Prerequisites
- Jenkins with Configuration as Code plugin installed
- Access to Jenkins controller shell
- Basic familiarity with YAML and Jenkins plugins
1. Explore Example Configurations
The JCasC plugin demos on GitHub contain ready-made use cases:You can browse the demos directory for examples ranging from security setups to cloud integrations.
2. Configure Global Authorization
To set up a matrix-based authorization strategy, add the following to yourjenkins-casc.yaml:
3. Configure a Kubernetes Cloud
Click Config YAML under the Kubernetes demo to copy this snippet: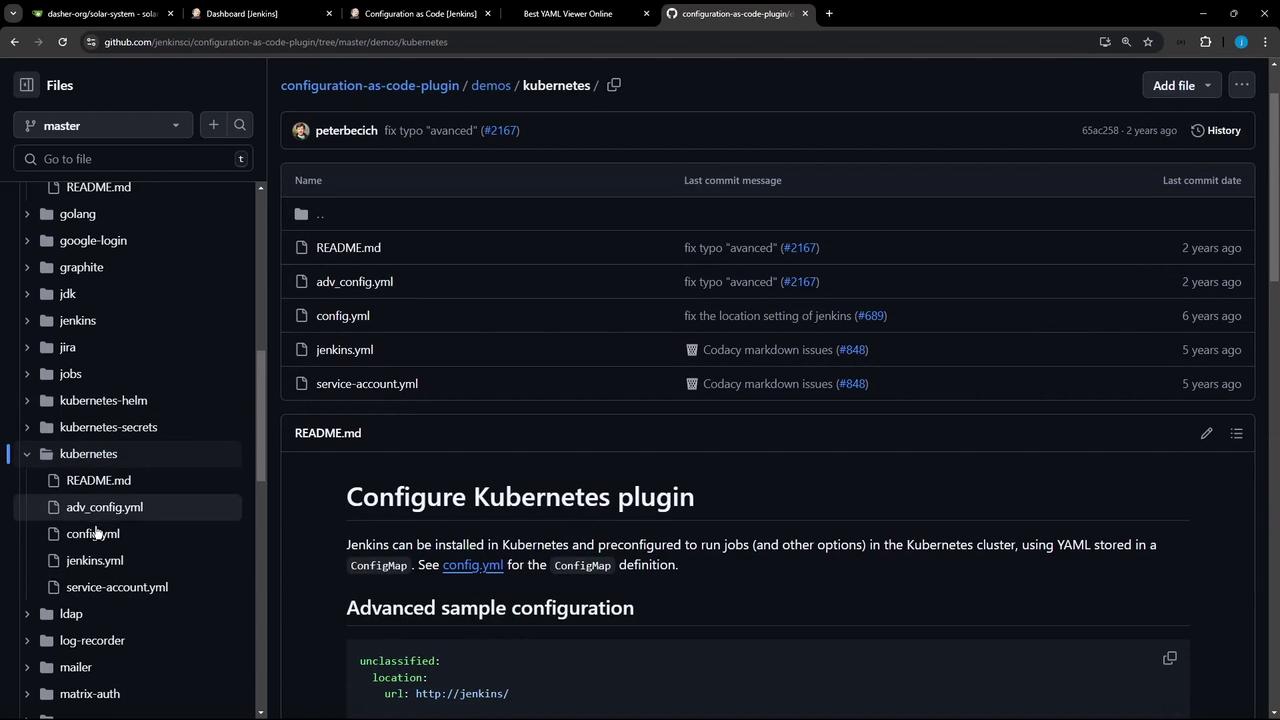
4. Install Build Tools
You can also install Node.js, Git, Maven, and SonarQube Scanner using JCasC. Here’s an example for Node.js:Tool Installation Summary
| Tool | Version Identifier | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Node.js | 12.11.1 | Auto-installed; refreshes npm packages every 48 hours |
| Git | Default | Uses system git binary |
| Maven | 3.9.8 | Managed via internal installer |
| SonarQube Scanner | 6.10 | Installed through the SonarRunner installer |
5. Edit Your jenkins-casc.yaml
On the controller, open or create your configuration file:6. Define Pipeline Jobs with Job DSL
In the demos folder, there’s a sample that uses the Job DSL plugin to create a folder and pipeline job: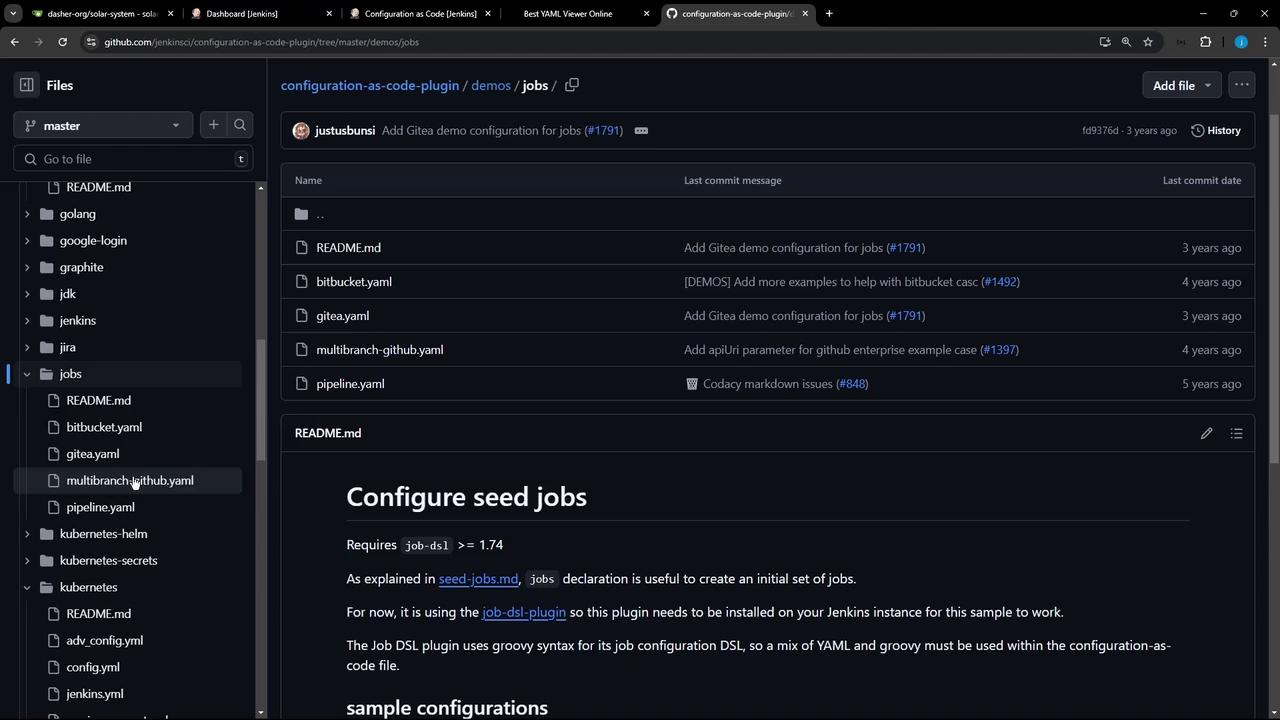
jenkins-casc.yaml:
7. Reload Configuration and Troubleshoot
After saving, go to Manage Jenkins → Configuration as Code → Reload Existing Configuration. You may see: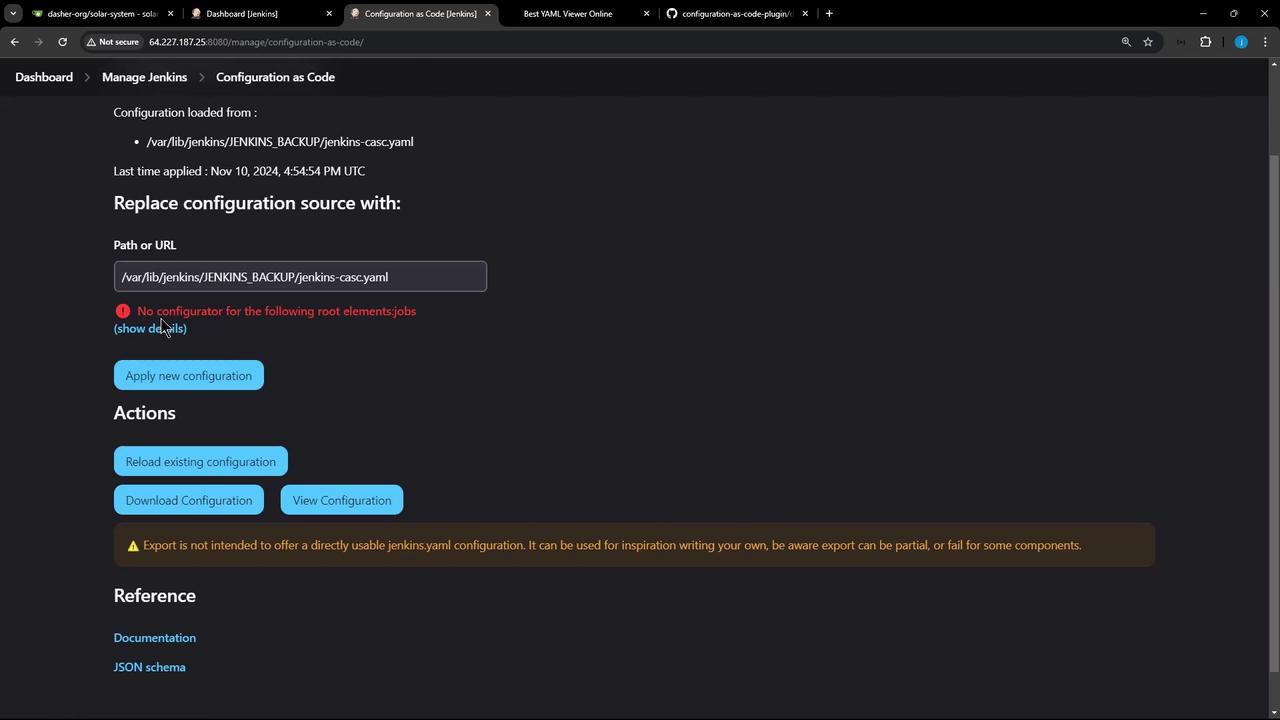
If you encounter
UnknownConfiguratorException: No configurator for the following root elements: jobs, it means the Job DSL plugin is not installed.- Manage Jenkins → Manage Plugins
- Search for Job DSL and install.
- Reload or reapply your JCasC configuration.
8. Verify Jobs and Tools
Once the DSL plugin is active, Jenkins will create thetest-jobs folder and the default-agent pipeline automatically. You can also confirm tool installations under Manage Jenkins → Global Tool Configuration: