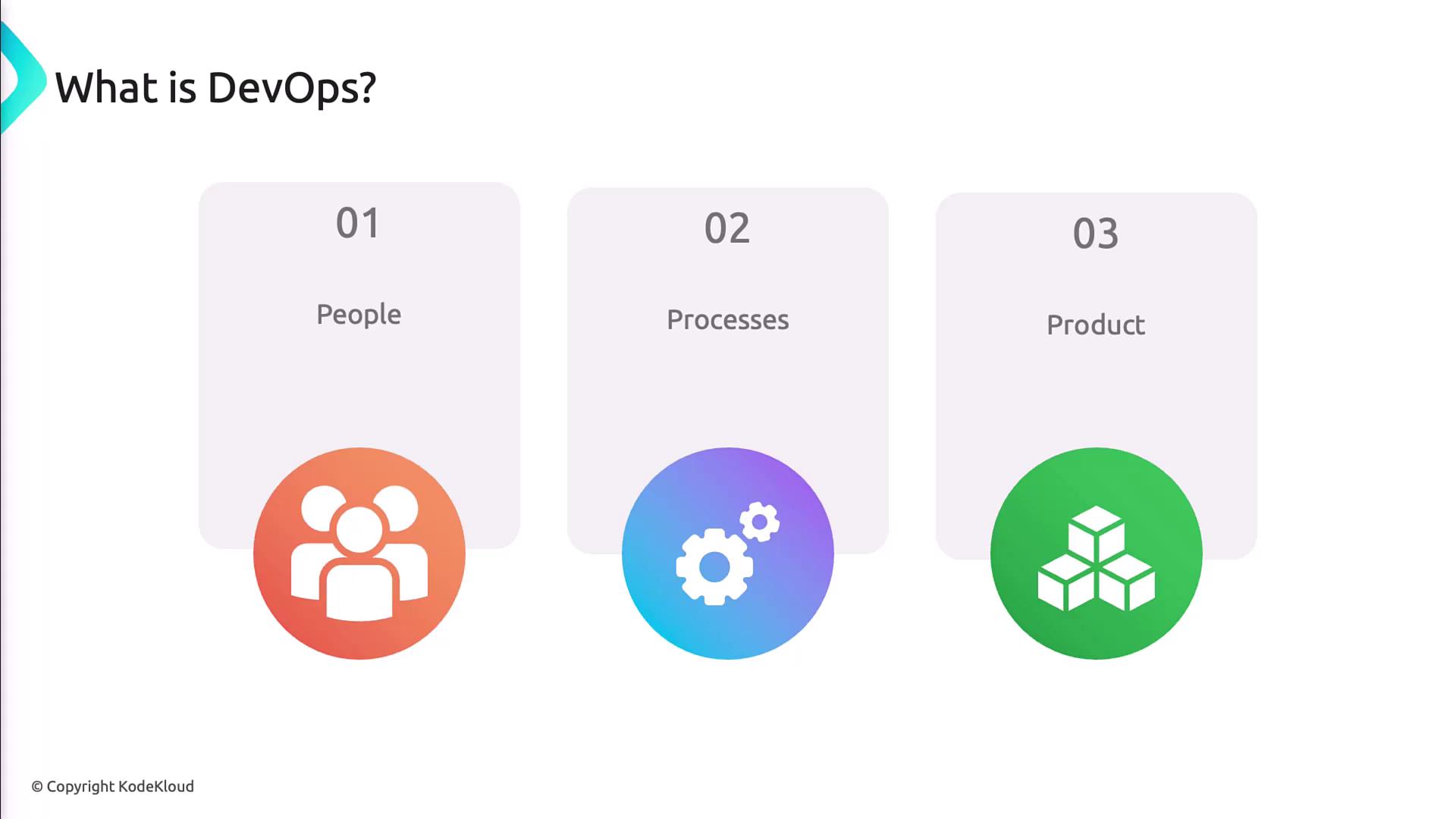
Definition of DevOps
DevOps is more than a buzzword—it’s a cultural and technical movement. According to Microsoft,DevOps is a union of people, processes, and products to quickly deliver value to users.The emphasis on “value” underscores that shipping software rapidly only matters when it solves real problems and delights users. People
Cross-functional teams break down silos between developers, operations, QA, and security. Shared goals and collaborative practices foster trust and accountability. Processes
Agile workflows, value-stream mapping, and data-driven insights enable continuous improvement. Automation and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines eliminate manual handoffs and reduce errors. Products
Toolchains for source control, build automation, infrastructure as code, monitoring, and feedback loops support end-to-end delivery.
Focusing on value delivery ensures your DevOps initiatives align with business outcomes and user satisfaction.
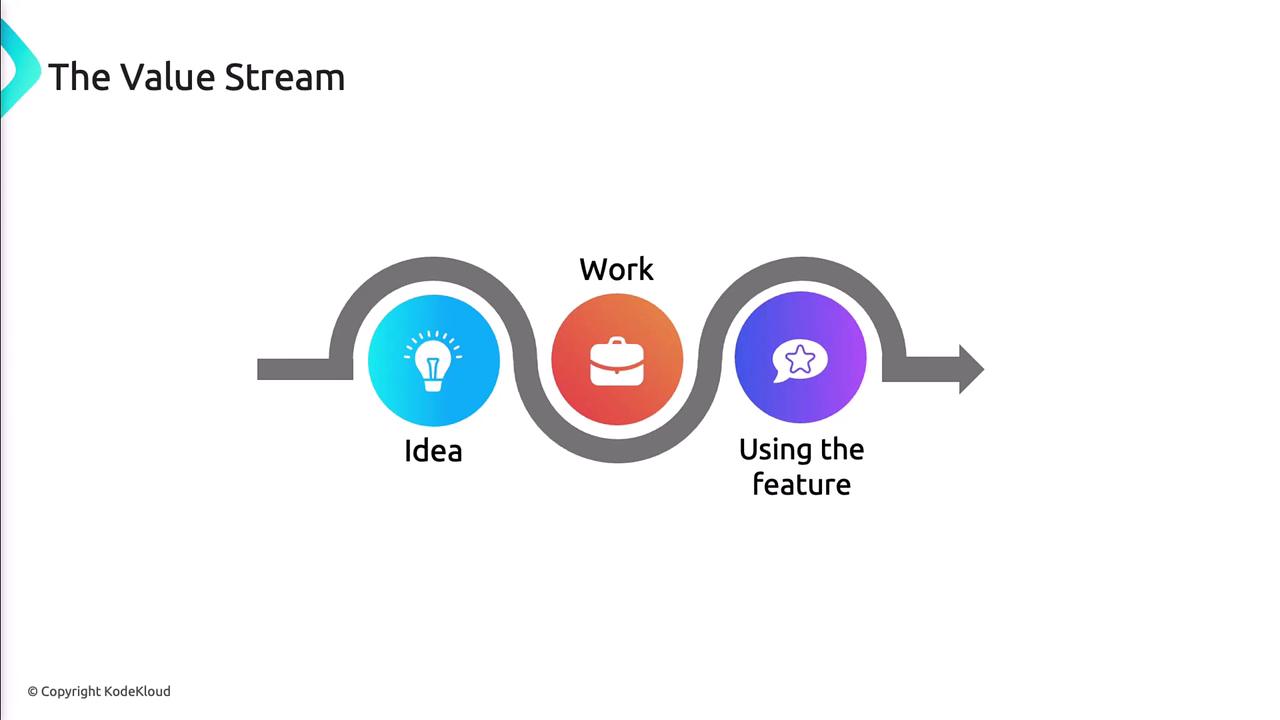
Azure DevOps and the Value Stream
Azure DevOps provides integrated services to manage the entire value stream—from idea to production. A value stream captures each step in delivering a feature or service:- Ideation and requirements
- Development and testing
- Deployment and operations
The Three Ways: Flow, Feedback, and Experimentation
In The DevOps Handbook, three principles—known as the Three Ways—guide successful DevOps adoption:-
Flow
Map, measure, and optimize each step in your value stream. Remove handoffs and automate repetitive tasks to establish a fast, reliable path to production. -
Feedback
Implement continuous monitoring, logging, and alerting. Rapidly detect and resolve failures, and loop customer and application telemetry back into planning and development. -
Experimentation
Cultivate a culture of continuous learning. Use small, safe-to-fail experiments to test hypotheses, improve processes, and validate new features.
DevOps Application Lifecycle
Let’s break down how DevOps transforms each phase of software delivery: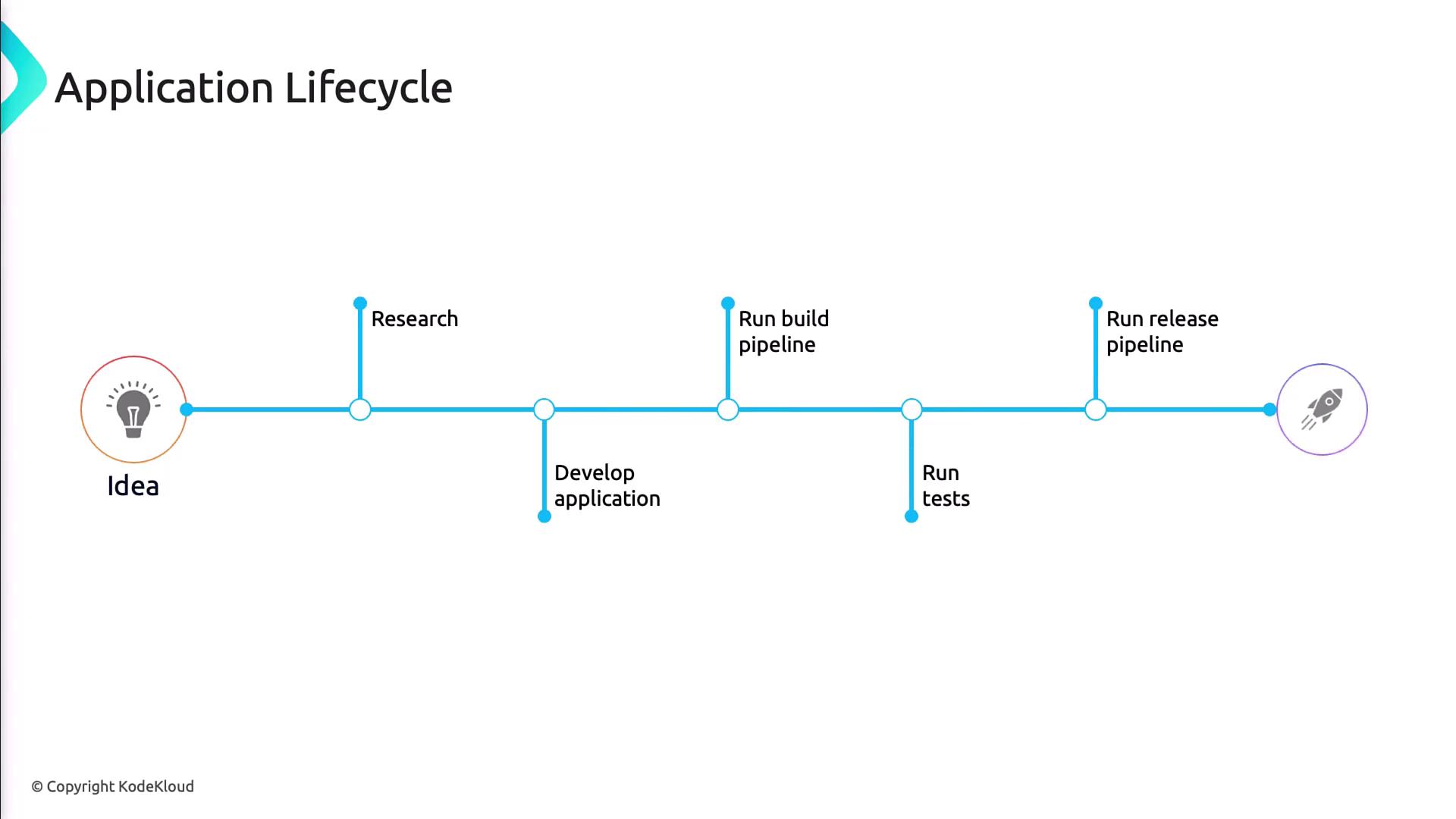
- Refine the backlog, define acceptance criteria, and slice features into user stories.
- Tools: Azure Boards, backlog grooming, sprint planning.
- Implement code in small increments, enforce code reviews, and run automated tests.
- Tools: Git repos, pull requests, static analysis, unit testing.
- Push validated builds through CI/CD pipelines with approval gates and deployment strategies.
- Tools: Azure Pipelines, artifacts, environment approvals.
- Monitor performance, manage incidents, and tune applications for reliability.
- Tools: Azure Monitor, Application Insights, logging, alert rules.
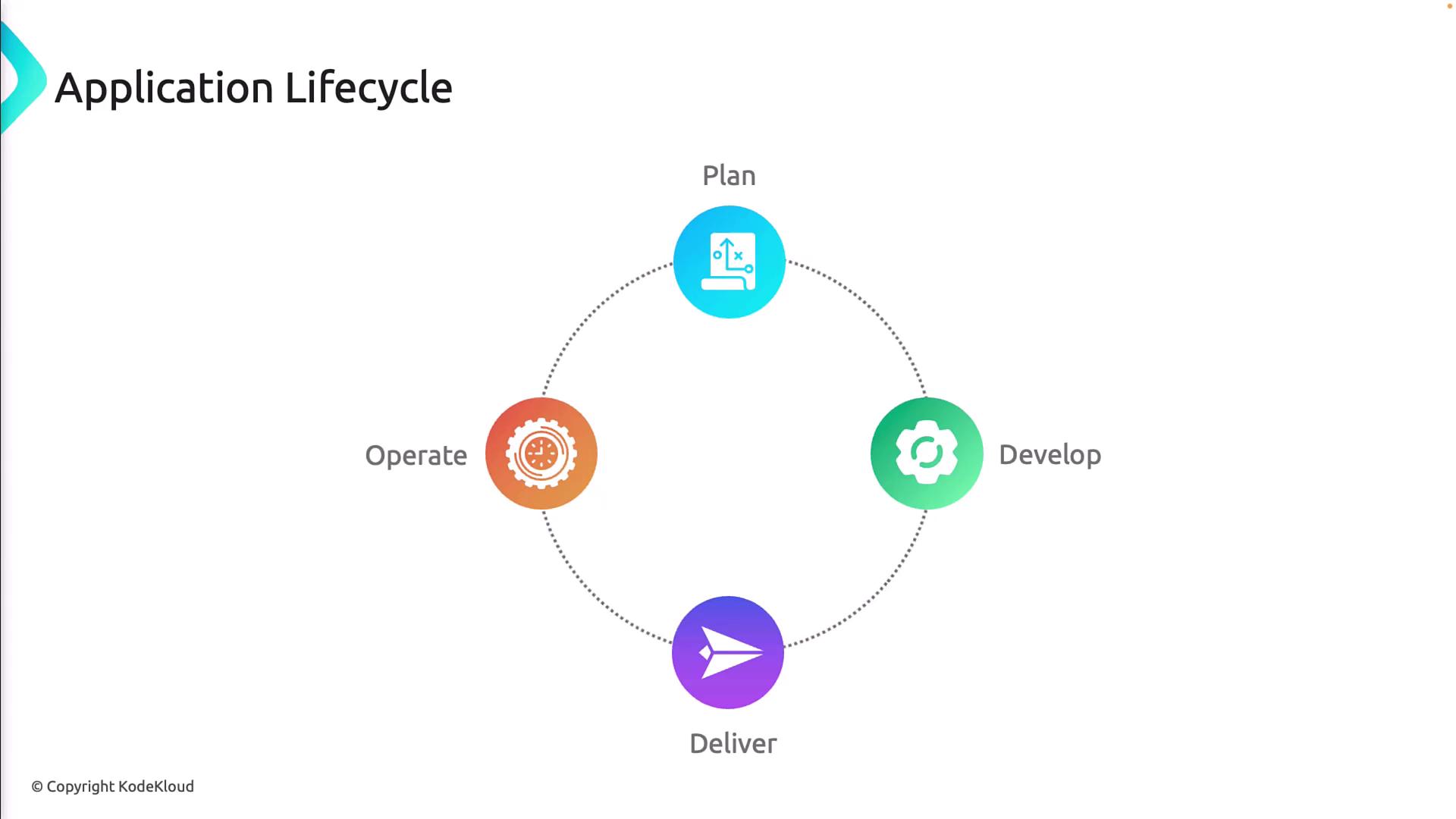
Integrating feedback and telemetry into each phase ensures continuous improvement and faster mean time to recovery (MTTR).
From Waterfall to DevOps
Legacy waterfall models follow a rigid sequence—design, build, test, deploy—often leading to long lead times, silos, and late discovery of defects. DevOps dismantles these barriers through automation, collaboration, and cloud-native practices.| Model | Release Cadence | Collaboration | Automation | Feedback Loops |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waterfall | Quarterly or longer | Functional silos | Minimal | Slow |
| DevOps | Continuous (weekly to daily) | Cross-functional teams | Extensive CI/CD | Rapid |
Maintaining a strict waterfall process can create costly rework and degraded deployment quality. Consider adopting incremental delivery early.