AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Implement Security and Validate Code Bases for Compliance
Working with open source software
Open source software (OSS) is foundational to modern development workflows. By leveraging established libraries and tools, teams can accelerate delivery, foster innovation, and collaborate across global communities. However, integrating OSS also introduces unique challenges—ranging from security vulnerabilities to licensing obligations. This guide covers best practices for evaluating, adopting, and managing open source components in your projects.
Common Concerns with Open Source Components
Organizations often hesitate to adopt OSS because of perceived risks in:
- Maintainability
- Reliability
- Performance
It’s critical to assess each dependency before integration, ensuring that it meets your quality and security standards.
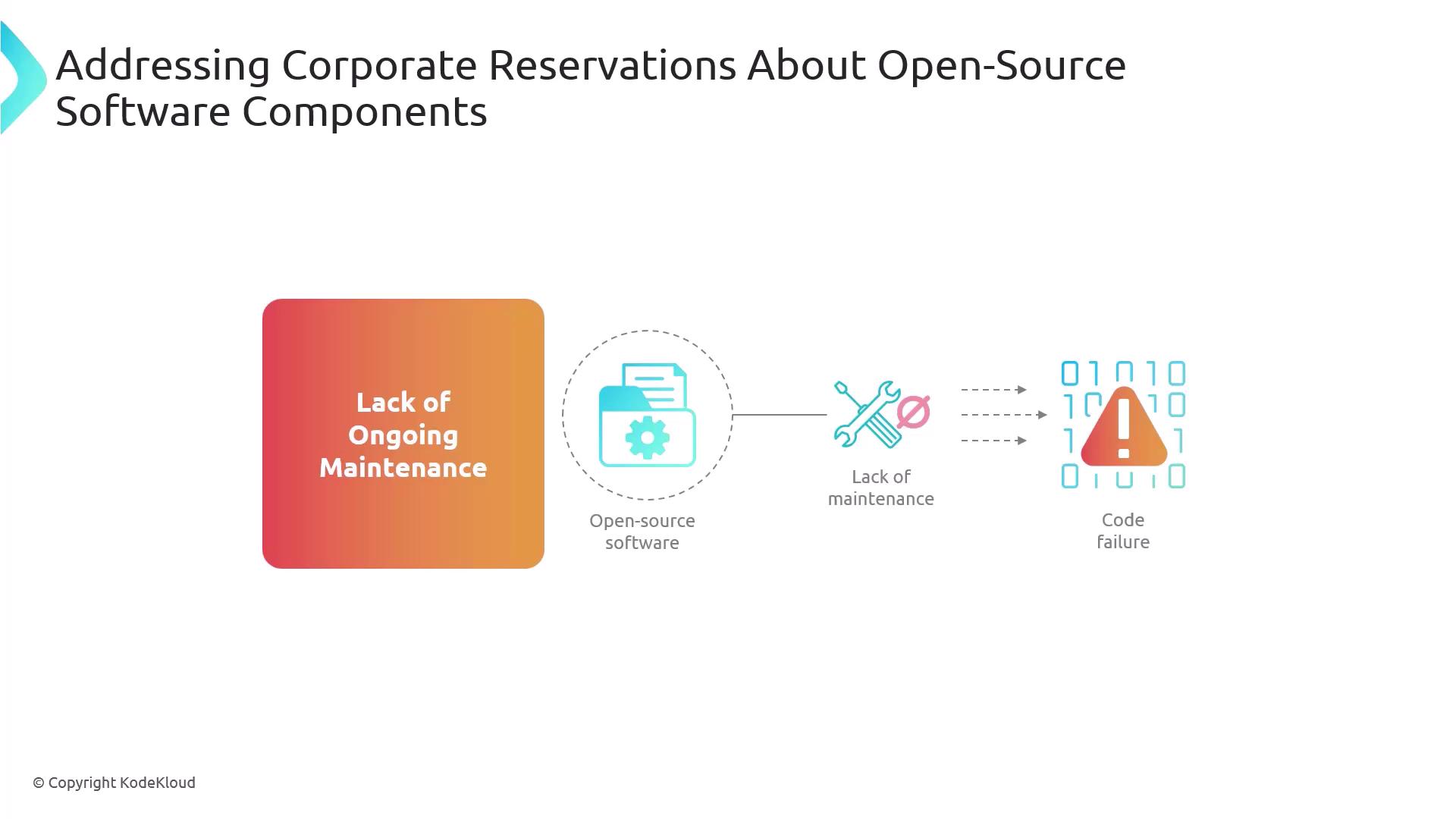
Lack of Ongoing Maintenance
Projects without active maintainers can stagnate, exposing your systems to compatibility issues and unpatched vulnerabilities.
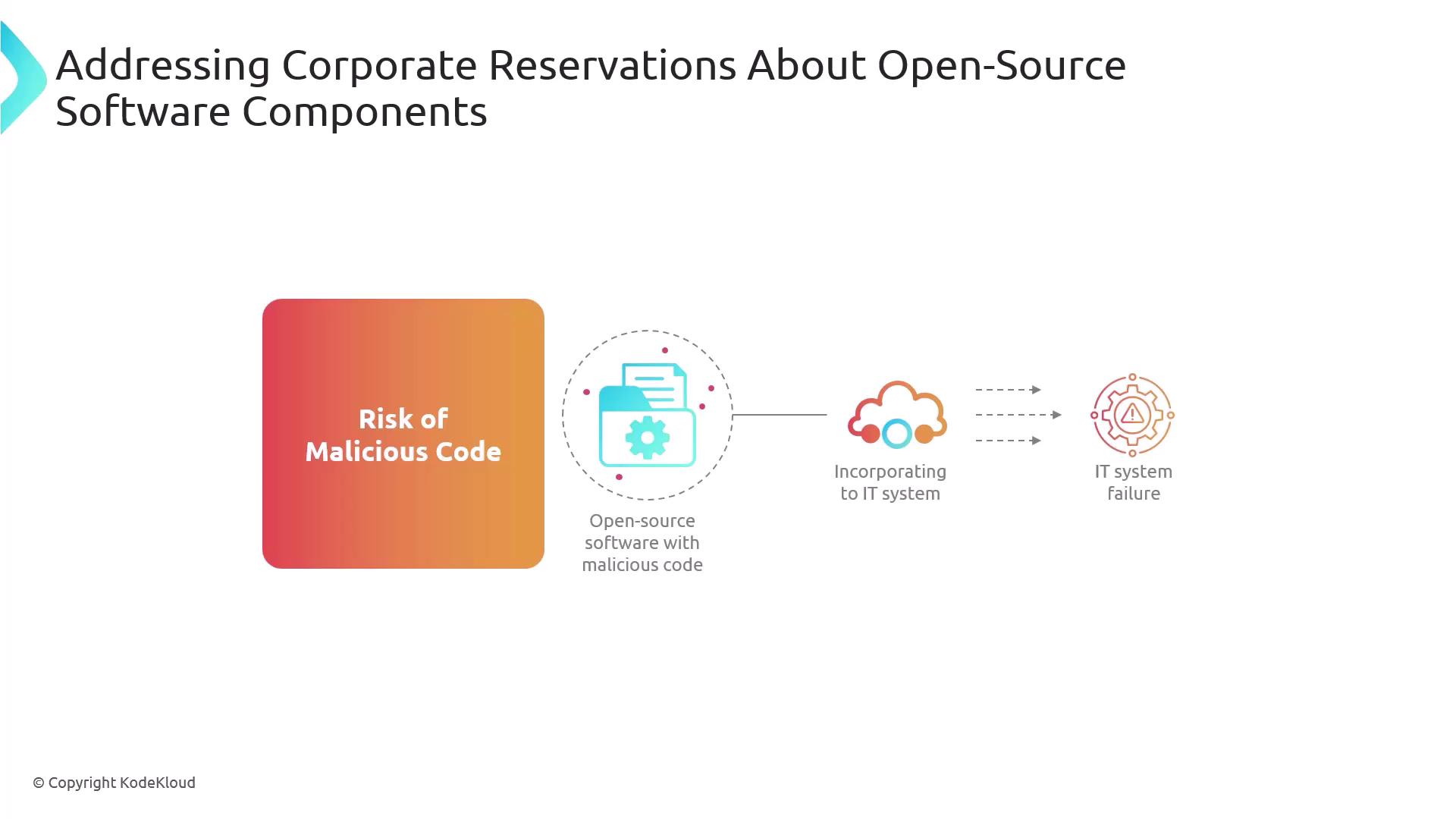
Malicious Code Injection
Although rare, attackers may sneak harmful payloads into OSS packages. These can compromise your entire infrastructure if undetected.
Security Warning
Always run automated security scans (e.g., Snyk, Dependabot) and perform manual code reviews on new dependencies.
Vulnerability Management
Your application’s security posture is only as strong as its weakest dependency. Subscribe to security advisories and apply patches promptly.
Licensing Terms
Open source licenses dictate how you can use, modify, and distribute software. Noncompliance may lead to legal exposure or forced disclosure of proprietary code. Always review licenses before adoption.
Essentials of Open-Source Licensing
All OSI-approved licenses share these core freedoms:
Unhindered Redistribution
Permission to distribute the software openly.Access to Source Code
Full source must be available for inspection and audit.
Freedom to Modify
Ability to adapt the code and create derivatives.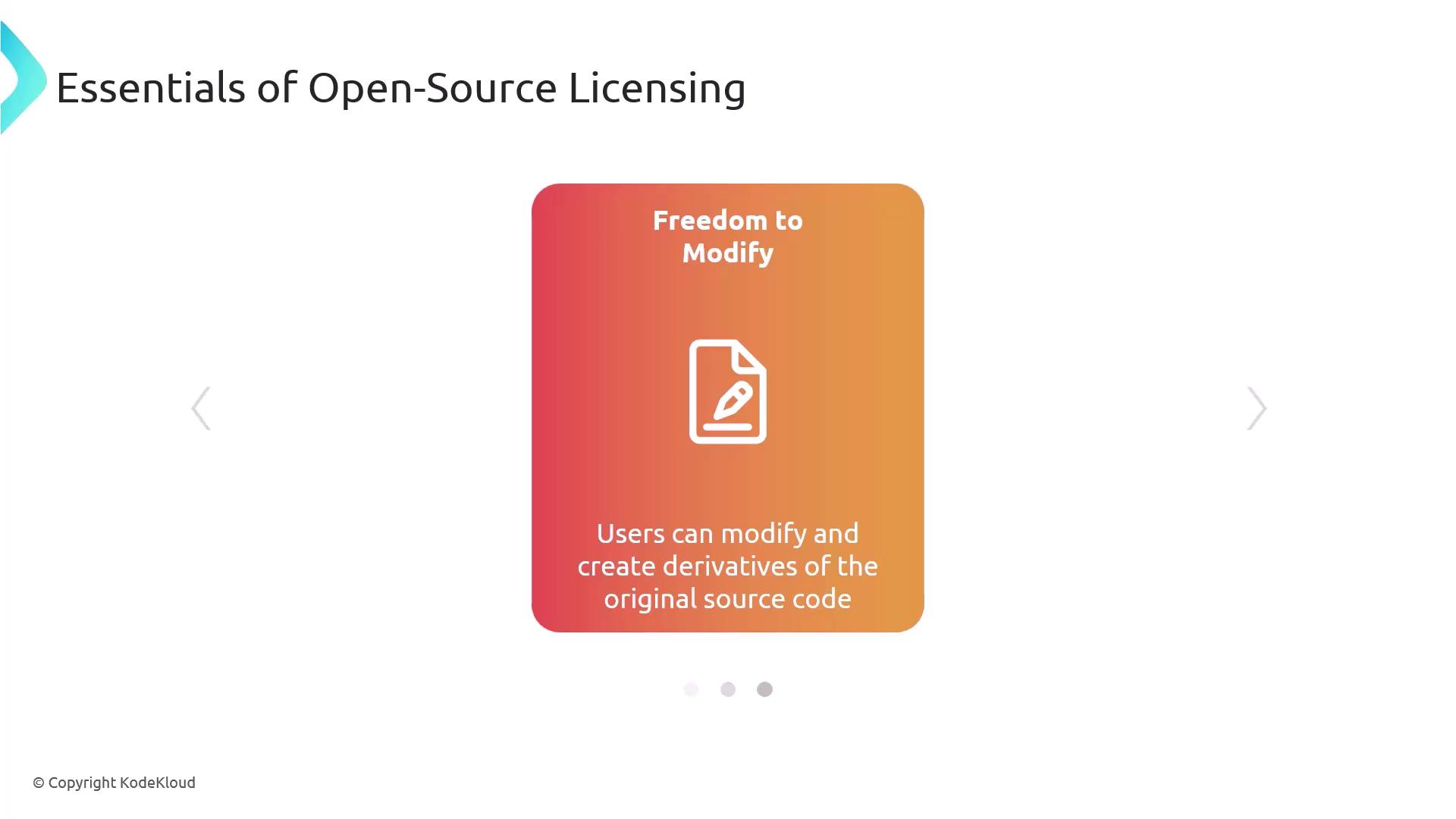
Integrity of Author’s Source Code
Authors can maintain a canonical version and issue patches.Non-Discrimination
No restrictions based on user identity or field of use.
Field of Endeavor Neutrality
Software may be used in any domain—business, research, or personal.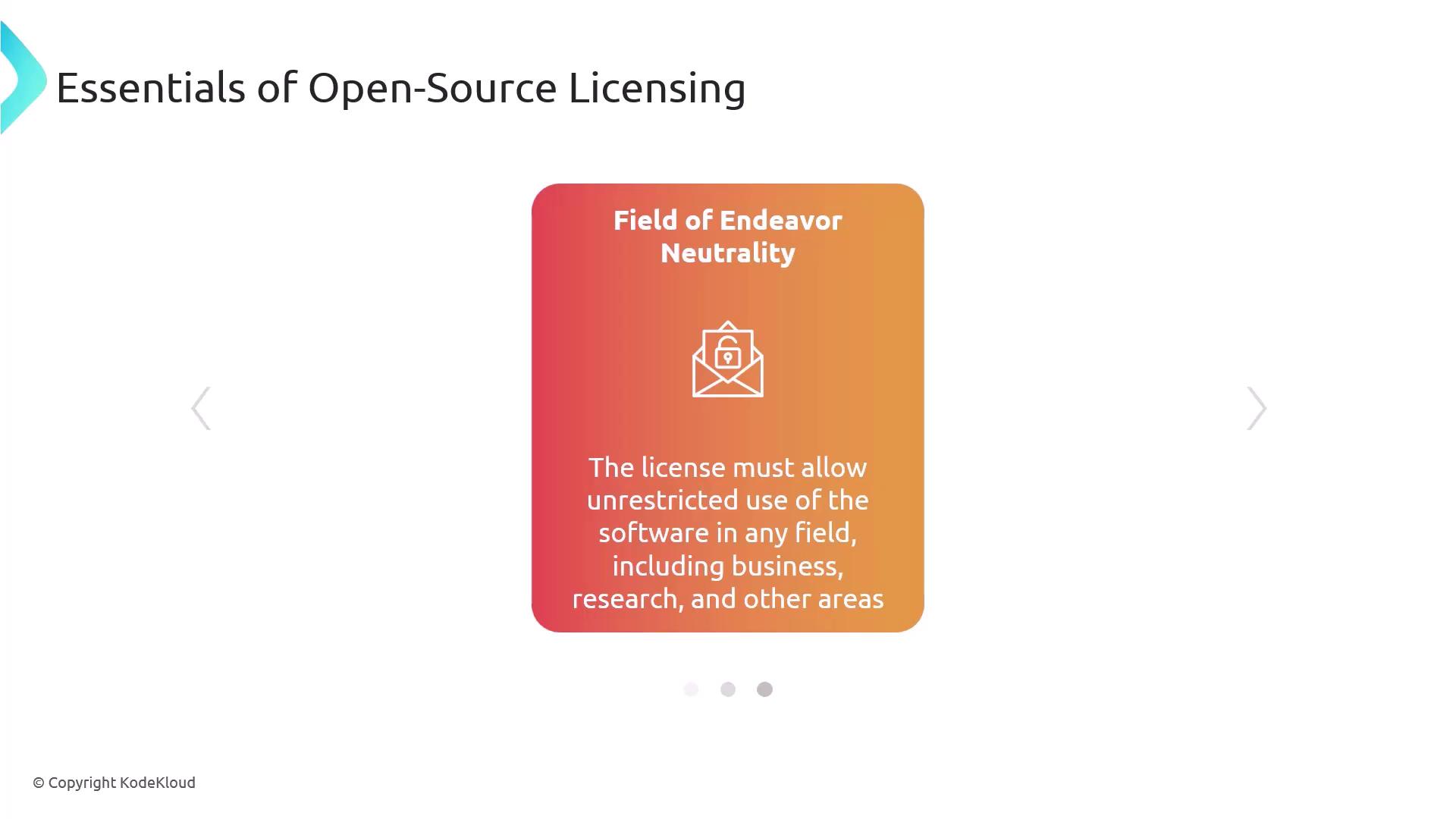
Product Neutrality
No requirement to tie usage to a specific product.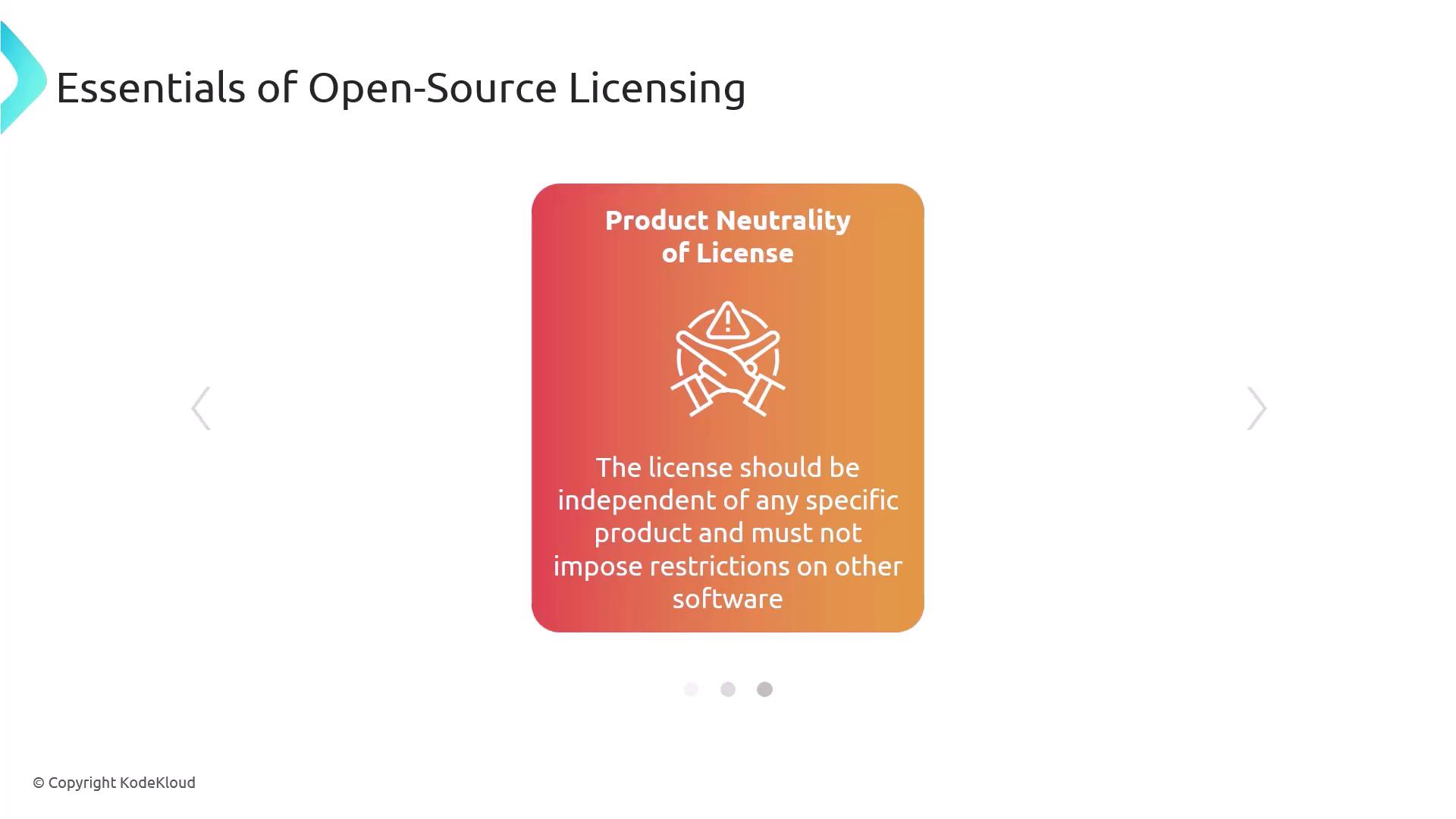
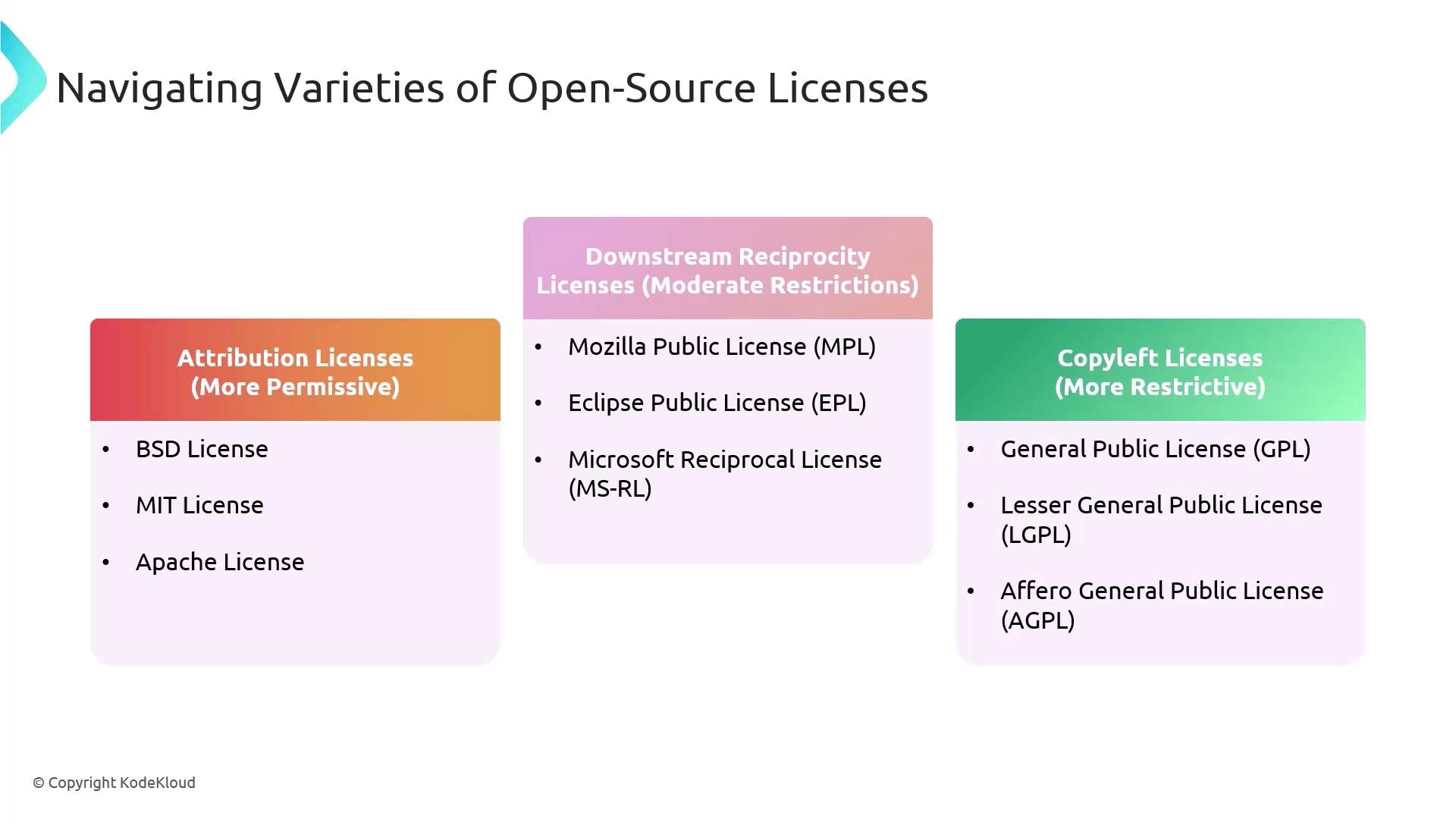
Types of Open-Source Licenses
Choose a license model that aligns with your project’s distribution and contribution strategy:
| License Category | Restrictions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Attribution (Permissive) | Credit required | MIT, BSD, Apache 2.0 |
| Downstream Reciprocity | Share modifications | Mozilla Public License (MPL) |
| Strong Copyleft | Derivatives under same terms | GNU GPL v3 |
Assessing License Impact
Before adopting, document each dependency’s license and its implications:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| License Impact Level | High, Medium, or Low (legal obligations) |
| License Significance | Compliance requirements, IP rights, usage rights |

When in doubt, consult your legal team or open source office before proceeding with adoption.
Links and References
Remember: compliance with open source licenses is mandatory. Review and document license terms for every third-party component before integrating it into your codebase.
Watch Video
Watch video content