GitOps Repository Architecture
A typical GitOps workflow relies on two separate Git repositories:| Repository Type | Contents | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Application Repository | Source code, configuration files, certificates, optional container images in Git | Triggers CI builds and houses application assets |
| Configuration (Manifests) Repo | Kubernetes YAML manifests for Deployments, Services, ConfigMaps, Secrets | Single source of truth for cluster state |
Keep secrets out of Git or use an external secrets manager. Never store plain-text credentials in your manifests.
ArgoCD: The GitOps Operator
ArgoCD runs inside your Kubernetes cluster and continuously:- Monitors the configuration repository for changes
- Pulls updated manifests
- Applies those manifests to synchronize cluster state with Git
CI/CD Pipeline Workflow
When a developer pushes changes to the application repository (for example, updating code or adding a Jenkinsfile), a CI/CD pipeline—often implemented in Jenkins—executes the following stages:| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit Tests | Run npm test, pytest, or equivalent |
| Build Docker Image | docker build -t myapp:${VERSION} . |
| Push to Docker Registry | docker push myapp:${VERSION} |
- Clone the configuration repository
- Modify the image tag in
deployment.yaml - Commit changes to a feature branch
- Open a Pull Request against
main
Avoid force-pushing to the default branch. Always use pull requests to maintain an auditable history.
Rolling Back
ArgoCD’s history and rollback features enable you to revert to a stable release in minutes: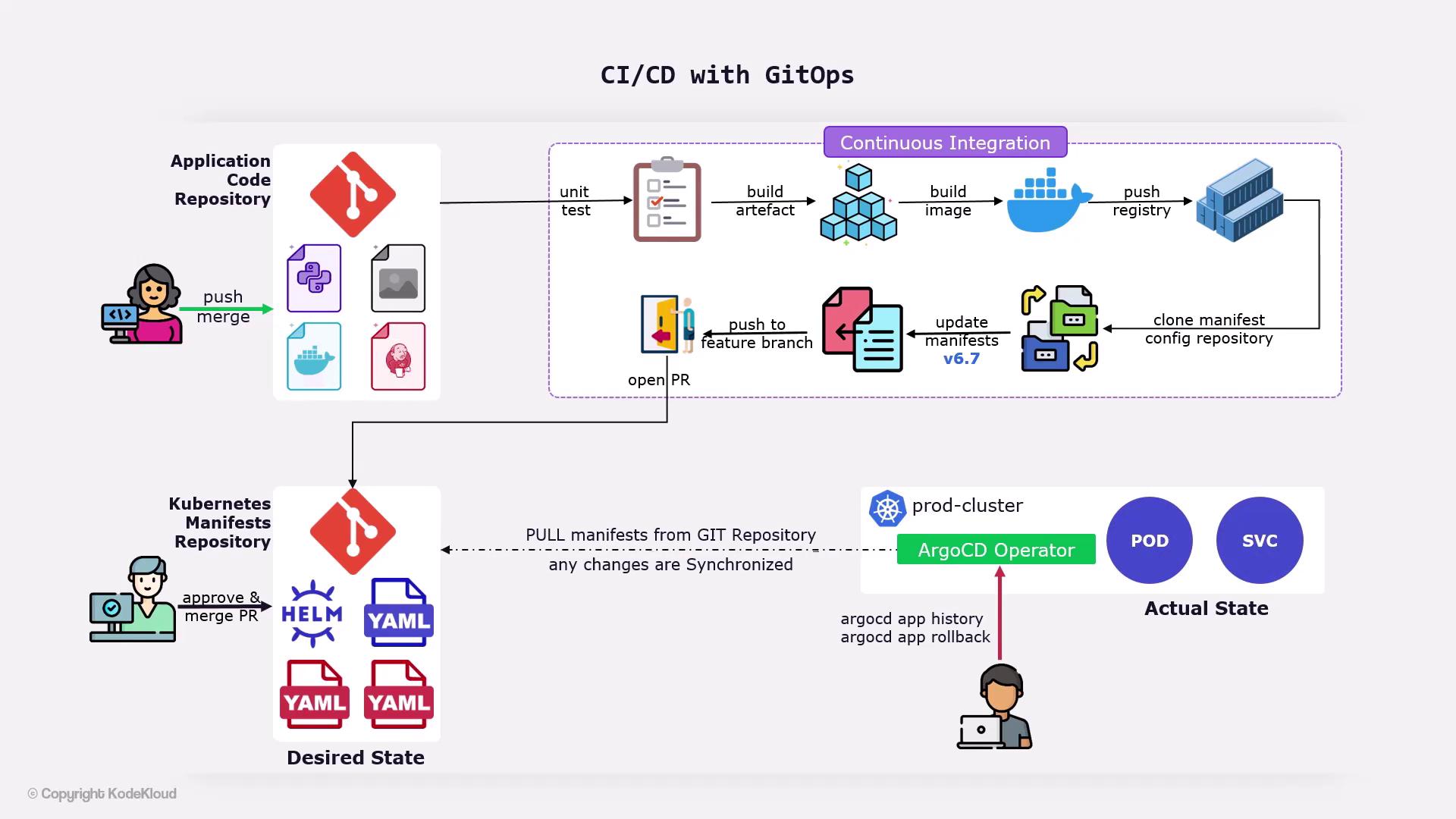
Demo Preview
In the upcoming demos, you will:- Create a Jenkinsfile defining all pipeline stages
- Open a pull request to update the Kubernetes manifests repository
- Watch ArgoCD synchronize changes and perform rollbacks if necessary