- Inspecting the Jenkins Workspace
- Creating the S3 Bucket
- Configuring IAM and Jenkins Credentials
- Installing the Pipeline: AWS Steps Plugin
- Generating an S3 Upload Snippet
- Adding the Upload Stage to the Jenkinsfile
- Authenticating with AWS in the Pipeline
- Running the Pipeline
- Reviewing the Console Output
- Verifying Artifacts in S3
- Links and References
Inspecting the Jenkins Workspace
First, browse your Jenkins workspace via the Classic UI to verify all generated reports are present: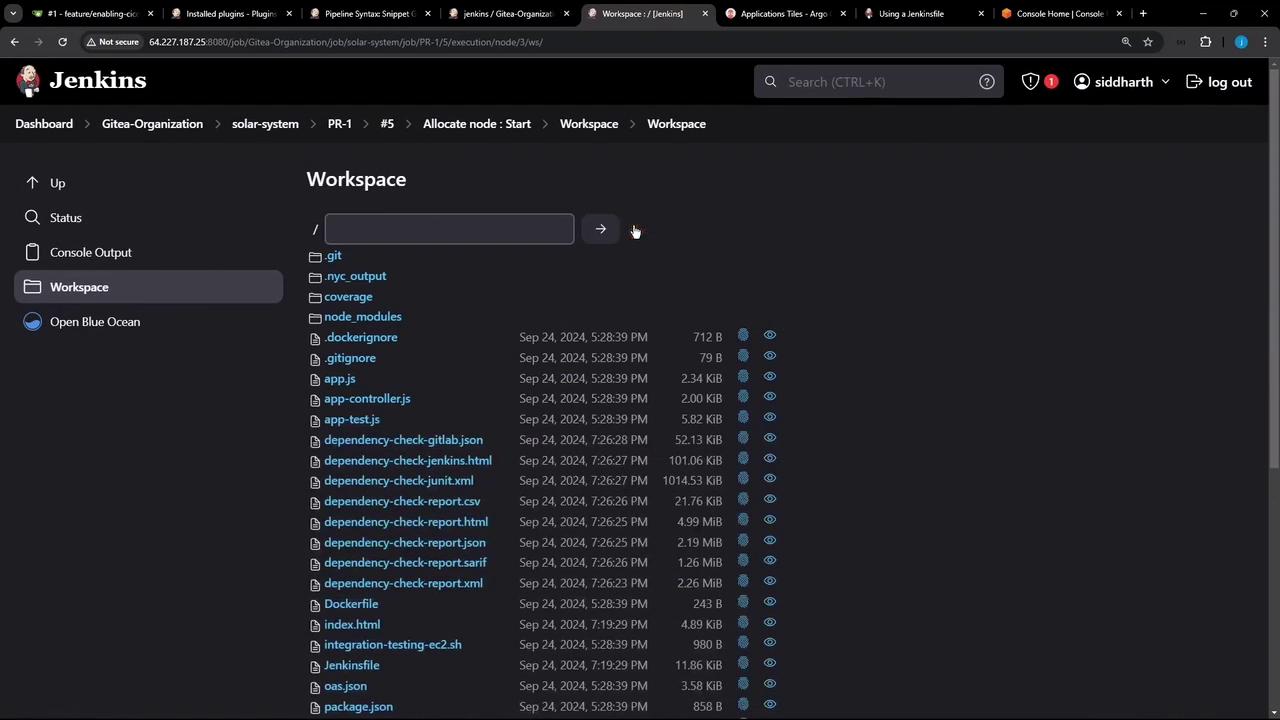
| Report Type | Directory / File Pattern |
|---|---|
| Code coverage | coverage/ |
| Dependency-check | dependency-check-report.html, etc. |
| Unit test results | test-results.xml |
| Container scans | trivy*.* |
| OWASP ZAP scans | zap*.* |
Creating the S3 Bucket
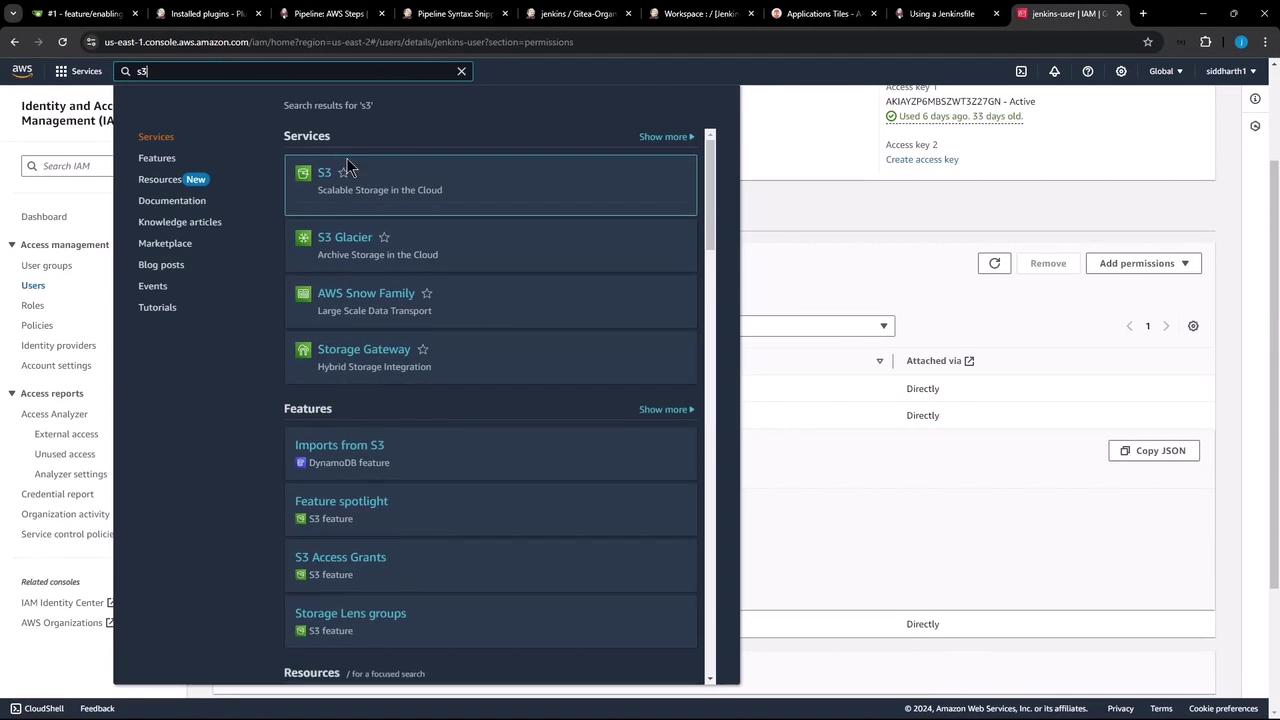
In the AWS S3 console, create a new bucket (e.g.,solar-system-jenkins-reports-bucket) in US East (Ohio). This bucket will house all your Jenkins reports:
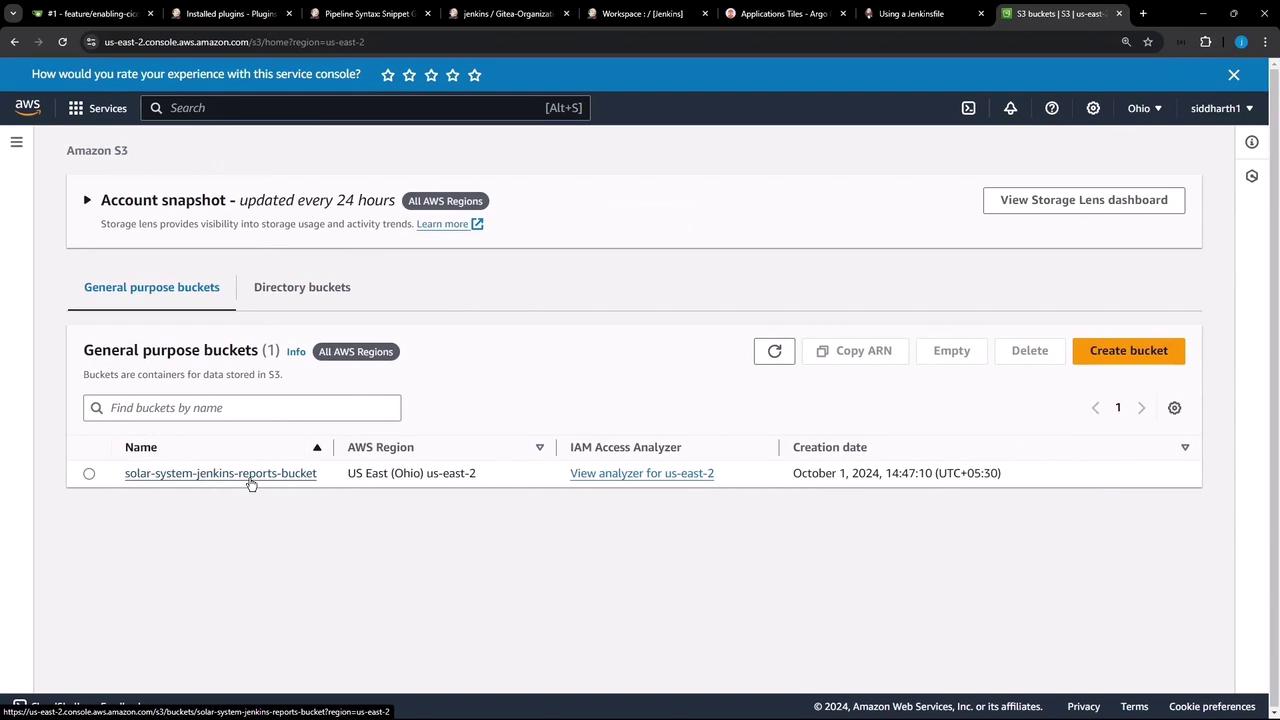
Configuring IAM and Jenkins Credentials
- In AWS IAM, create or select a user with the
AmazonS3FullAccesspolicy. - In Jenkins, go to Credentials and add a new AWS Credentials entry. Set the ID to
aws-s3-ec2-lambda-creds.
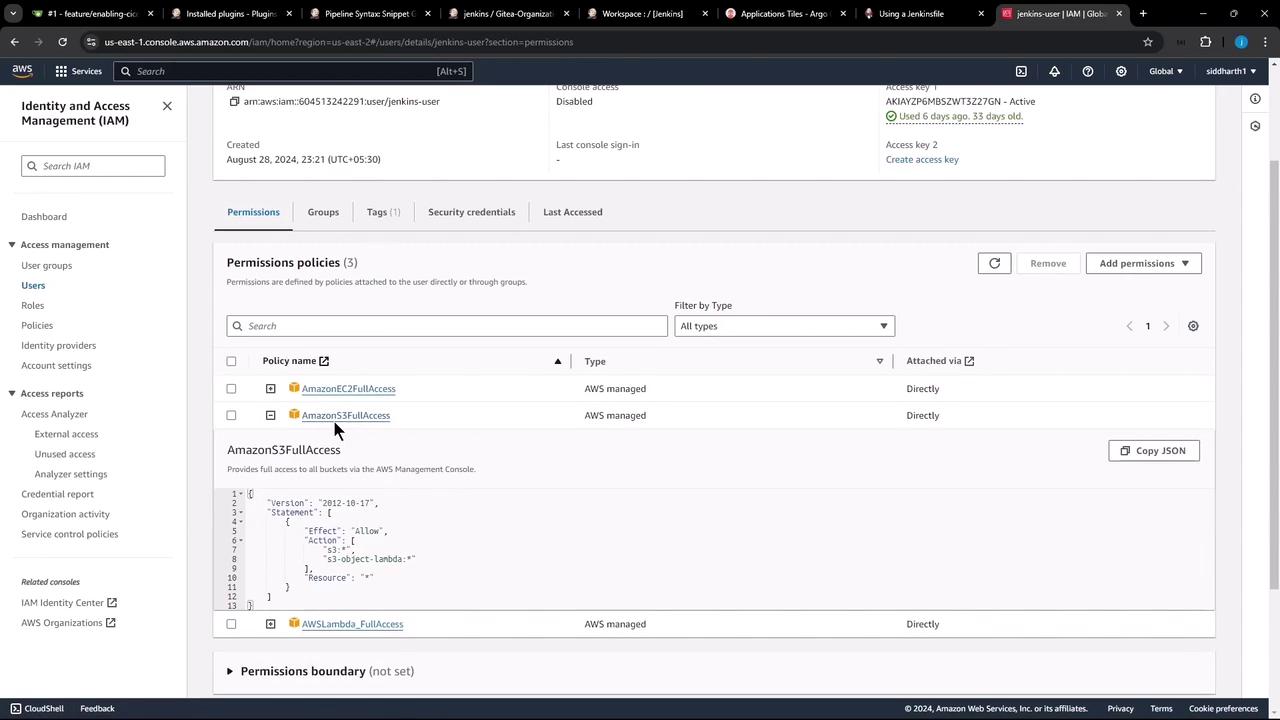
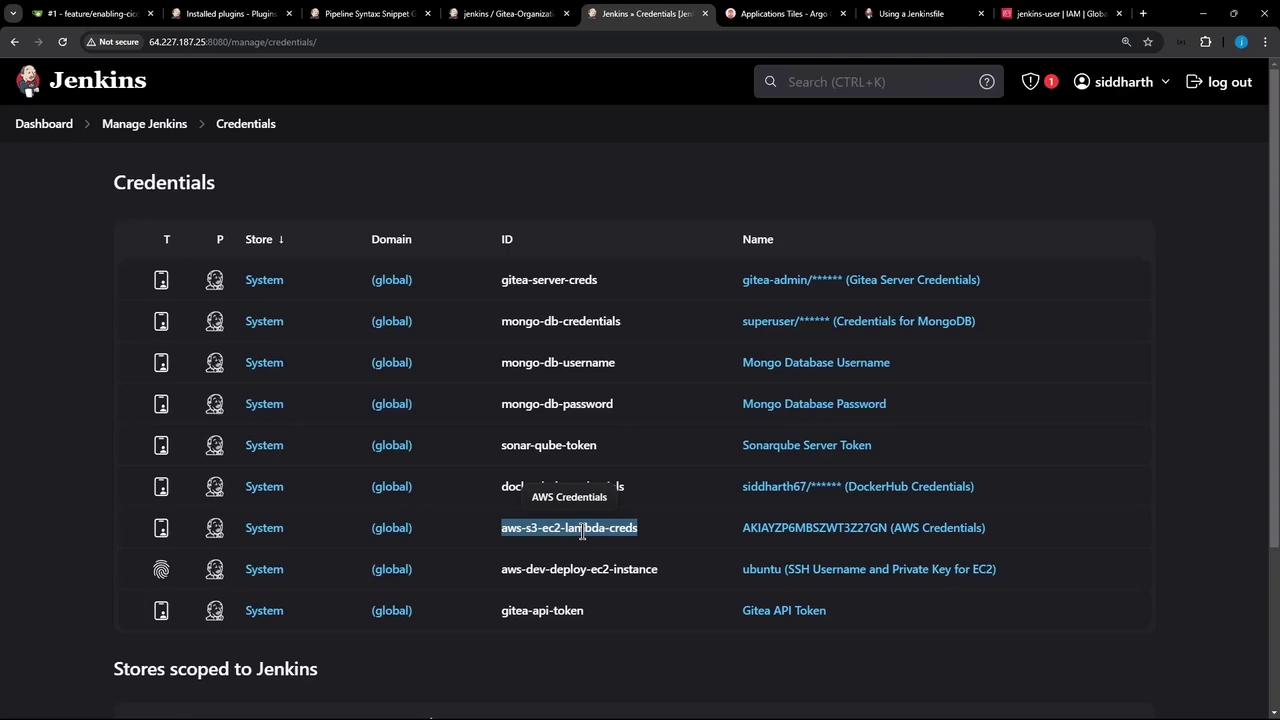
Do not hard-code AWS keys in your
Jenkinsfile. Always use Jenkins Credentials and the withAWS wrapper.Installing the Pipeline: AWS Steps Plugin
Install Pipeline: AWS Steps via Manage Jenkins → Manage Plugins. This plugin provides thes3Upload and withAWS steps you’ll need.
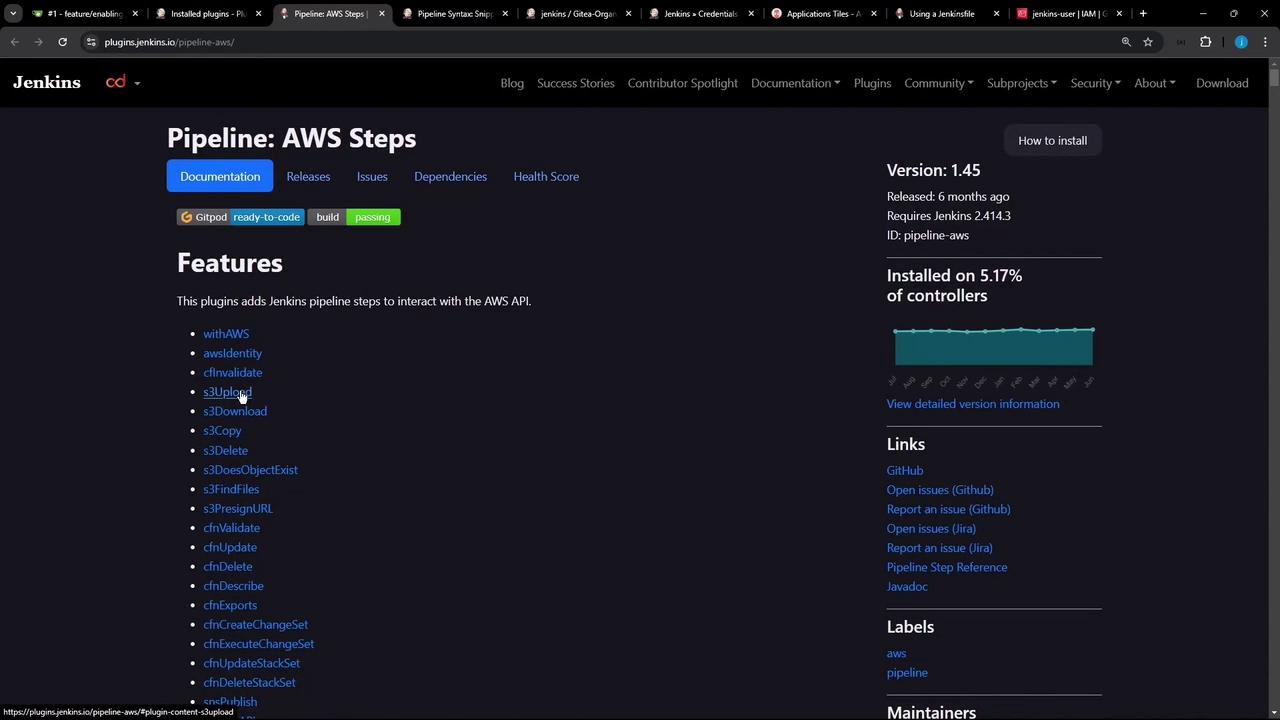
Generating an S3 Upload Snippet
Use Jenkins’s Snippet Generator to preview thes3Upload syntax and options:
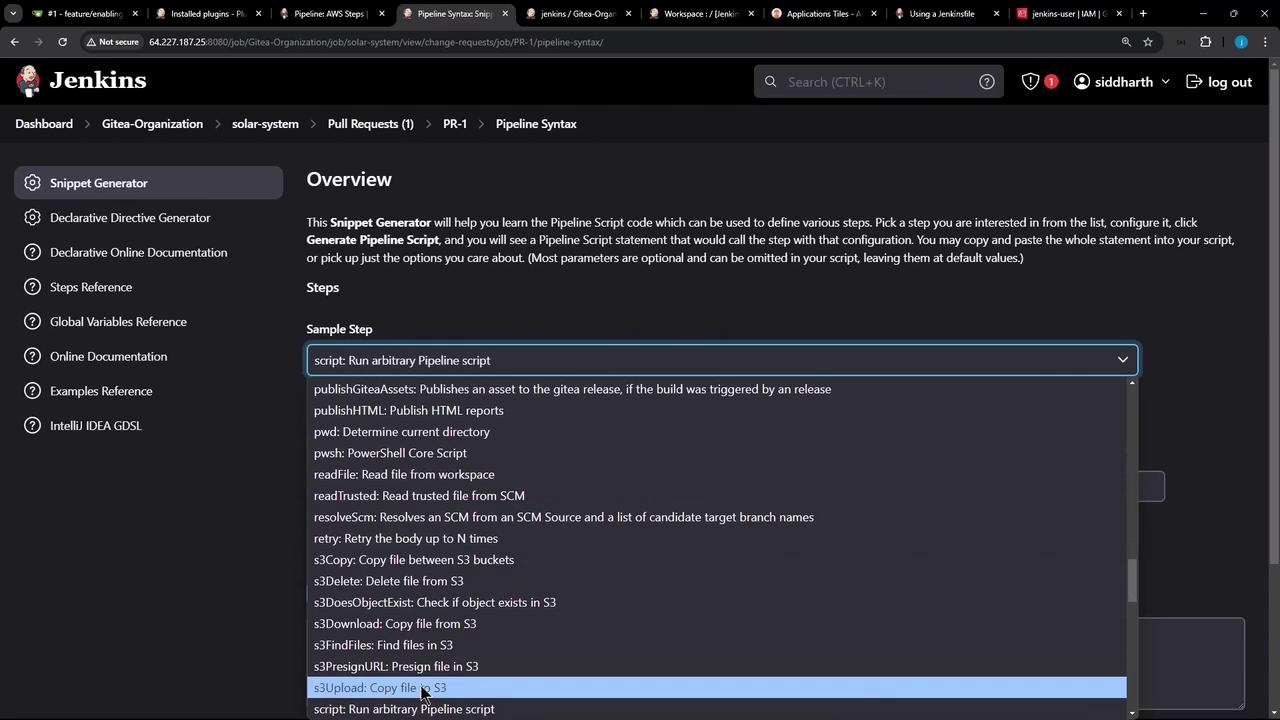
Adding the Upload Stage to the Jenkinsfile
Add a new stage named Upload – AWS S3 that runs only on PR branches. It will:- Create a
reports-$BUILD_IDdirectory - Copy all relevant reports into it
- Upload the folder to your S3 bucket
Use double quotes for Groovy string interpolation (
You can adjust
"reports-$BUILD_ID").You can adjust
path: to organize reports by job, branch, or date.Authenticating with AWS in the Pipeline
ThewithAWS step injects your IAM credentials and region into the build. Generate this snippet in the Snippet Generator by searching for withAWS.
Running the Pipeline
Commit and push your updatedJenkinsfile to trigger a build. The Upload – AWS S3 stage should appear and complete successfully:
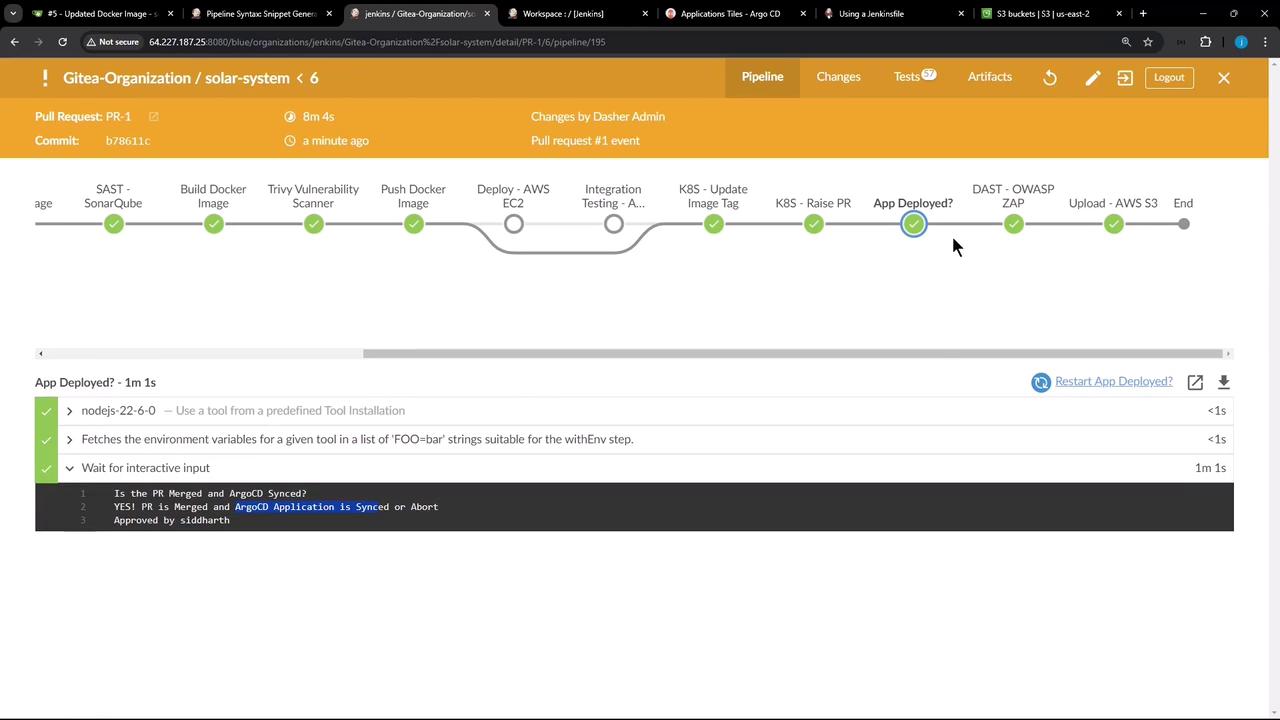
Reviewing the Console Output
Inspect the logs to verify the file listing, directory creation, copy commands, and S3 upload progress:Verifying Artifacts in S3
Head back to the S3 console and navigate into your bucket. You should see ajenkins-<build_id>/ folder with all your copied reports.
That’s it! You’ve successfully configured your Jenkins pipeline to publish test, coverage, and security reports to Amazon S3.