Opening the Chat and Selecting Models
Press Command-L (Mac) or Control-L (Windows/Linux) to open the Composer chat pane. You’ll find three tabs:- Agent mode
- Cursor Ask mode
- Edit mode
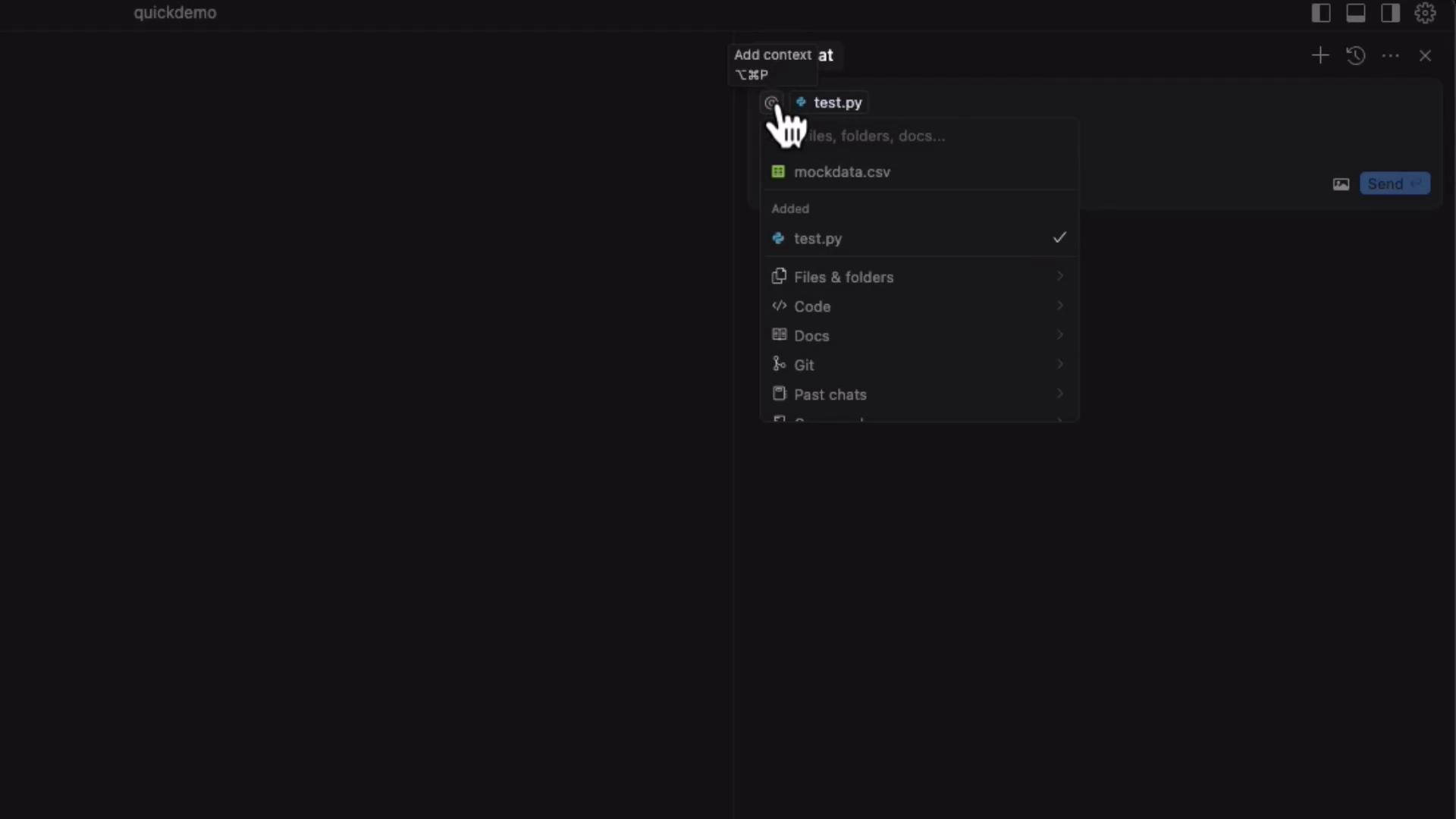
Adding Files as Context
Composer can reference files or entire folders when generating or editing code. To upload files:- In the Files & Folders panel, right-click and select Add context.
- Choose your file (e.g.,
test.pyorgrades.csv).
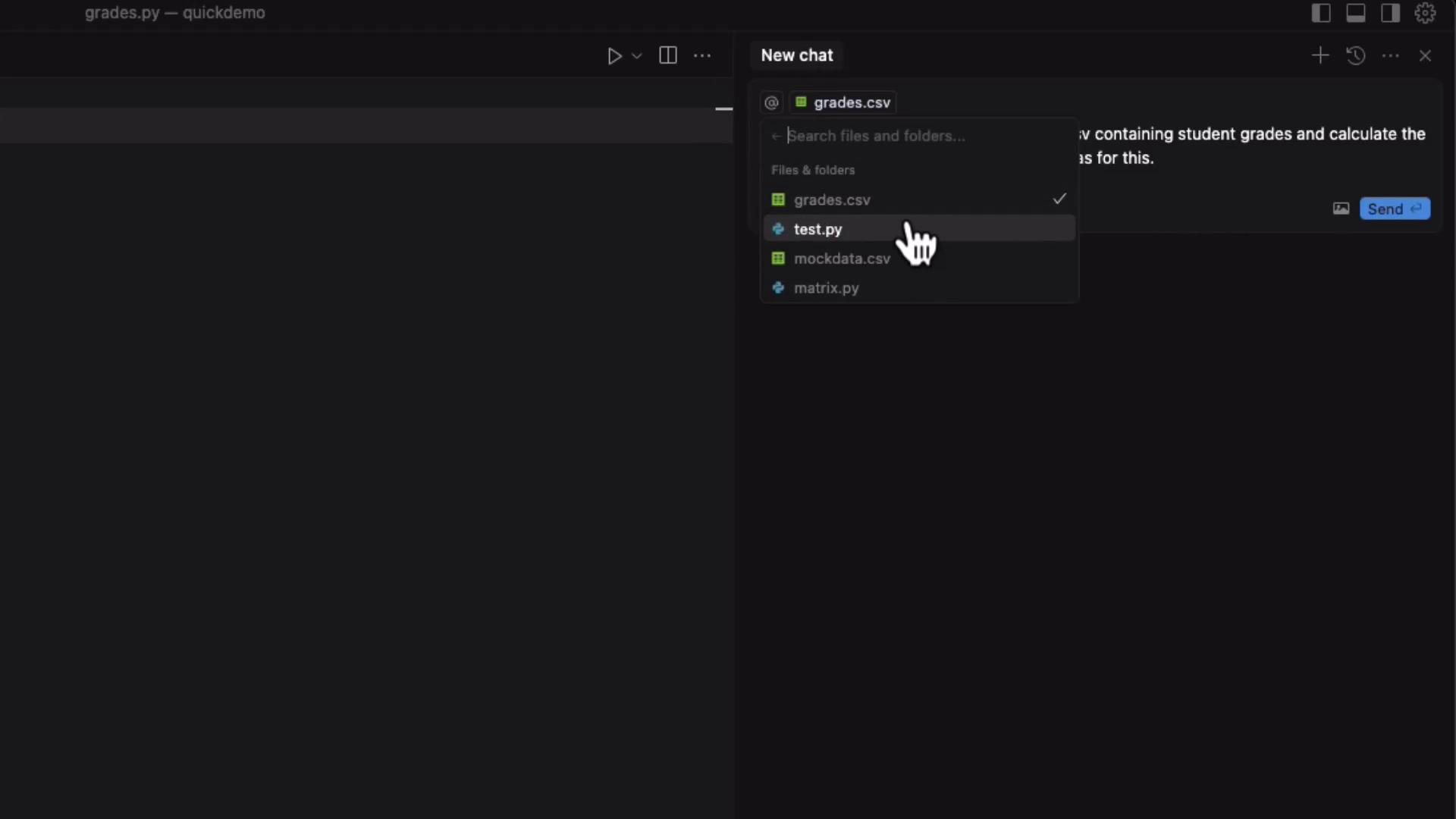
Example: Generating a grades.py Script
Suppose you have a CSV file named grades.csv:
-
In Files & Folders, search for
grades.csvand add it as context. -
Switch to Cursor Ask mode and enter:
Write a Python function to parse
grades.csvcontaining student grades and calculate the average score for each student, using Pandas. Apply it togrades.py.
grades.py is empty and suggest code. Click Apply to grades.py:
grades.py:
Before running the script, install Pandas:
Zero-Shot Prompts
You’re not limited to files in context. In a new chat, ask for any snippet:Create a function to fetch current weather data from the OpenWeatherMap API for a given city.Composer returns:
Inline Edits with Edit Mode
In Edit mode, select existing code, press Control-K, and provide instructions. For example, highlightcalculate_student_averages and say:
Optimize this function for performance.Or:
Add a timing decorator to measure execution time.Composer refactors inline, generating:
python grades.py again to see timing information alongside the results.
Summary
Composer’s three modes enable you to:| Mode | Function | Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Agent mode | Orchestrate multi-step workflows | Command-L / Ctrl-L |
| Cursor Ask | Generate new files or code based on context | Command-L / Ctrl-L |
| Edit mode | Inline AI-assisted refactoring and documentation | Select code + Control-K |