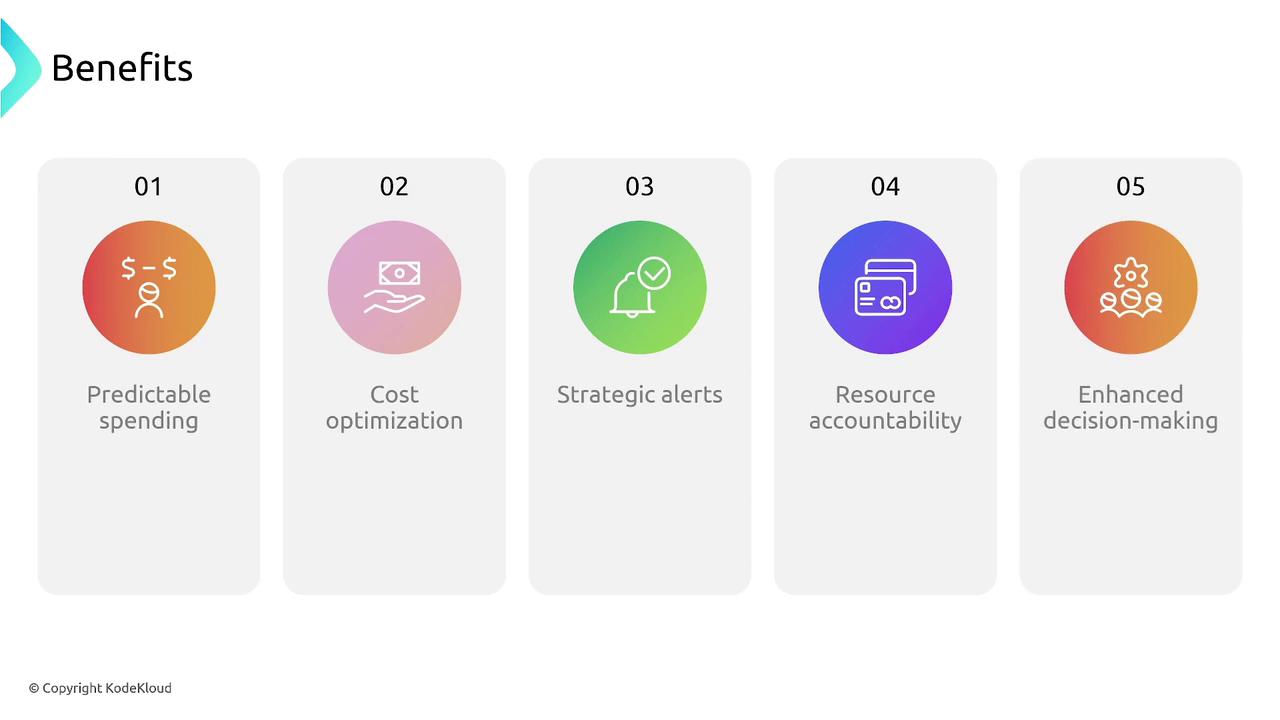
The main advantages of using AWS Budgets include:
- Predictable spending in a pay-as-you-go cloud environment.
- Cost optimization by tracking expenditures across multiple AWS services.
- Strategic alerts and automated decision making.
- Enhanced accountability and informed decision-making with detailed analytics.
Types of Budgets in AWS
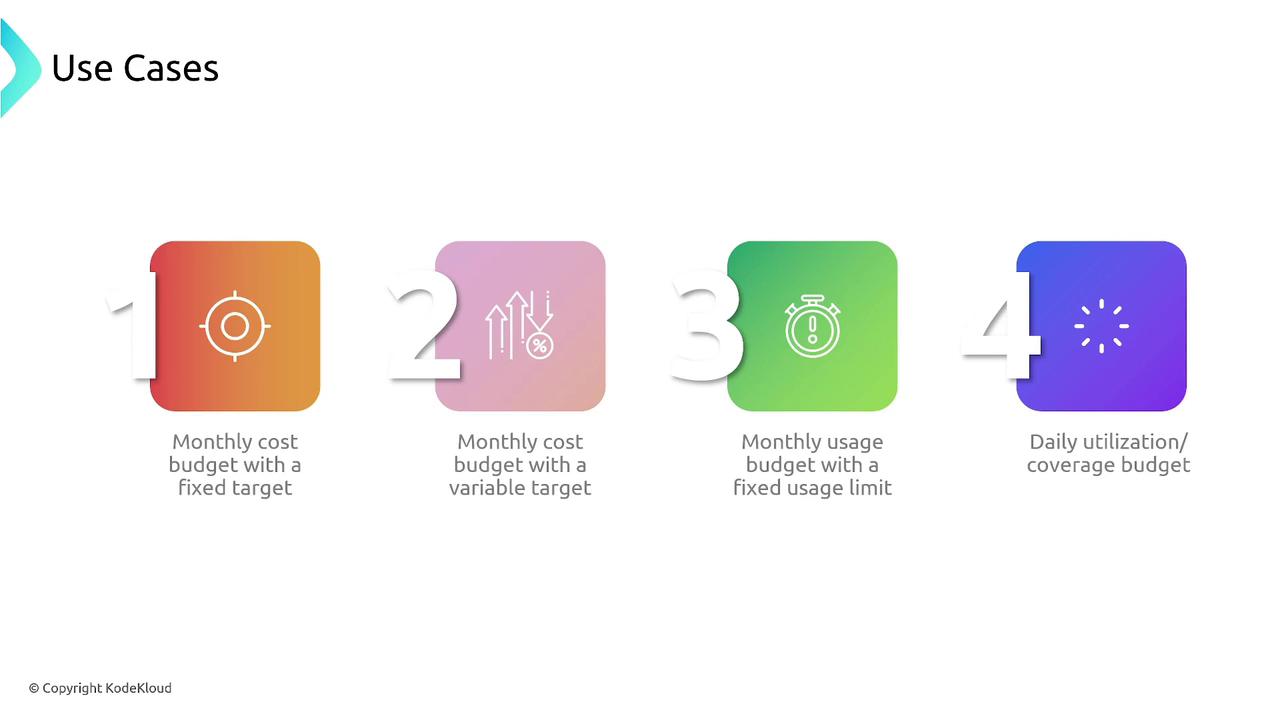
AWS Budgets supports several budget types. Understanding these types can help you tailor your monitoring approach based on your cost-management needs:- Cost Budgets: Track your overall spending over a specified period.
- Usage Budgets: Monitor how much you utilize specific AWS services.
- Utilization Budgets: Keep an eye on reserved instance usage to ensure optimal performance.
- Coverage Budgets: Verify that you have sufficient coverage for your reserved instances.
- Savings Plans Budgets: Observe the utilization and coverage of your Savings Plans.

- Cost budget
- Usage budget
- Savings Plans budget
- Reservation budget

Configuring Your Budget
Follow these steps to set up your AWS Budget:-
Select the Budget Type:
Choose from the four available budget types based on your requirements. -
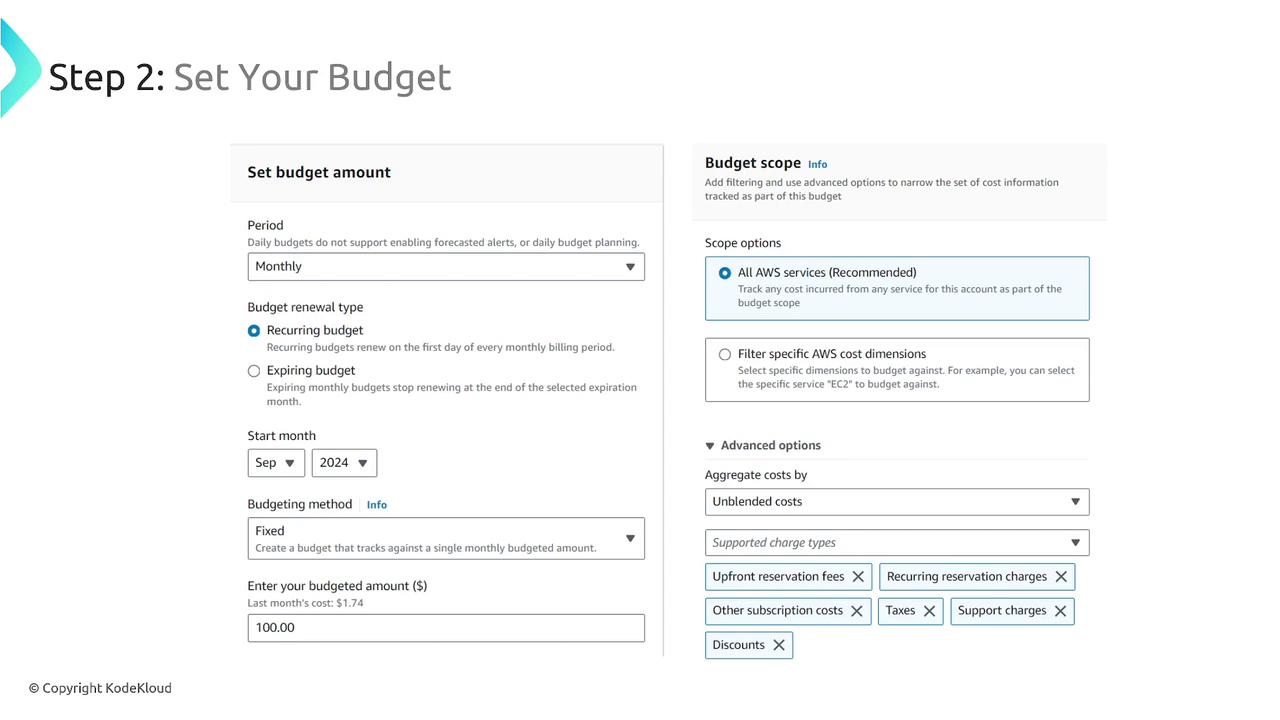
Specify the Budget Amount and Time Period:
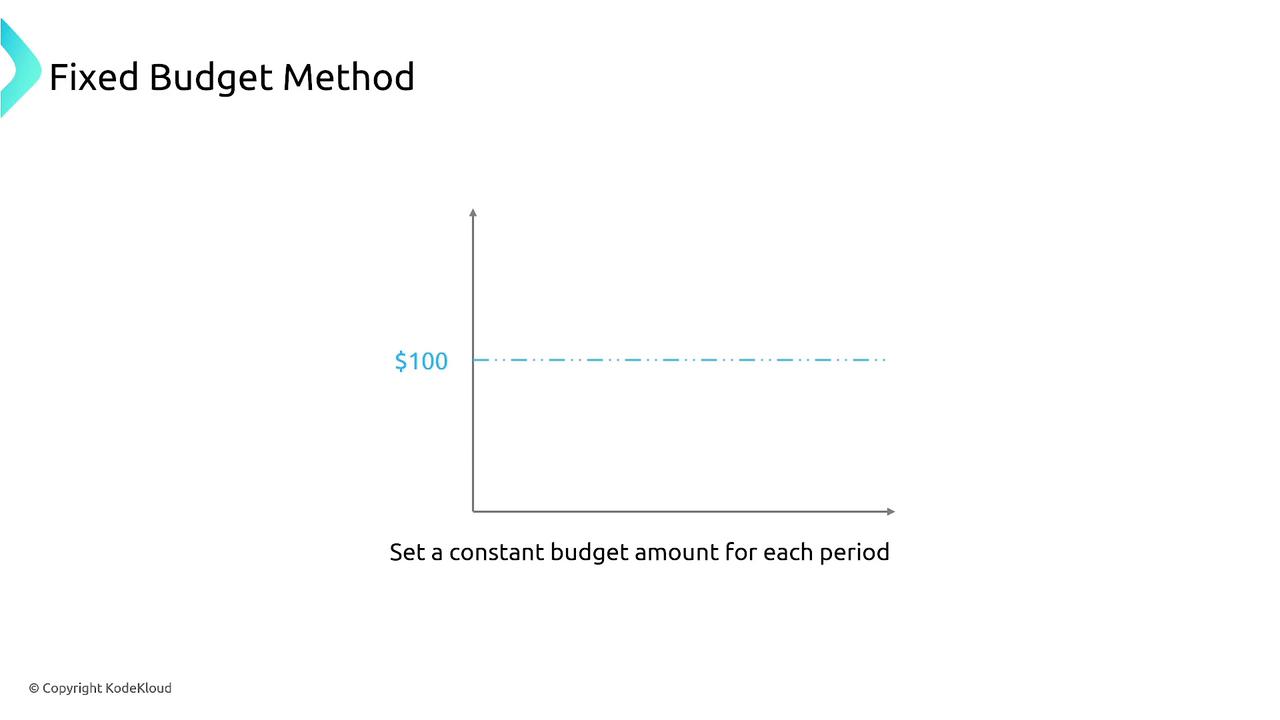
Define your desired period (monthly, quarterly, or yearly) and decide whether the budget is fixed or variable. In the case of a variable budget, AWS Budgets can automatically adjust your budget using historical data. For example, if your average spend over the past six months was 100, with alerts initiated if significant deviations occur.
-
Define the Scope and Apply Filters:
Customize your budget by applying filters related to specific services, accounts, regions, instance types, or tags. This targeted approach allows you to focus on the areas most relevant to your spending. Common filters include service, account, region, and instance type, although advanced options like API operations and billing entities are also available. -
Set Up Alerts and Actions:
Configure notifications to alert you when spending reaches a defined percentage of your budget. Beyond alerts, you can attach automated actions. For instance, you could set an action to automatically stop or terminate EC2 instances if your spending exceeds a specified limit.

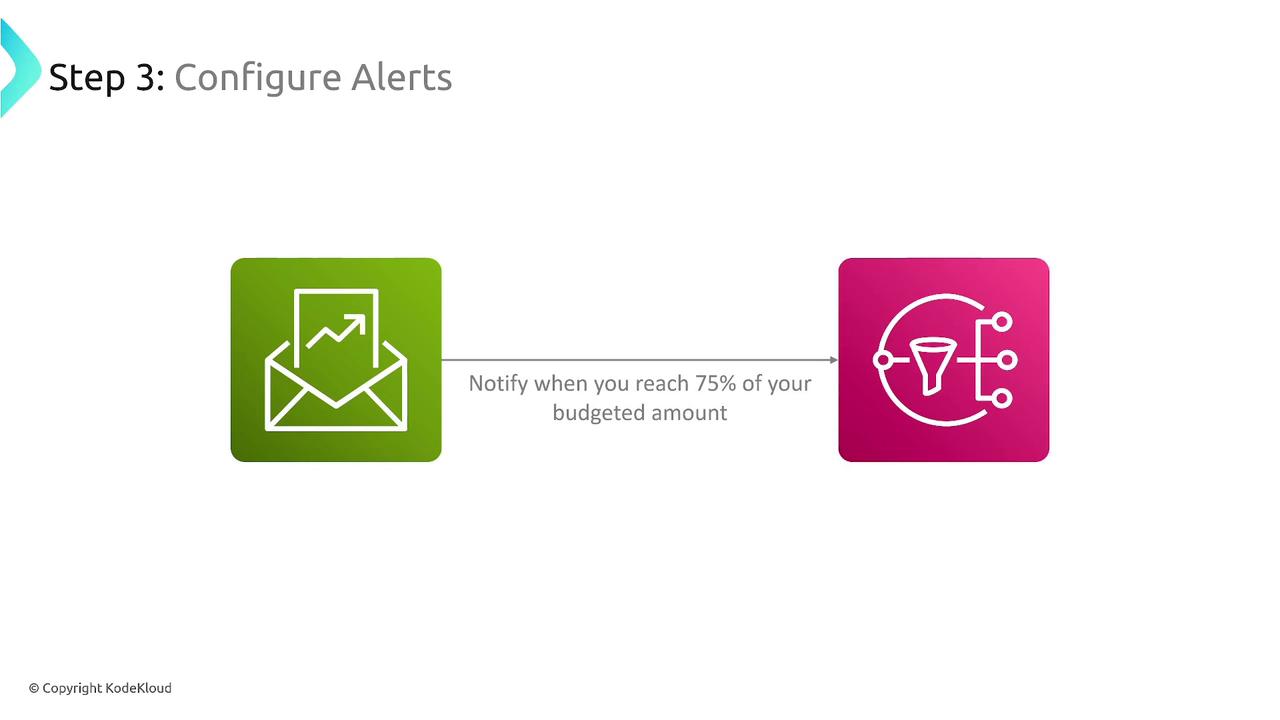
Configuring Alerts and Actions
After setting up your budget, configure alerts to ensure you stay informed:- Set a notification to trigger when your spending reaches, for example, 75% of your budget.
- Choose whether the notification should only alert you or also execute automated actions.

Automating cost control measures through budget actions minimizes manual oversight, ensuring that your account expenses are managed efficiently.