AWS Certified AI Practitioner
Guidelines for Responsible AI
Human centered Design for Explainable AI
Welcome students. In this lesson, we explore the importance of human-centered design for explainable AI. Explainability and interpretability are fundamental for ensuring transparency, especially in high-stakes environments where decision-makers rely on clear insights. Our mission is to create AI systems that are not only accurate but also user-friendly and equitable.
Human-centered design prioritizes human needs in AI development. By focusing on making complex technologies accessible, it ensures that users—regardless of their technical expertise—can understand, trust, and effectively utilize explainable AI.
When applying these principles to explainable AI, the emphasis is not just on the system’s functionality but on clear, actionable information that addresses user needs. The design must guide users towards making informed, ethical decisions.
There are three key human-centered design principles for explainable AI:
- Amplified Decision-Making
- Unbiased Decision-Making
- Human and AI Learning
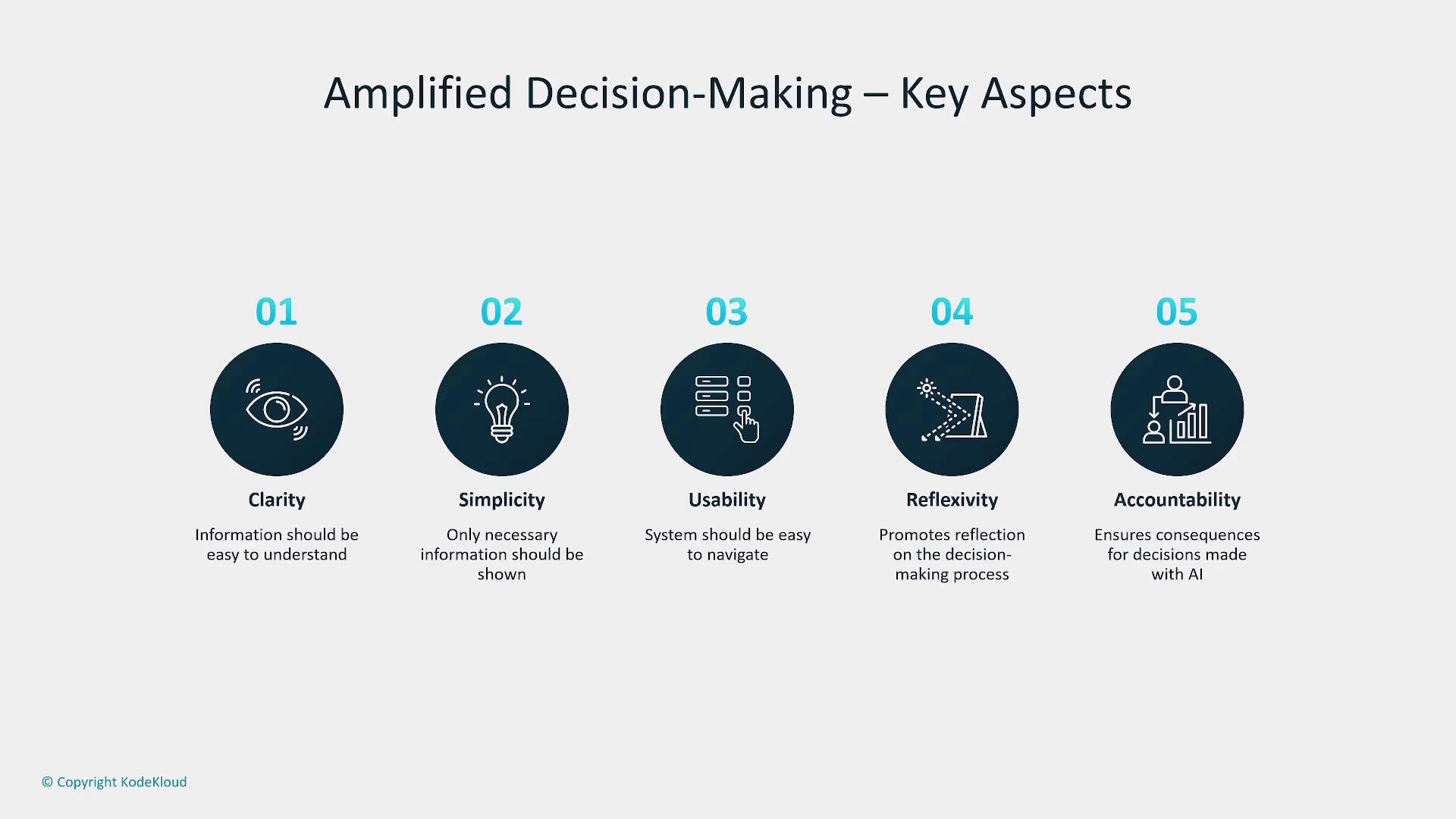
1. Designing for Amplified Decision-Making
In high-pressure environments, clear and rapid decision-making is crucial. Designing AI systems for amplified decision-making means presenting information in a clear, concise, and discoverable manner. The user interface must be intuitive, ensuring that critical insights are readily accessible and that users are encouraged to reflect on their choices with accountability and ethical considerations.
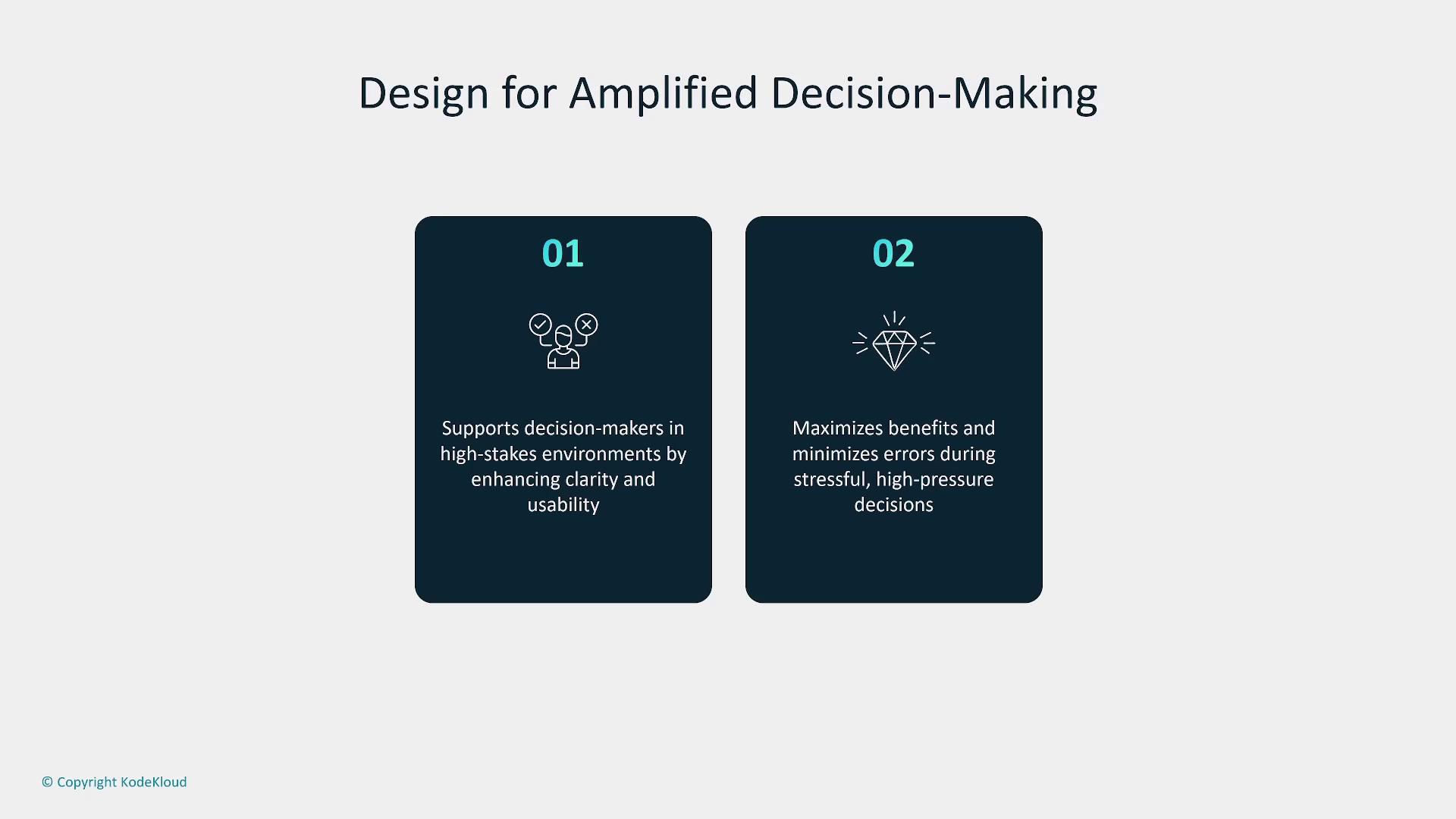
Key aspects of this design approach include clarity, simplicity, usability, reflexivity, and accountability.
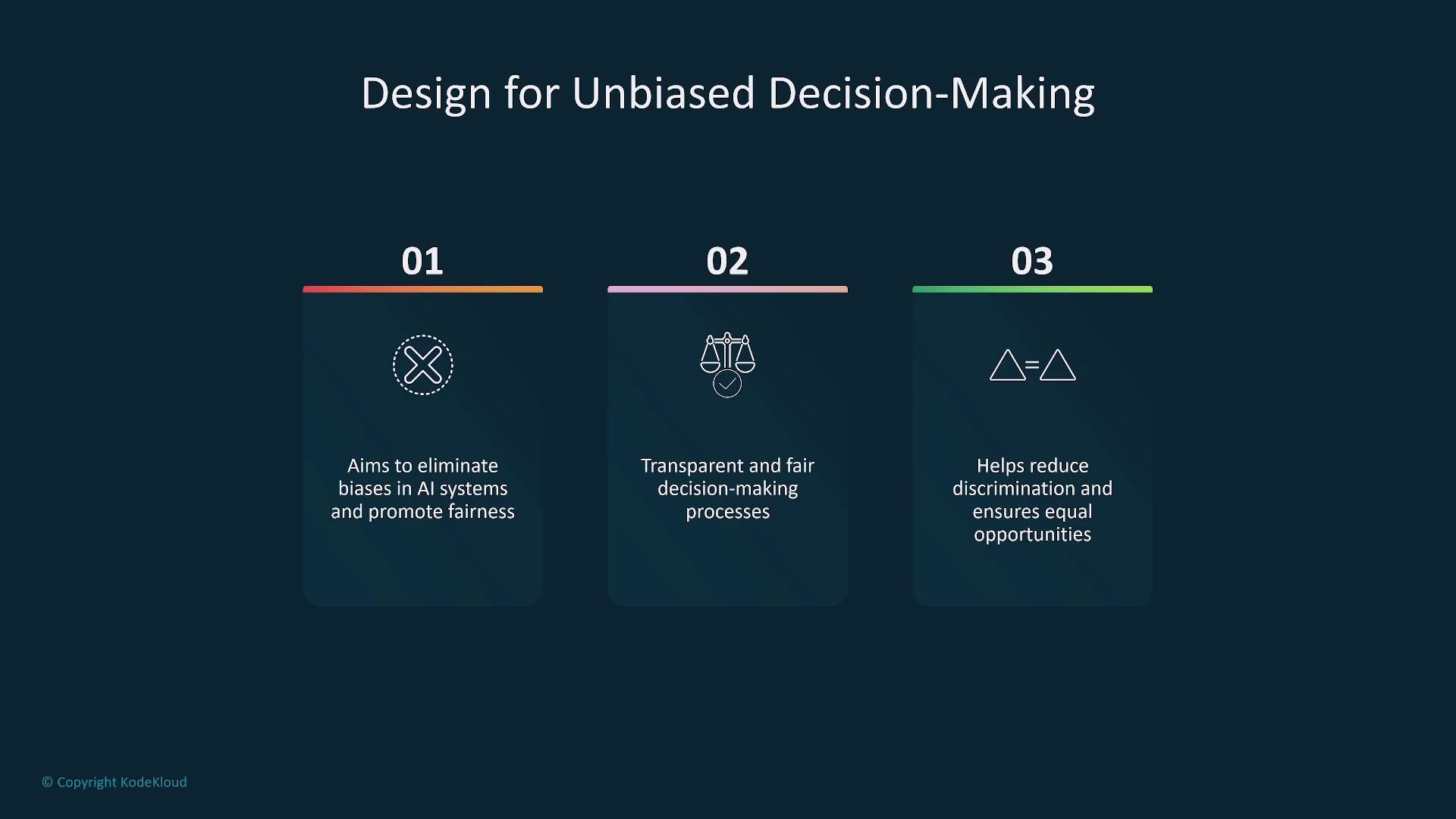
2. Designing for Unbiased Decision-Making
Ensuring fairness in AI systems is essential to eliminate bias. Transparent processes and balanced data help prevent discrimination and promote equal opportunities. By routinely checking for biases in model outputs and using balanced datasets, designers can cultivate transparency and fairness in AI operations.
Key Considerations
- Employ balanced datasets and regular bias checks.
- Enhance fairness through transparent decision-making processes.
- Implement robust training practices to minimize predispositions.
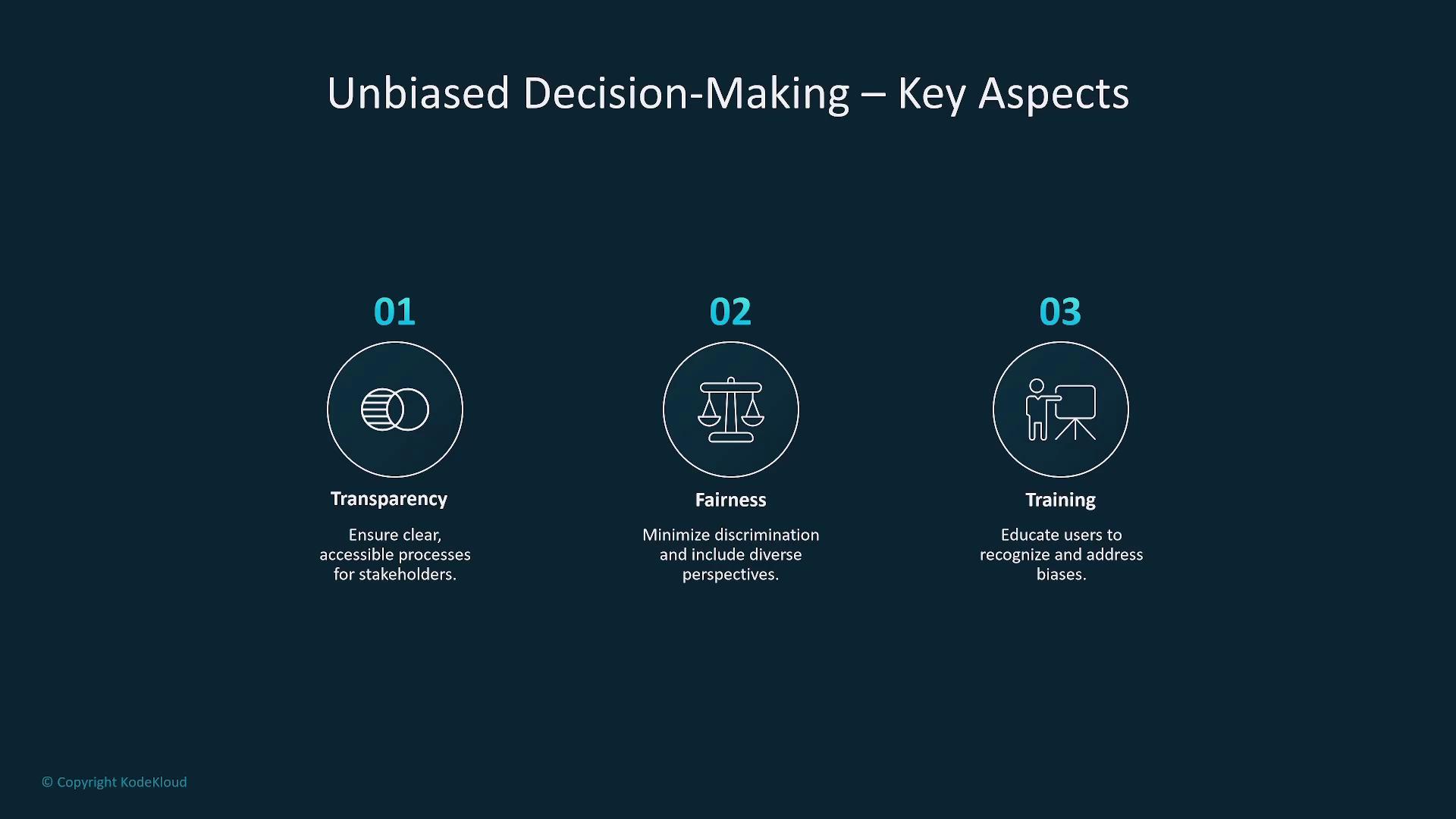
Transparency, fairness, and continuous training are fundamental in building unbiased AI systems.
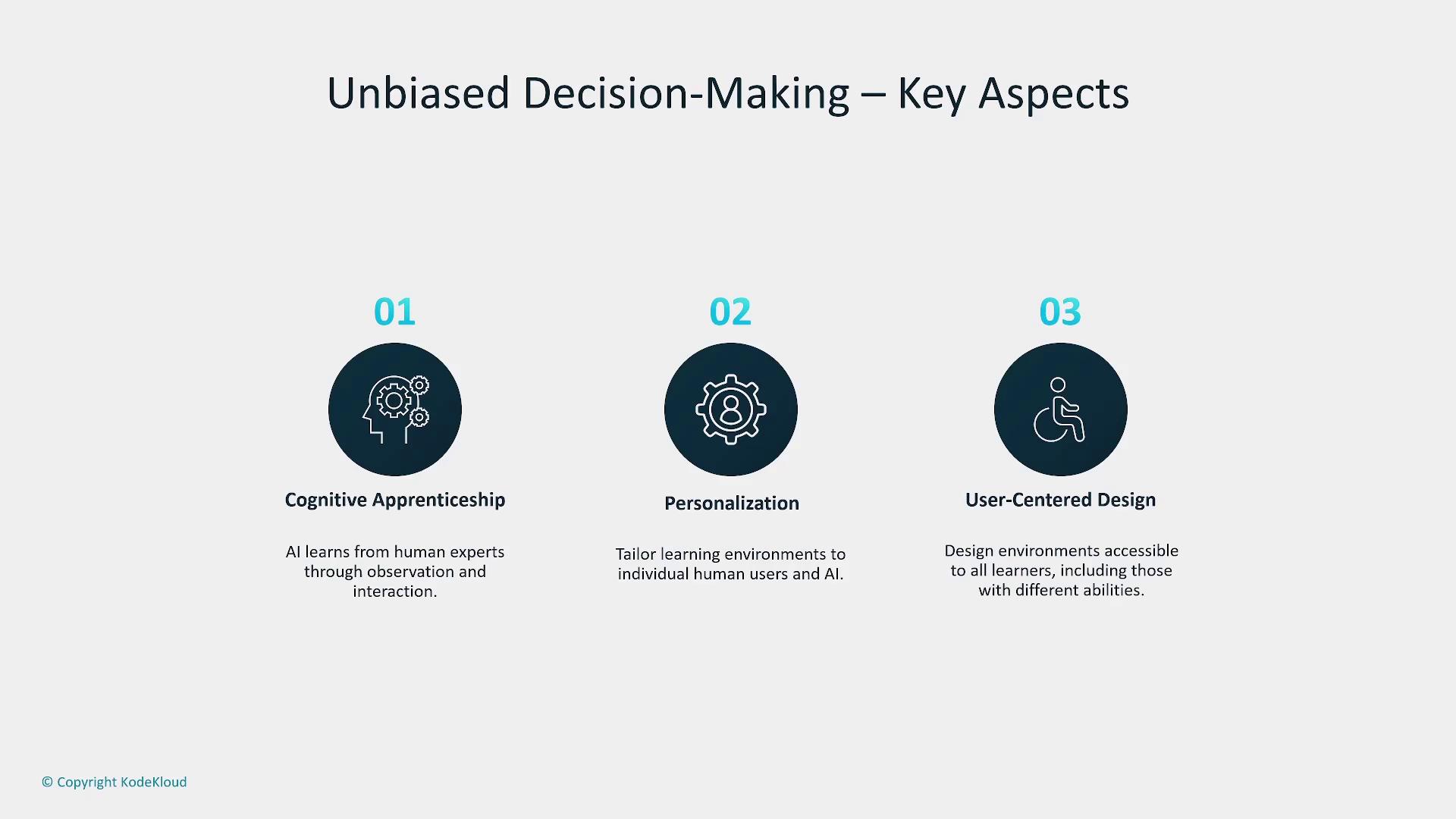
3. Designing for Human and AI Learning
Designing environments where both humans and AI systems can continuously learn is vital. This approach promotes a cognitive apprenticeship where AI evolves by learning from human interactions, leading to a more personalized and adaptive user experience. Emphasizing accessibility ensures that these systems are inclusive and accommodate varied abilities.
Techniques such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) further enhance this interaction. In RLHF, the AI model generates outputs that are evaluated by humans, who then provide feedback. This iterative process refines the model's performance to handle complex scenarios and improve user satisfaction.
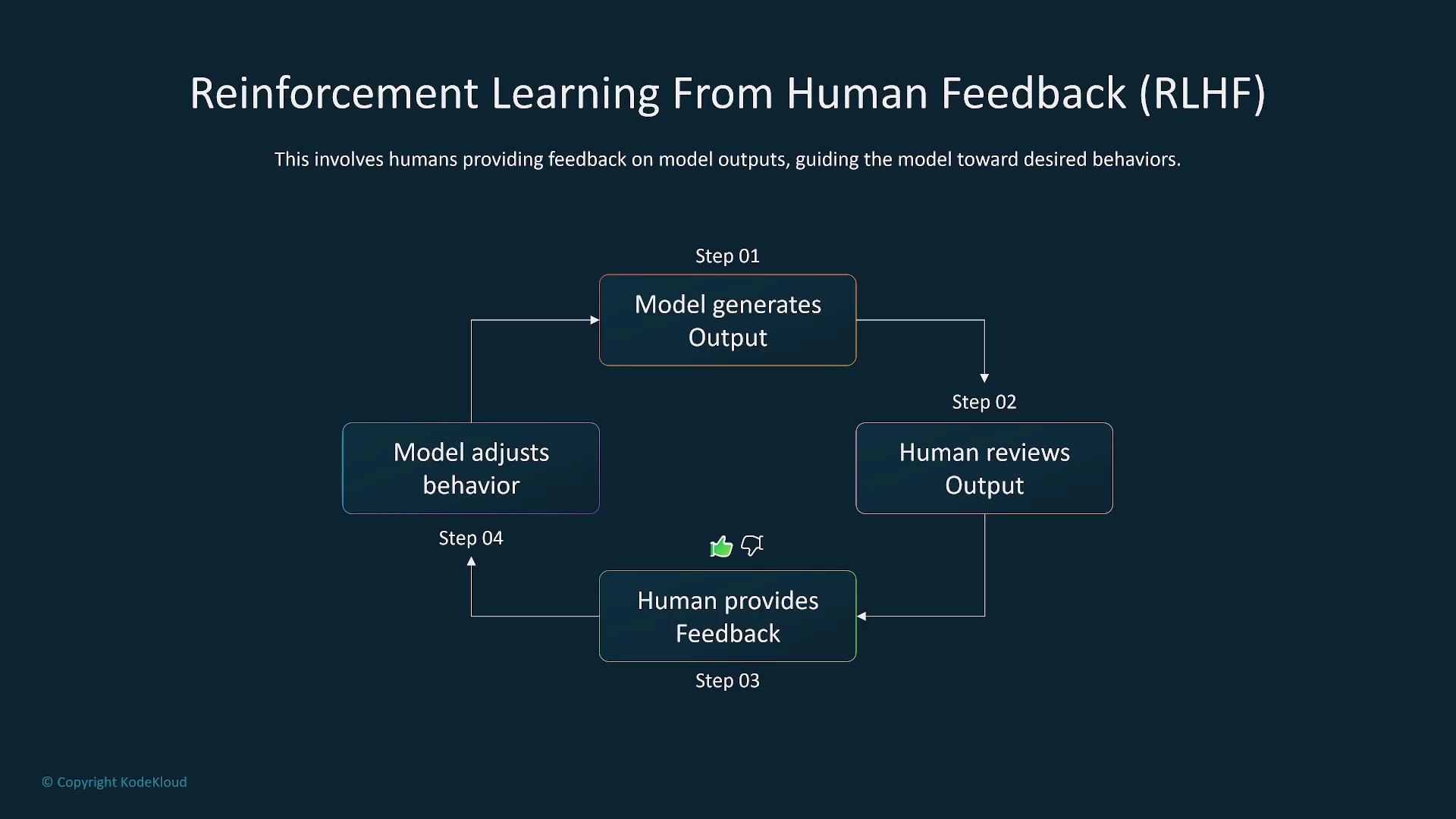
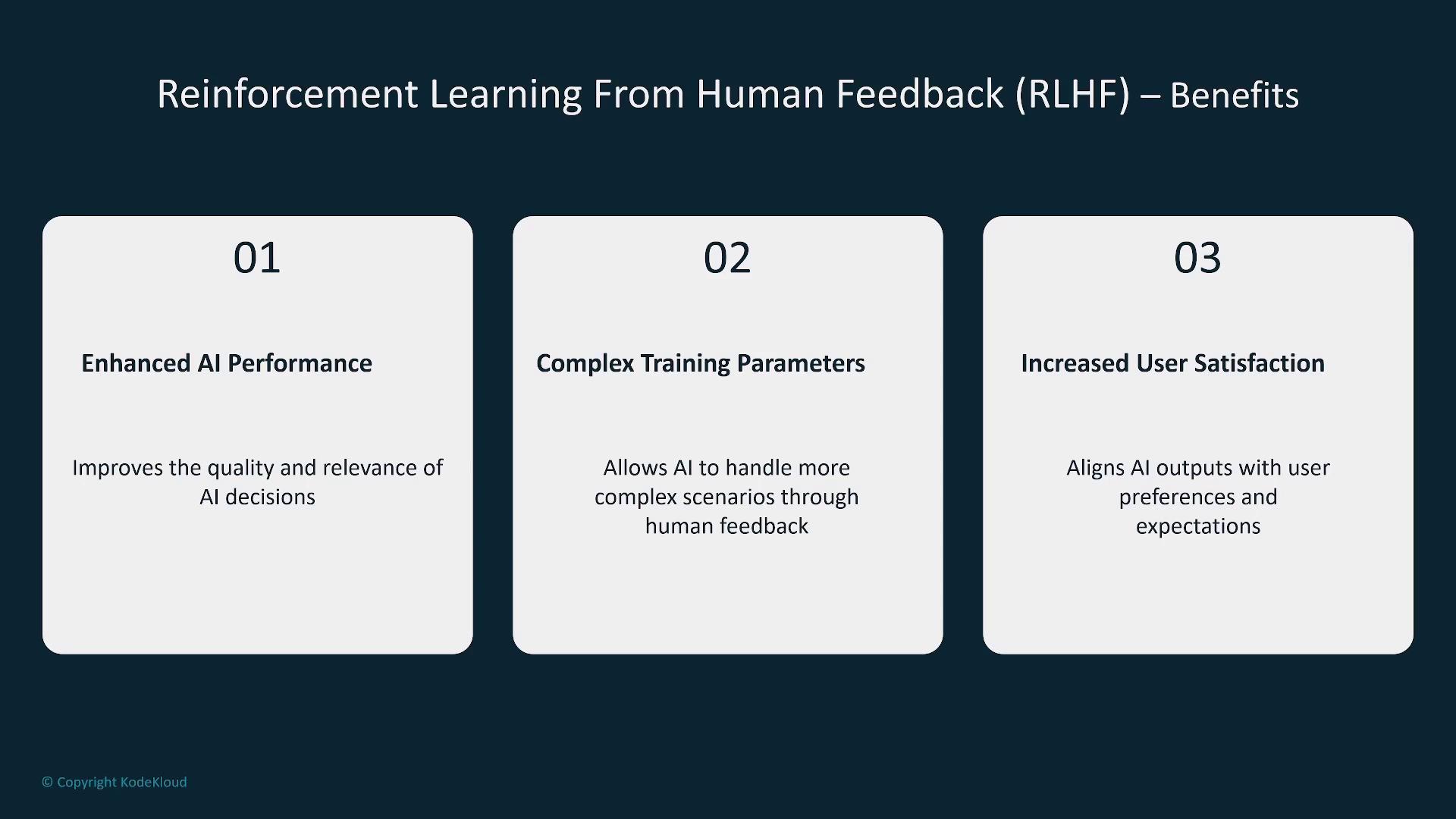
The advantages of RLHF include:
- Enhanced AI performance
- Improved handling of complex scenarios
- Increased overall user satisfaction
For example, SageMaker Ground Truth facilitates human-in-the-loop learning by enabling both private and public workforces to improve model accuracy through ranking, classification, and direct feedback.
In summary, incorporating the principles of human-centered design—amplified decision-making, unbiased decision-making, and human and AI learning—ensures the development of trustworthy, user-friendly, and explainable AI systems.

This concludes our lesson on human-centered design for explainable AI. We look forward to exploring more topics in the next section.
Watch Video
Watch video content