| Pipe Type | Symbol/Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Named Pipe | mkfifo / FIFO | Creates a persistent file endpoint for inter-process communication. | |
| Anonymous Pipe | ` | ` | Chains commands on the fly, passing stdout to stdin. |
Named Pipes (FIFOs)
Named pipes, also known as FIFOs, are special files you create with
mkfifo. They let processes communicate through a named file path. Here, < and > redirect standard input and output to or from file resources, sometimes referred to as file-based piping.abc.txt contains five unsorted letters. You can sort them and save the results:
< abc.txtfeeds the contents ofabc.txtintosort.> abc_sorted.txtwrites the sorted output toabc_sorted.txt.cat abc_sorted.txtdisplays the sorted list.
Anonymous Pipes
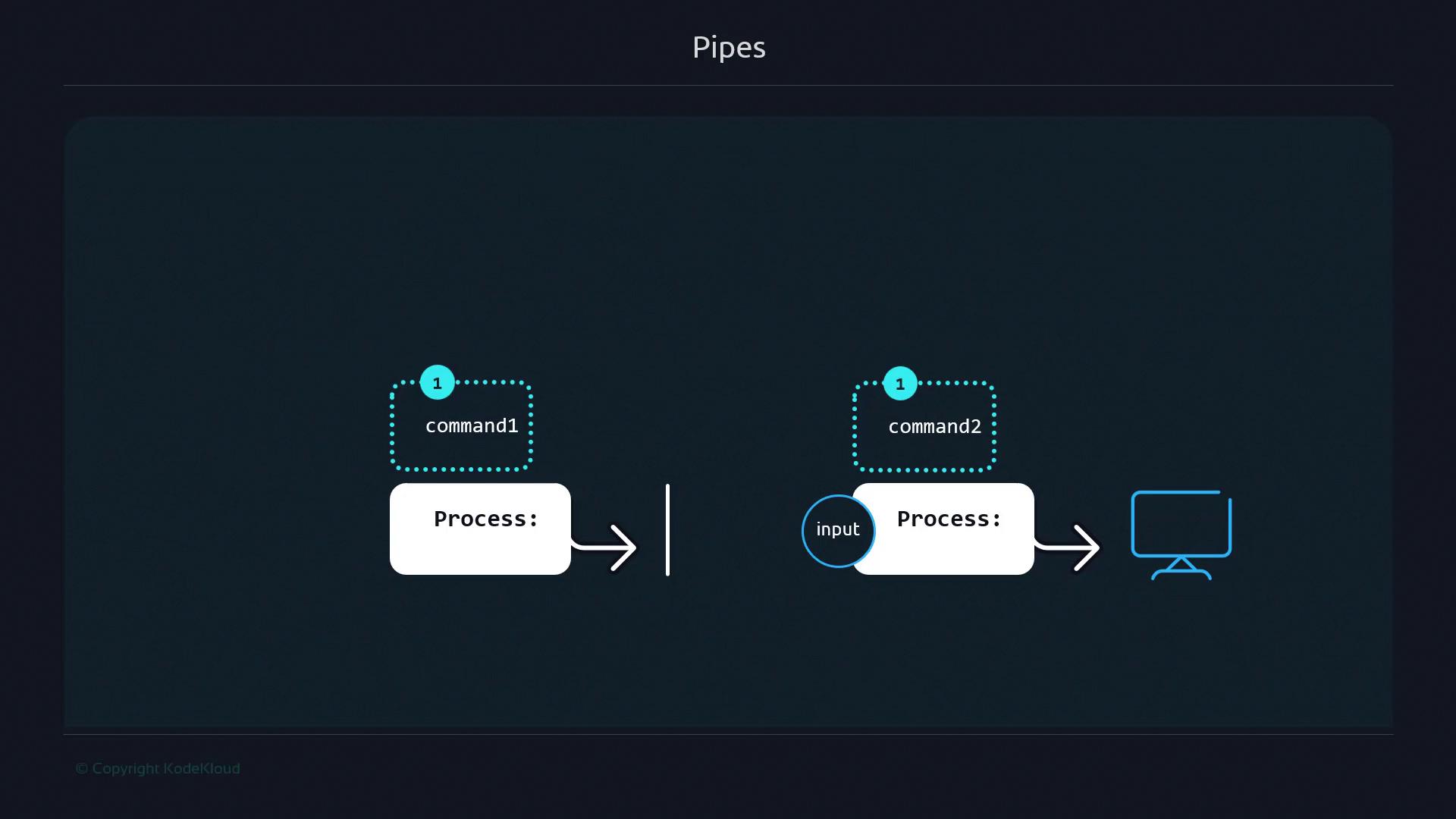
Anonymous pipes use the| symbol to pass commands’ output directly as input to the next command, without creating files.

- The first command produces data.
- Each subsequent command processes the incoming data and passes it along.
- The final output appears in your terminal.
Example: Filtering and Sorting a List
Givenanimals.txt containing unsorted names (with duplicates):
cat animals.txtreads the list.grep -i "o"selects lines with “o” (case-insensitive).sortorders the filtered names.
|, letting each stage transform the data in sequence.
Handling Errors in Pipelines
By default, pipelines only pass standard output (stdout) to the next command. Errors (stderr) are displayed directly on the terminal, and the pipeline continues.Errors are not piped between commands. Use redirection like
2>&1 if you need to capture stderr in your pipeline.