AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Authentication and Authorization Methods
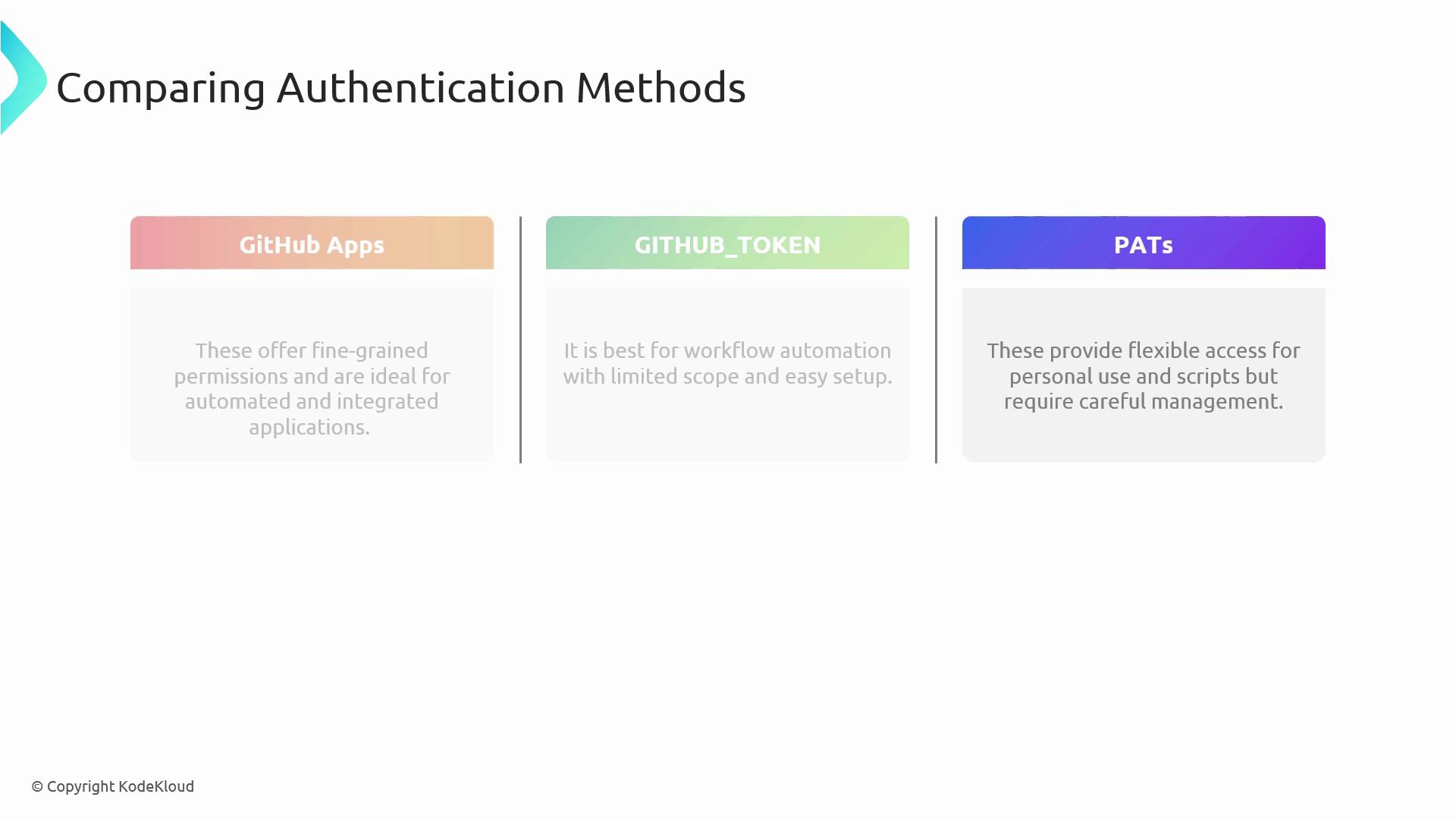
Implement and manage GitHub Authentication
Effective GitHub authentication is critical for securing your repositories, workflows, and API interactions. In this guide, we cover three primary methods:
- GitHub Apps
- GITHUB_TOKEN
- Personal Access Tokens (PATs)
Each approach has unique advantages, scope, and security considerations. Read on to determine which fits your DevOps and CI/CD pipelines best.
1. GitHub Apps
GitHub Apps act on behalf of your application—independent from user credentials. They can be installed on organizations or user accounts to interact with repositories, respond to events, and automate tasks like code reviews, CI/CD, and issue management.
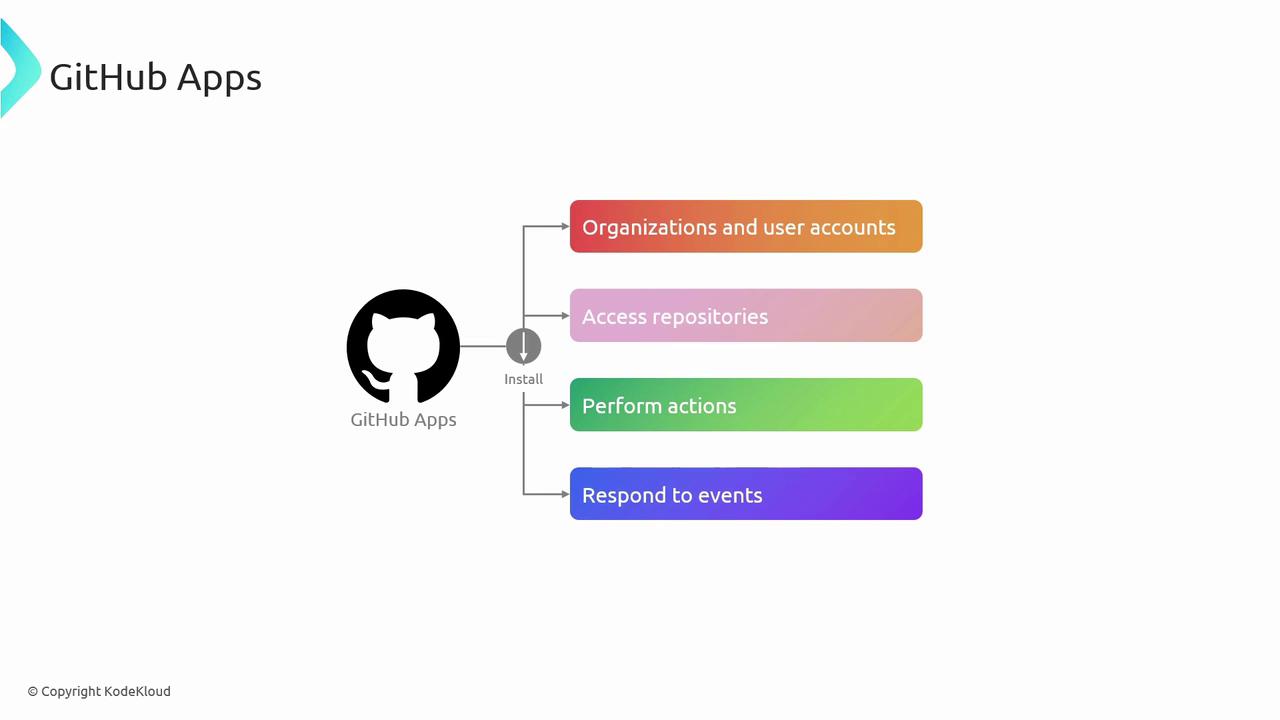
Benefits
- Fine-grained permissions scoped to required actions
- Enhanced security by separating app identity from user credentials
- Detailed audit logs and install-based access control
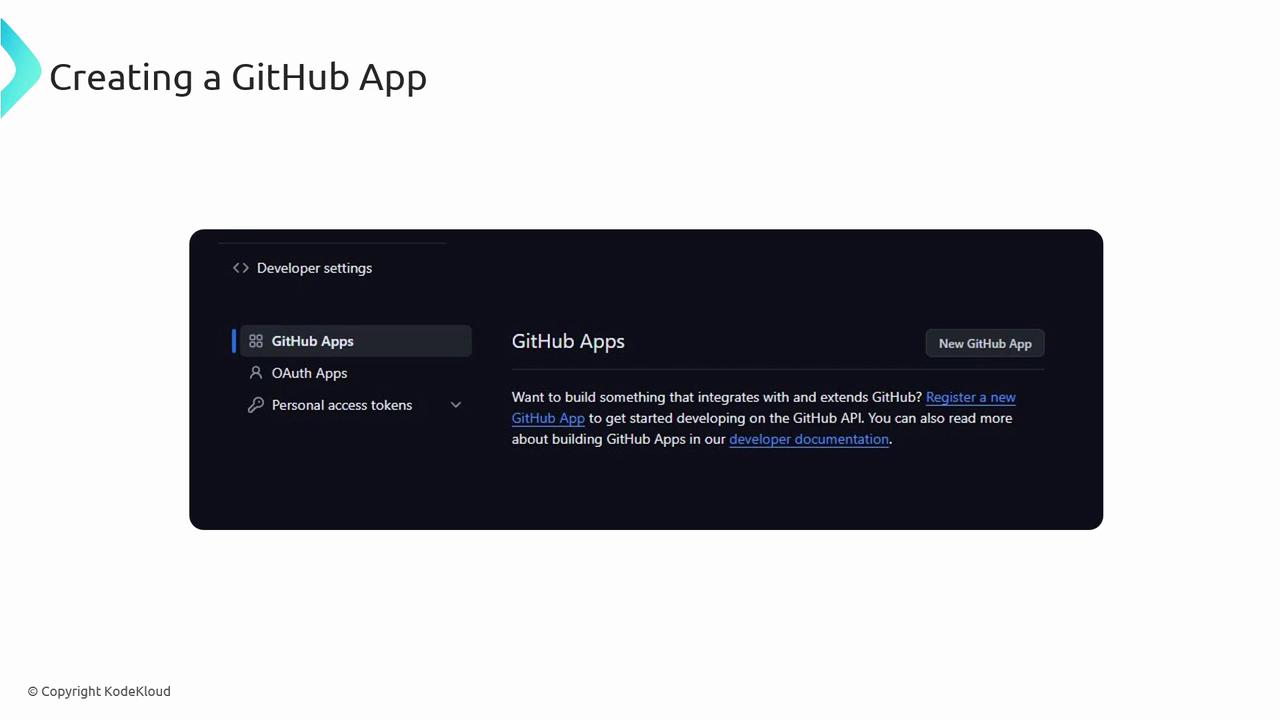
Creating a GitHub App
- Navigate to GitHub Settings → Developer Settings.
- Select GitHub Apps and click New GitHub App.
- Provide the App name, homepage URL, and callback URL.
- Configure the required permissions and subscribe to relevant events.
- Save and download the private key for authentication.
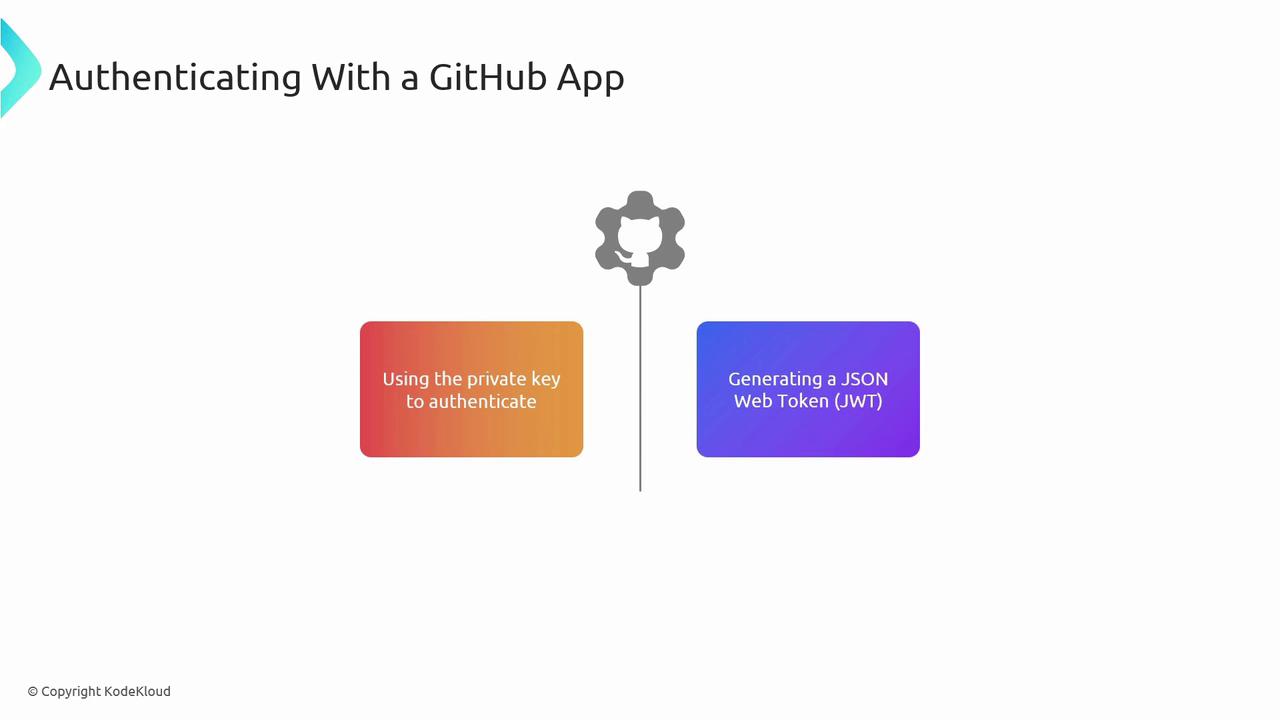
Authenticating with a GitHub App
Authentication is a two-step process:
- Generate a JSON Web Token (JWT) using your App’s private key.
- Exchange the JWT for an installation access token via GitHub’s API.
Example: Generate a JWT in Python (replace APP_ID and PRIVATE_KEY).
import jwt, time
payload = {
"iat": int(time.time()),
"exp": int(time.time()) + 600,
"iss": APP_ID
}
jwt_token = jwt.encode(payload, PRIVATE_KEY, algorithm="RS256")
Use the resulting jwt_token to request an installation access token:
curl -X POST https://api.github.com/app/installations/INSTALLATION_ID/access_tokens \
-H "Authorization: Bearer jwt_token" \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json"
Note
After updating permissions, you must regenerate the installation access token for changes to take effect.
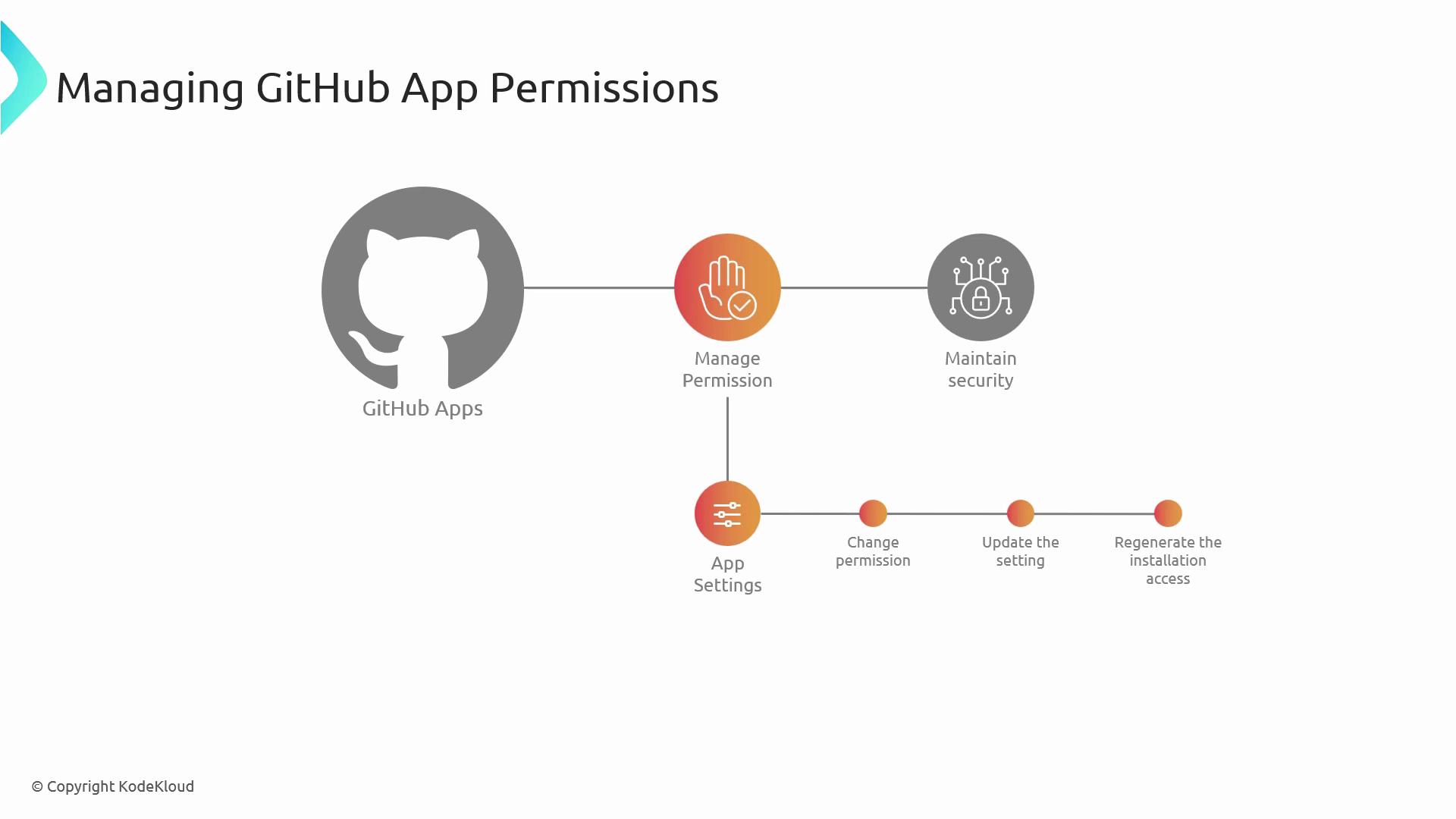
Managing Permissions
Regularly audit your App’s permissions in Settings. Use the App’s dashboard or API to adjust scopes and monitor usage.
2. GITHUB_TOKEN
GITHUB_TOKEN is an automatically generated secret available in GitHub Actions workflows. It provides repository-scoped authentication for checkout, API calls, and publishing packages—without manual secret management.
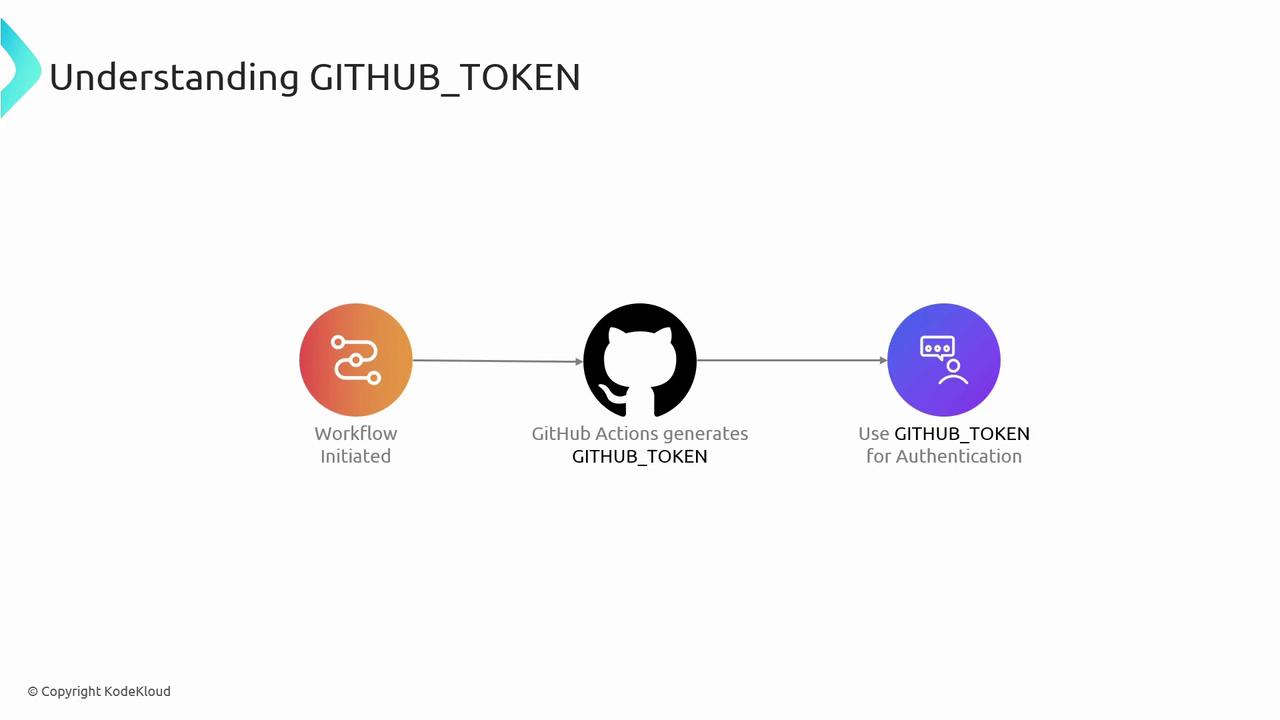
Benefits
- Auto-generated for every workflow run
- Limited to current repository to minimize blast radius
- No manual rotation or storage needed

Usage Example
Use GITHUB_TOKEN from the secrets context:
name: CI Workflow
on: [push]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
Warning
Do not expose GITHUB_TOKEN to external URLs or untrusted actions—limit usage to internal steps only.
3. Personal Access Tokens (PATs)
Personal Access Tokens (PATs) provide user-level authentication for GitHub APIs and Git operations. You can choose classic or fine-grained tokens to control scope and expiration.
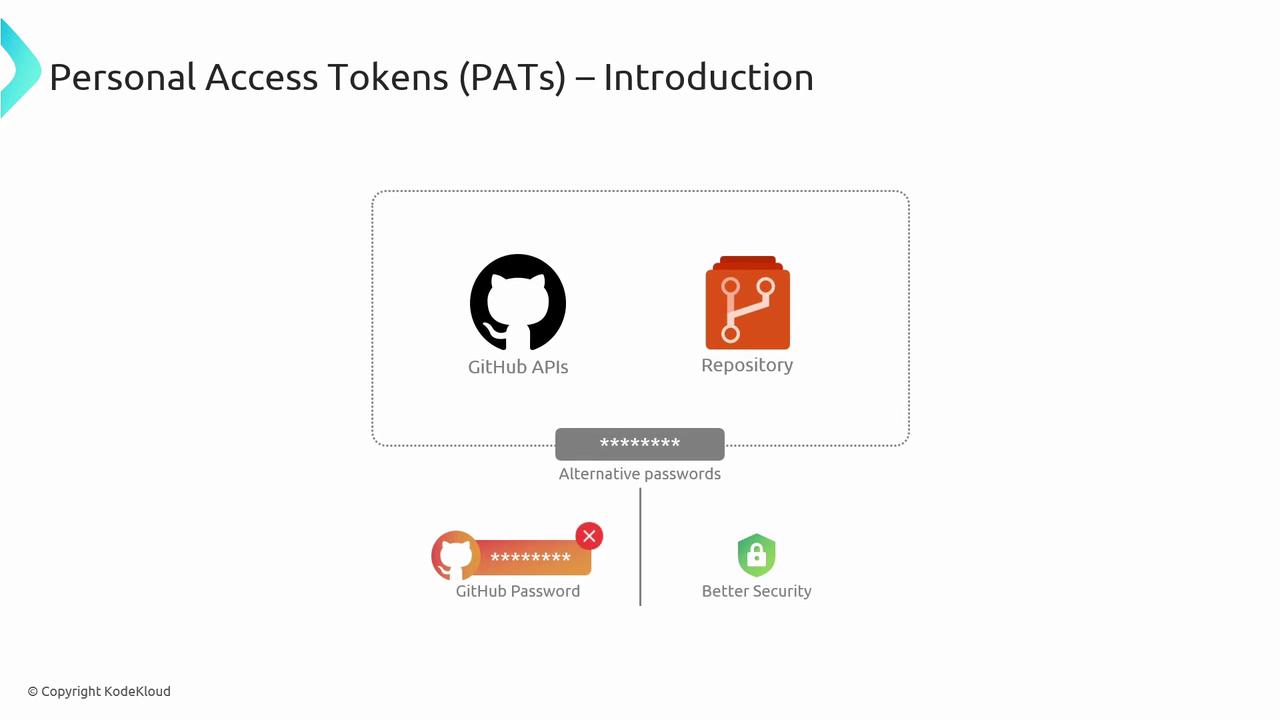
Use Cases
- CLI or script-based Git operations
- REST or GraphQL API integrations
- Third-party service authentication
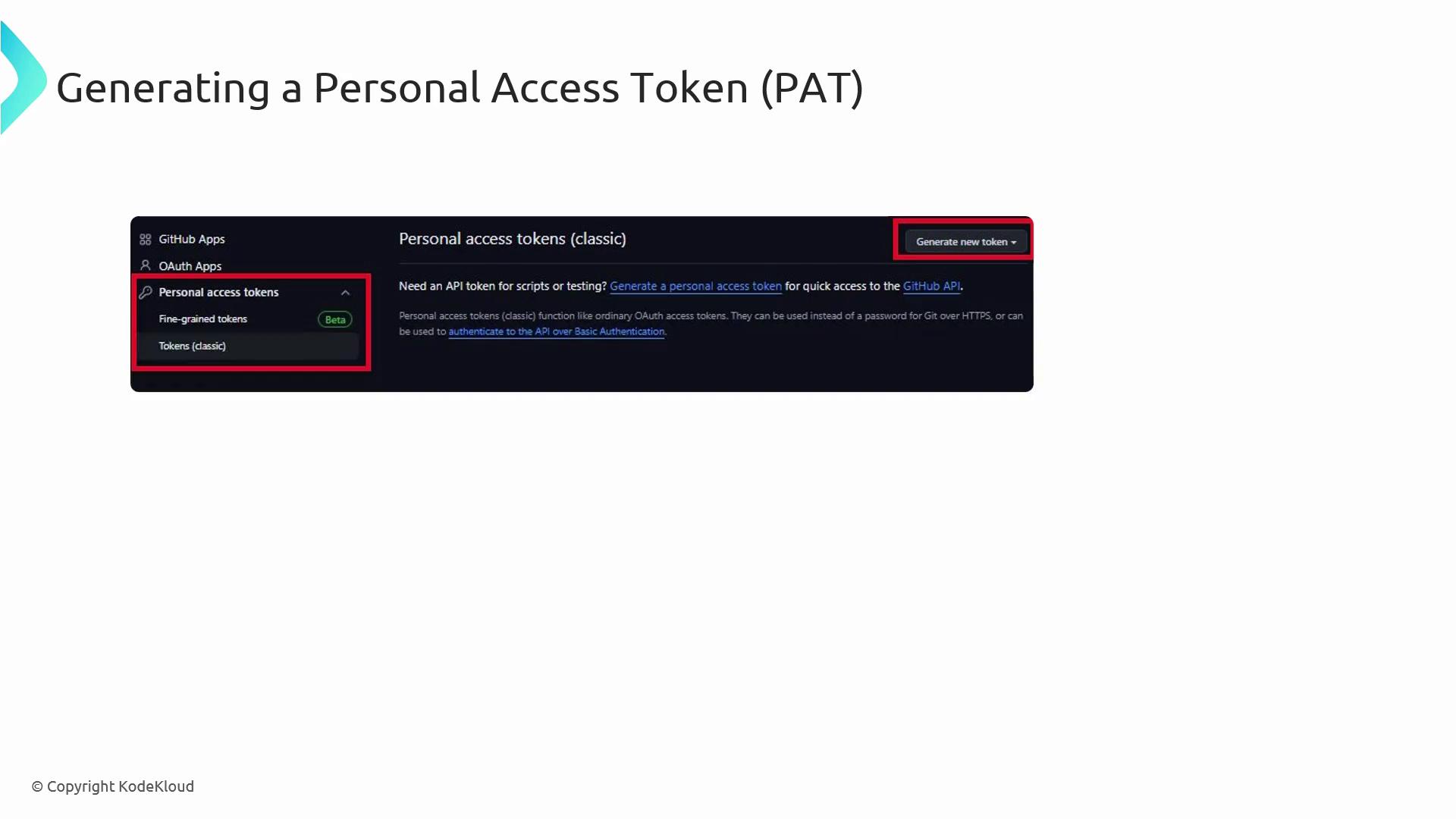
Generating a PAT
- In GitHub Settings, open Developer Settings → Personal access tokens.
- Click Generate new token.
- Choose classic or fine-grained.
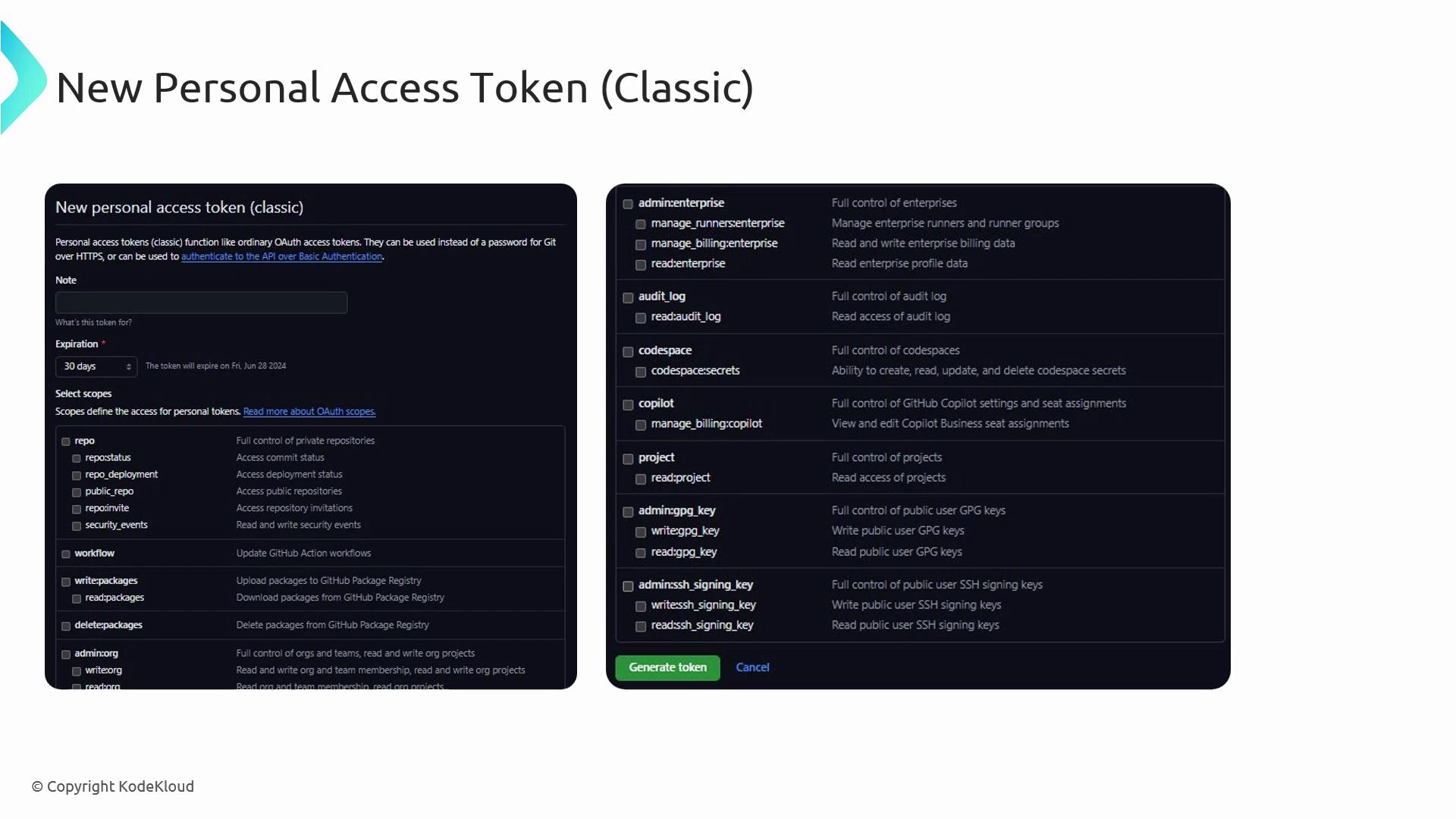
- Select scopes (e.g.,
repo,workflow,admin:org). - Generate the token and store it securely.
Authenticating with a PAT
Include the token in the Authorization header for API calls:
curl -H "Authorization: token <PAT>" https://api.github.com/user/repos
Note
Store PATs in a secure vault or GitHub Secrets, rotate them regularly, and avoid embedding them in code.
Method Comparison and Best Practices
| Method | Scope | Rotation | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| GitHub Apps | Org & repo, fine-grained | Manual/API | Integrations, bots, automated workflows |
| GITHUB_TOKEN | Single repo | Auto-rotated | GitHub Actions workflows |
| PATs | User-level, broad or narrow | Manual | CLI scripts, local development, third-party tools |
Security Best Practices
- Grant the minimum required permissions.
- Rotate keys and tokens frequently.
- Monitor audit logs for unauthorized access.
- Enforce SAML SSO, OAuth apps, and branch protection rules.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content