required APIs or databases. -
Token Storage
Securely cache tokens and reuse them based on your scheduling and refresh logic.
Mobile Applications
A mobile app—whether on iOS or Android—like an employee meeting room booking system, follows a comparable integration process:-
Registration and Kickstart
Register the mobile application with Azure AD to establish its configuration. -
API Permissions Configuration
Define API permissions for the mobile app to access services like the Microsoft Booking API or any custom internal API. -
Token Acquisition and Caching
After authentication, acquire a token and cache it appropriately for future API calls.
Desktop Console Applications
Desktop applications, such as a .NET Core console application for system administrators managing user roles, involve these steps:-
App Registration
Register the desktop app in Azure AD to initiate its setup. -
Workflow Options
- Silent Flow: For domain-joined machines, implement a silent flow using Windows authentication or Kerberos for automatic token acquisition.
- Interactive Sign-In: Alternatively, prompt the user for sign-in if silent authentication isn’t available.
-
API Permissions and Token Handling
Grant permissions (e.g., to Microsoft Graph API) and store the tokens securely for reuse.
Overall Workflow and Diagram
Across all these application types, the common integration steps include:- App Registration
- Code Configuration and Implementation
- Token Validation
- Secrets and Certificate Management
- API Permissions and Access Control
- Token Caching/Storage
These standardized steps ensure a consistent authentication and authorization process across SPAs, web apps, web APIs, background processes, mobile apps, and desktop applications.
Registering an Application
In every scenario, application registration is the first and most critical step. Up next, we will explore how to register an application with Azure AD (now Microsoft Entra ID). This essential process lays the foundation for configuring identity services, token management, and permissions.By following the steps outlined in this lesson, you’ll build a strong foundation in integrating Azure AD across diverse application architectures, ensuring secure authentication and effective authorization.