AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Infrastructure as Code IaC
Introduction to Bicep
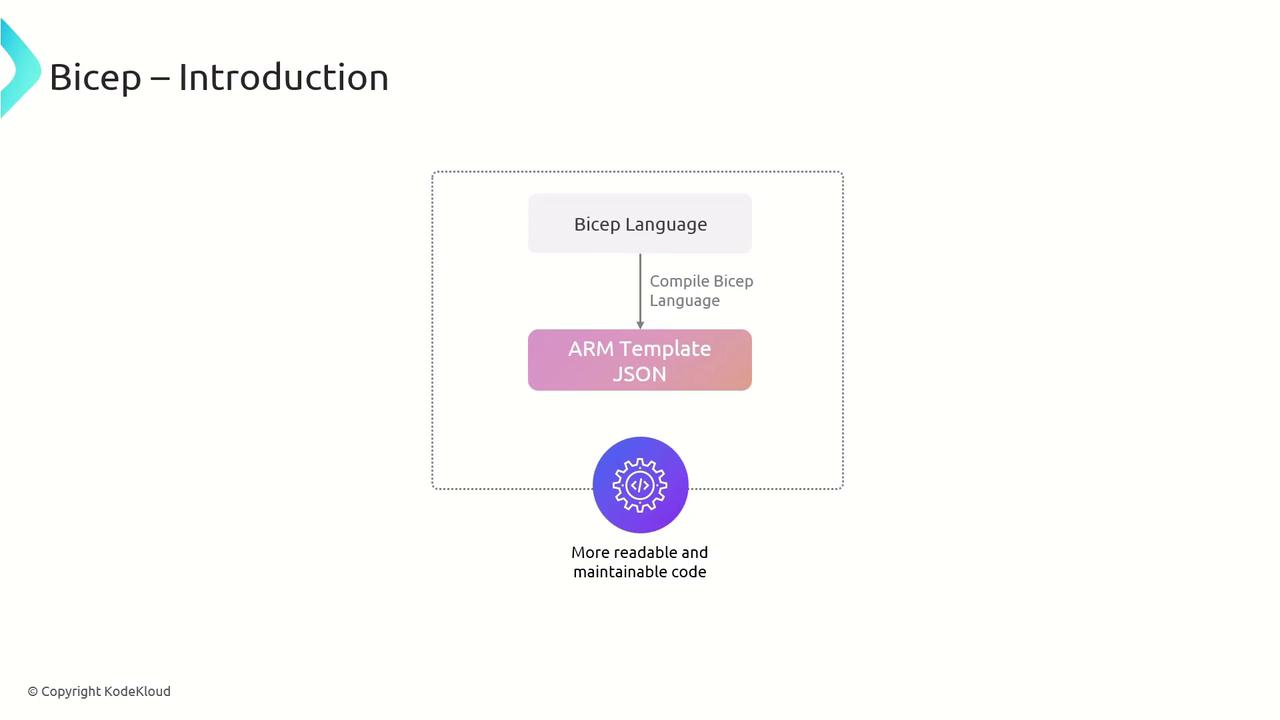
Azure Bicep is a domain-specific language for declaratively provisioning Azure resources. It builds on ARM templates by offering clearer syntax, built-in modularity, and first-class support for parameters and loops. In this guide, you’ll learn how Bicep works, its core benefits, how to install the Bicep CLI, and best practices for authoring and deploying Bicep code.
How Bicep Works
You write infrastructure definitions in concise Bicep syntax instead of ARM JSON. The Bicep CLI then compiles your code into a standard ARM template, ensuring compatibility with all Azure services while improving readability and maintainability.
Key Benefits
Adopting Bicep over raw ARM JSON gives you:
- Readable syntax that’s easier to navigate and review.
- Modularity with native support for reusable modules.
- First-class parameters & loops to reduce boilerplate and scale deployments.
Note
Bicep compiles directly to ARM templates under the hood, so you retain full compatibility with Azure Resource Manager.
Example Bicep Template
Here’s a simple Bicep file that deploys an Azure Storage account. Notice the concise syntax and built-in property types:
@description('Specifies the location for resources.')
param location string = 'eastus'
resource storageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-02-01' = {
name: 'examplestorageacct'
location: location
kind: 'StorageV2'
sku: {
name: 'Premium_LRS'
}
}
output storageAccountName string = storageAccount.name
Installing the Bicep CLI
You need the Azure CLI and the Bicep CLI to compile and deploy Bicep files.
Prerequisites
| Requirement | Minimum Version | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Azure CLI | 2.20.0 | Azure CLI |
| Visual Studio Code* | Latest | VS Code + Bicep extension |
*VS Code is optional but recommended for IntelliSense and snippets.
Note
Verify your Azure CLI version with az --version before installing Bicep.
Windows (PowerShell)
# Install or update Azure CLI if needed
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force
iwr -useb https://aka.ms/installbicep | iex
Linux (Bash)
# Download the latest Bicep binary
curl -Lo bicep https://github.com/Azure/bicep/releases/latest/download/bicep-linux-x64
chmod +x ./bicep
sudo mv ./bicep /usr/local/bin/bicep
macOS (Homebrew)
# Install Homebrew if not already installed
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# Install Bicep
brew tap azure/bicep
brew install bicep
Bicep File Structure
A typical Bicep file is organized into four sections:
- Parameters: External inputs to customize deployments.
- Variables: Reusable values within the template.
- Resources: Declarations of Azure resources to create or update.
- Outputs: Values returned after deployment.
Authoring Best Practices
Follow these guidelines to keep your Bicep code clean and maintainable:
- Use parameters and variables for configurable values.
- Break complex deployments into modules.
- Employ resource loops for bulk creation.
- Adopt consistent naming conventions.

Advanced Scripting Tips
- Run
bicep build --stdoutorbicep build --fileto validate logic before deployment. - Use output values to expose resource IDs and connection strings.
- Explicitly set dependsOn to control resource ordering.
- Manage secrets securely with Azure Key Vault.
Warning
Avoid hard-coding credentials or secrets directly in Bicep templates. Always reference Key Vault or Azure Managed Identities.

Deploying with Azure CLI
You can compile and deploy your Bicep files in one step using the Azure CLI:
- Ensure Azure CLI (with Bicep) is installed.
- Sign in to your Azure account (
az login). - Run
az deployment group createagainst a resource group or subscription.

Example Deployment
# Create a resource group
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location eastus
# Deploy the Bicep template
az deployment group create \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--template-file main.bicep \
--parameters storageAccountType=Premium_LRS
Visual Studio Code Integration
With the Bicep extension in VS Code, you get:
- IntelliSense for resource types and properties.
- Prebuilt code snippets for common patterns.
- In-editor deployments via Azure CLI commands.
Deploying in Azure Cloud Shell
You can also author and deploy Bicep files directly in Cloud Shell:
- Upload your
.bicepfile to Cloud Shell. - Run the same Azure CLI commands:
az group create --name ExampleGroup --location eastus
az deployment group create \
--resource-group ExampleGroup \
--template-file azureddeploy.bicep \
--parameters storageAccountType=Standard_GRS
Azure Automanage Machine Configuration
Azure Automanage Machine Configuration automates VM management by continuously applying best practices and security guidelines. It leverages Desired State Configuration (DSC) to ensure your virtual machines always conform to the specified configuration.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content