Certified Jenkins Engineer
Jenkins Pipelines
Demo Pipeline Script from SCM
In this tutorial, we’ll demonstrate how to source your Jenkins pipeline definition directly from a Source Control Management (SCM) system such as GitHub or Gitea. Moving your pipeline code into version control improves maintainability, traceability, and collaboration.
1. Inline Pipeline Definition (Not Recommended)
Defining a pipeline directly in the Jenkins UI is quick but hard to maintain. Changes aren’t versioned, and collaboration is limited.
Warning
Avoid storing pipeline scripts in the UI. Inline definitions lack versioning and code review.
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven 'M398'
}
stages {
stage('Echo Version') {
steps {
sh 'echo Print_Maven_Version'
sh 'mvn -version'
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
// Fetch source code
git 'http://139.84.159.194:5555/dasher-org/jenkins-hello-world.git'
// Package with Maven
// sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true'
}
}
stage('Unit Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
}
}
2. Creating a Jenkinsfile in Your Repository
Store your pipeline script as a Jenkinsfile at the root of your project repository:
- Navigate to your app repo on GitHub or Gitea.
- Click Add file → Create new file.
- Name it
Jenkinsfile. - Paste the pipeline script and commit to
main.
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
// Installs Maven configured as "M398"
maven "M398"
}
stages {
stage('Echo Version') {
steps {
sh 'echo Print Maven Version'
sh 'mvn -version'
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
// Auto-checkout not yet enabled
git 'http://139.84.159.194:5555/dasher-org/jenkins-hello-world.git'
sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true'
}
}
stage('Unit Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
}
}
3. Simplifying the Jenkinsfile
Once Jenkins auto-checks out your code, remove the explicit git step to simplify:
Note
Jenkins automatically clones the repository when using Pipeline script from SCM.
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven "M398"
}
stages {
stage('Echo Version') {
steps {
sh 'echo Print Maven Version'
sh 'mvn -version'
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
// Repository checked out automatically
sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true'
}
}
stage('Unit Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
}
}
4. Configuring “Pipeline script from SCM”
In Jenkins:
- Create (or open) a Pipeline job.
- Under Pipeline > Definition, select Pipeline script from SCM.
- Choose Git and enter your repository details:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Repository URL | http://139.84.159.194:5555/dasher-org/jenkins-hello-world.git |
| Branch Specifier | main |
| Script Path | Jenkinsfile |
If the URL is missing or invalid, Jenkins displays an error:
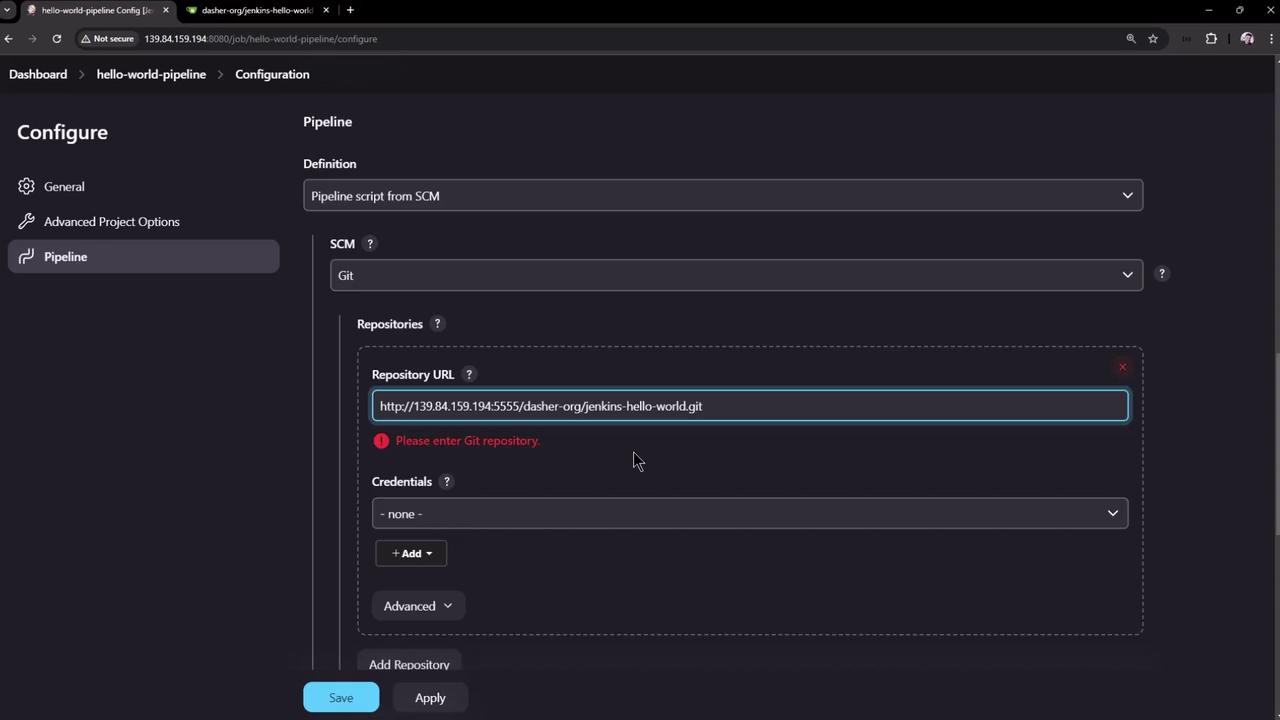
Save the job and click Build Now.
5. Observing Automatic Checkout and Build
When the pipeline runs, Jenkins adds a Checkout SCM stage:
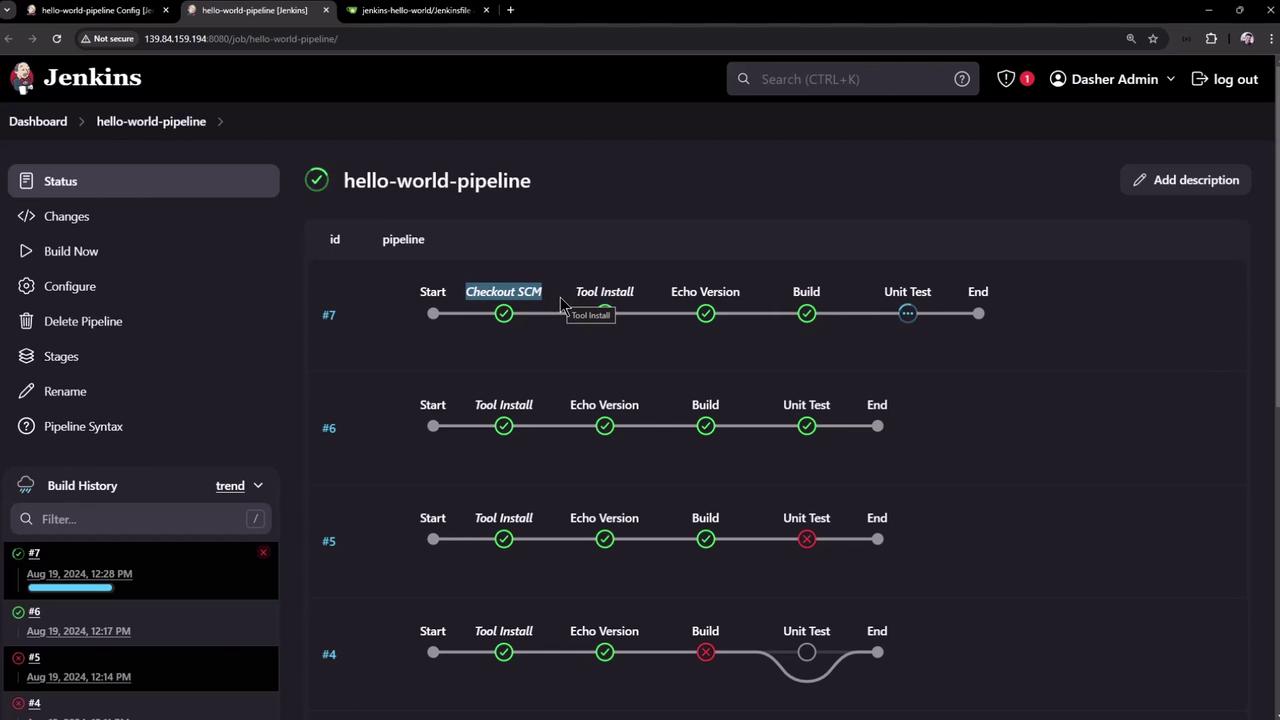
Console Output Highlights
> git rev-parse --resolve-git-dir /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/hello-world-pipeline/.git # timeout=10
> git config remote.origin.url http://139.84.159.194:5555/dasher-org/jenkins-hello-world.git # timeout=10
> git fetch origin +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/* # timeout=10
> git checkout -f origin/main # timeout=10
echo Print Maven Version
mvn --version
Apache Maven 3.9.8 (36645f6c9b5079805ea5009217e36cff344256)
Maven home: /var/lib/jenkins/tools/hudson.tasks.Maven_MavenInstallation/M398
Java version: 17.0.12, vendor: Ubuntu
Default locale: en_US, platform encoding: UTF-8
OS name: "linux", version: "6.8.0-39-generic", arch: "amd64"
6. Browsing the Repository in Your SCM
Verify your Jenkinsfile and project files in the web UI:
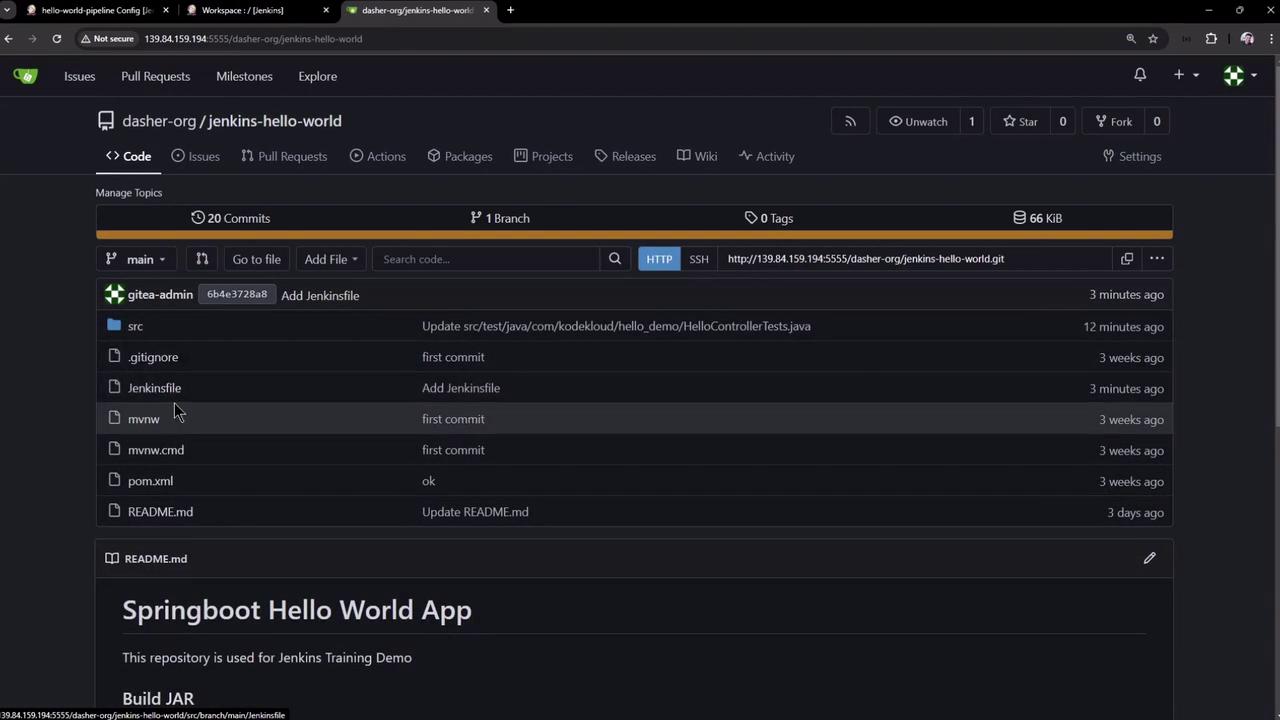
7. Exploring the Jenkins Workspace
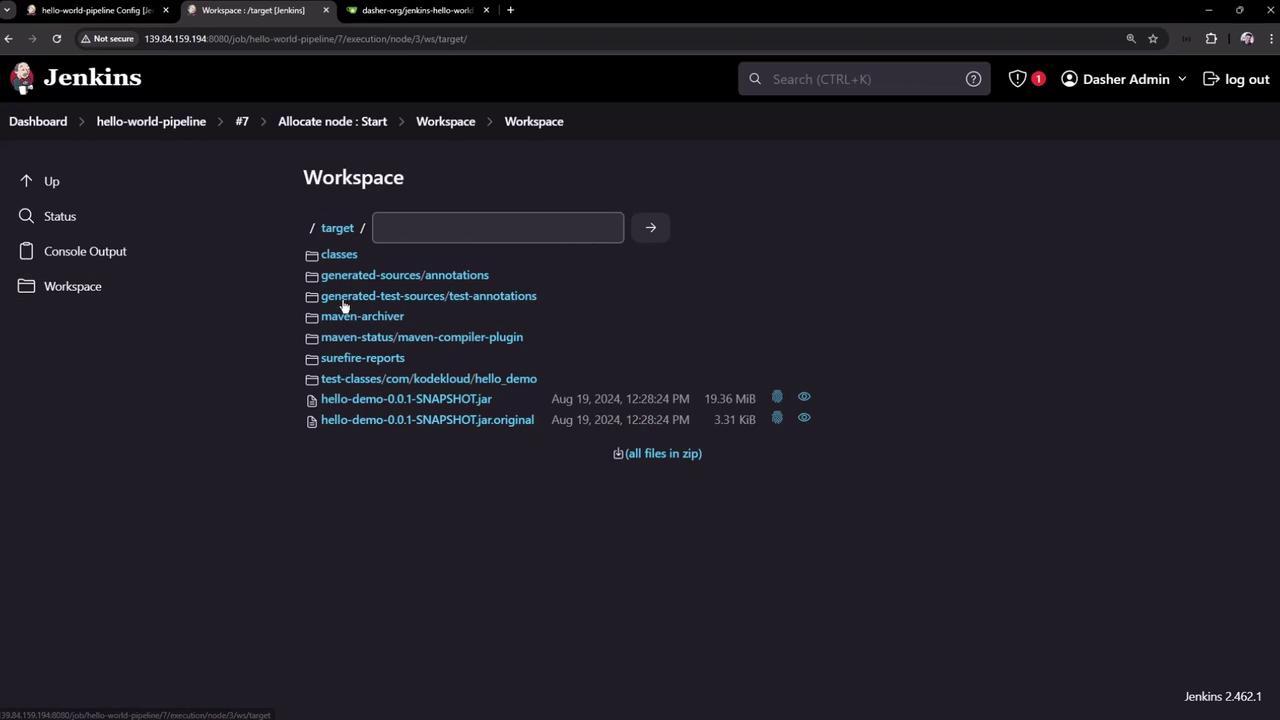
Click Workspace in the job sidebar to view checked-out files and build artifacts:
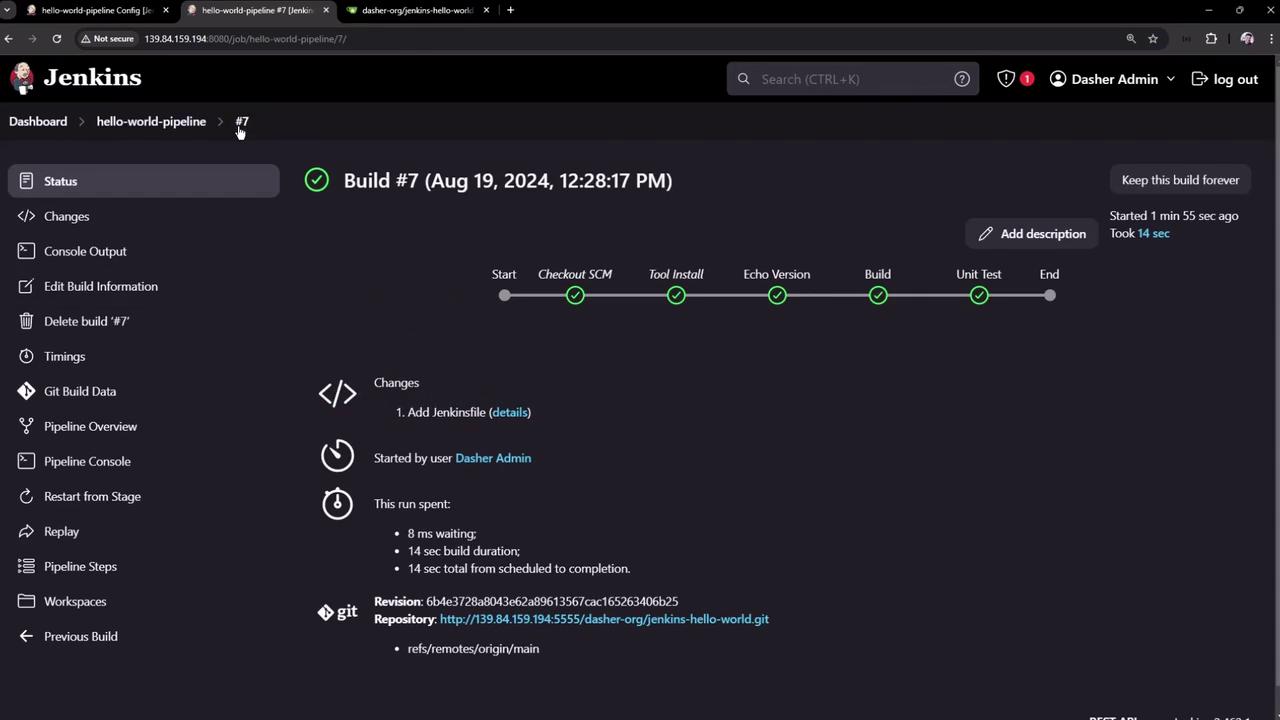
8. Reviewing Completed Build Details
Inspect completed builds and each pipeline stage:
9. Inspecting Jenkins Home and Workspaces on the Controller
Access your Jenkins controller via SSH to list directories:
# View Jenkins home directory
cd /var/lib/jenkins
ls -l
# List job workspaces
cd workspace/
ls -l
# Inspect hello-world-pipeline workspace
cd hello-world-pipeline
ls -l
That’s it! You’ve learned how to manage your Jenkins pipeline script in SCM, run builds, and explore both the SCM repo and Jenkins workspace.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab