Cursor AI
Understanding and Customizing Cursor
Demo Remote Development
Enable full-featured remote development over SSH on Linux, macOS, or Windows—all from the Cursor AI client. This guide leverages the Remote – SSH extension in Cursor, identical to Visual Studio Code’s setup.
Prerequisites
Note
– Ensure you have SSH access to your target machine (password or key-based).
– Cursor AI must be installed on your local computer.
– You’ll need network connectivity and the SSH daemon running on the remote host.
1. Install the Remote – SSH Extension
- Open Cursor AI.
- Go to the Extensions view (
Ctrl+Shift+X/⌘+Shift+X). - Search for Remote – SSH and click Install.
2. Configure a New SSH Host
- Click the >< icon in the status bar, then Add New SSH Host.
- Enter your connection string, e.g.:
[email protected] - Choose which SSH config file to update (usually
~/.ssh/config).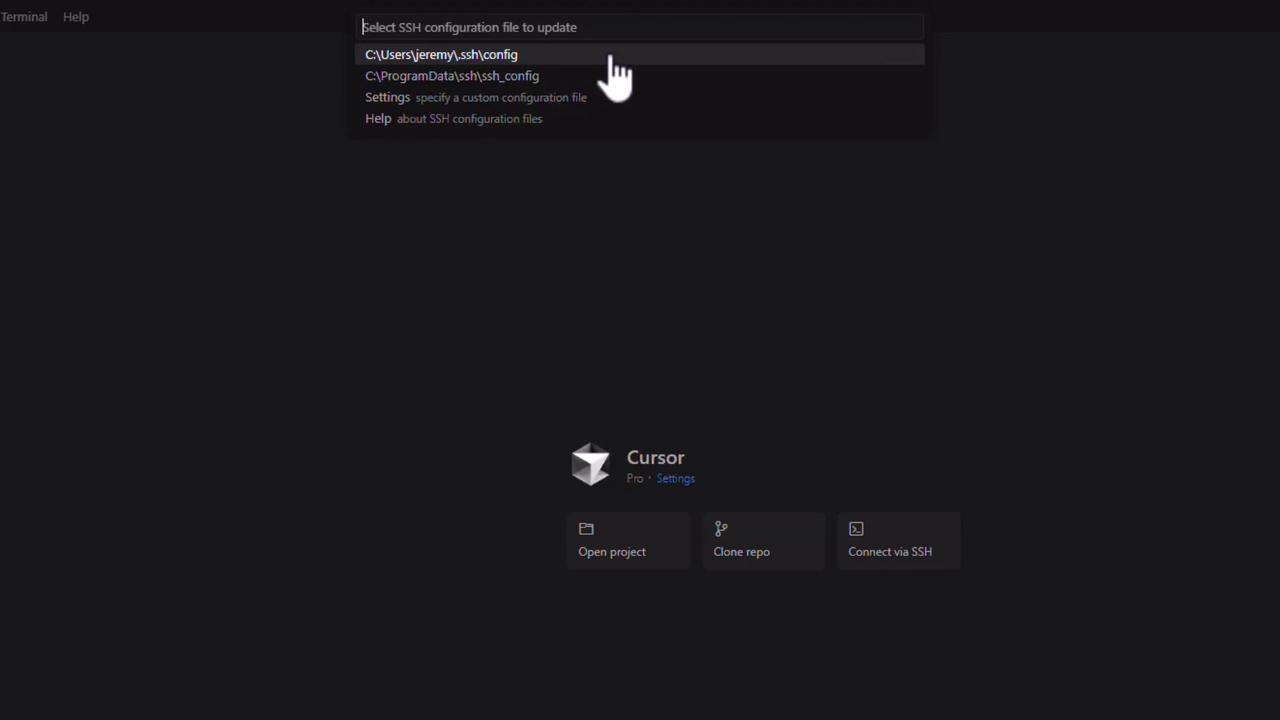
3. Connect to the Remote Host
- Open the Command Palette (
Ctrl+Shift+P/⌘+Shift+P) and select Remote-SSH: Connect to Host. - Choose [email protected].
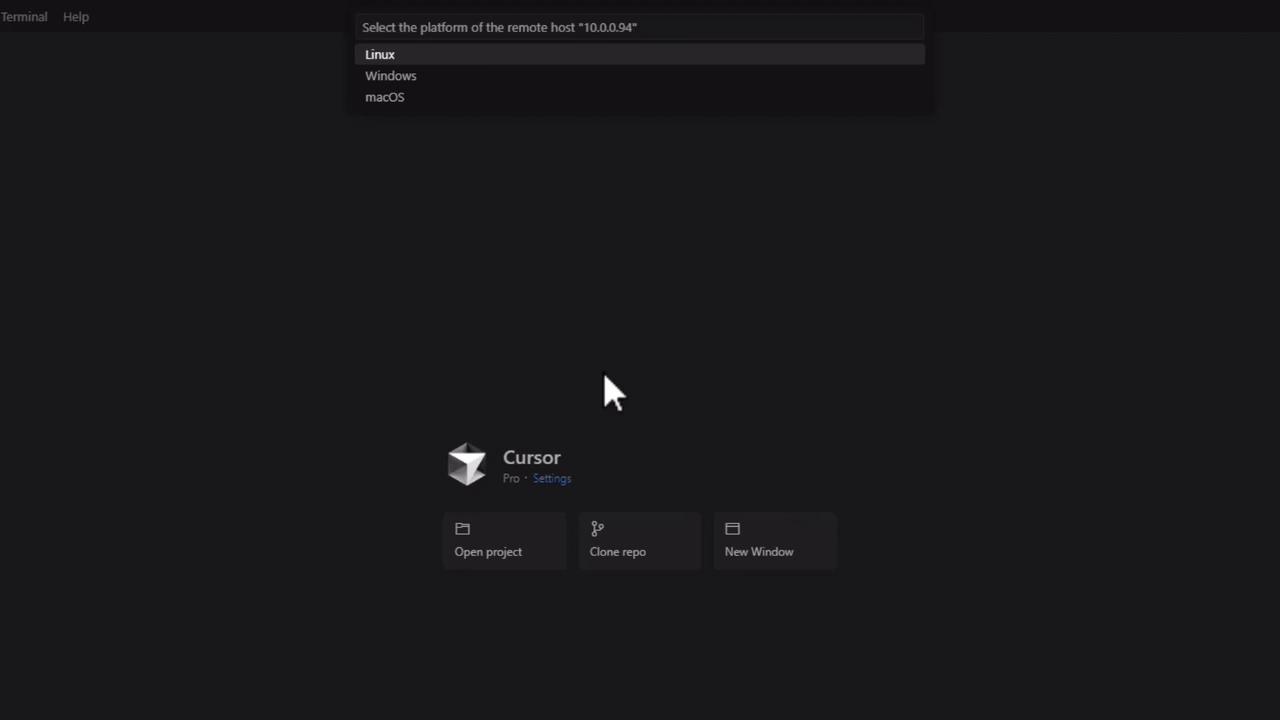
- When prompted, select the remote OS and accept the host fingerprint.
Remote Platform Description Linux Standard distributions (Ubuntu, Arch, etc.) macOS Apple M-series or Intel-based Windows Windows Server or Win10/11
Cursor AI will install the VS Code Server on the remote machine and open a new window.
4. Open a Remote Workspace
After connecting, use File > Open Folder or Git: Clone to start working in your remote project directory.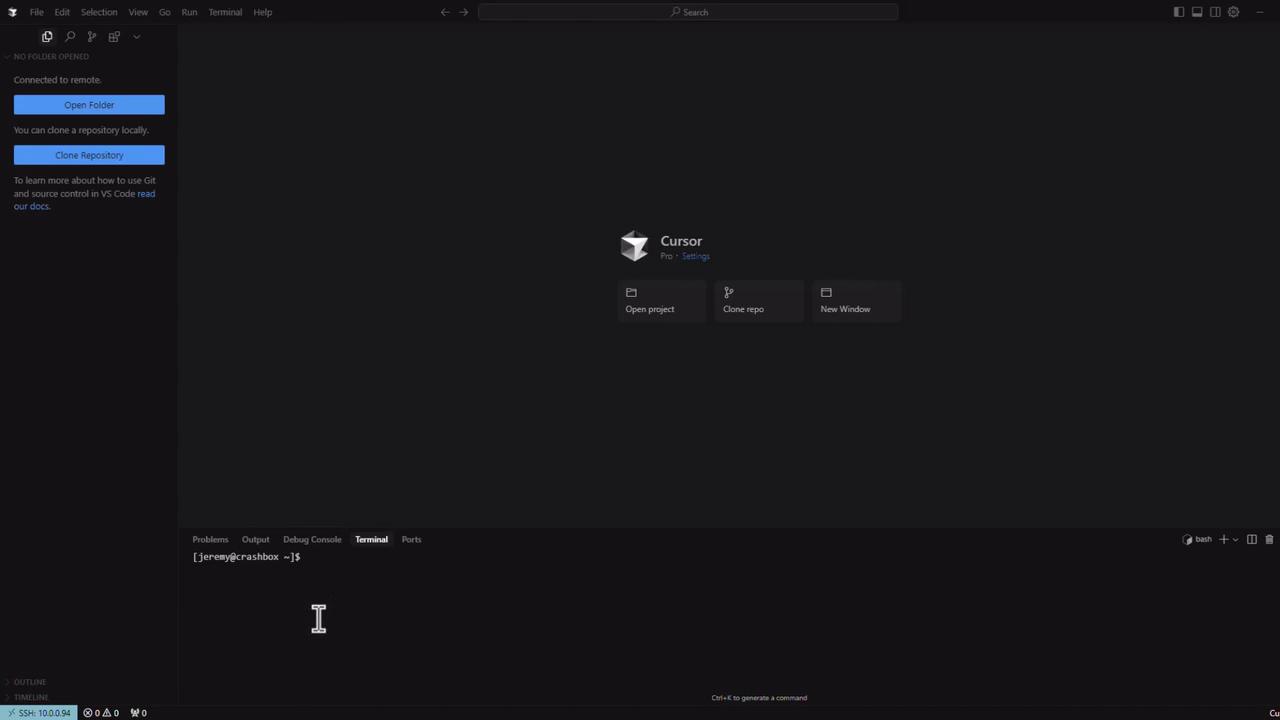
Example:
cd ~/KodeKloudTaskMan
5. Use the Integrated Terminal
Every new terminal is a shell session on the remote host:
$ ls -la
drwxr-xr-x 3 jeremy jeremy 4096 Mar 26 20:37 .cursor
-rw-r--r-- 1 jeremy jeremy 0 Mar 26 20:37 .DS_Store
drwxr-xr-x 3 jeremy jeremy 4096 Mar 26 20:37 KodeKloudTaskMan
Inspect running processes to verify the remote environment:
$ ps aux
jeremy 193885 0.0 0.0 4992 3360 pts/4 S 20:48 0:00 /usr/bin/python3 /home/jeremy/.cursor-server/extensions/ms.python.python-2024.12.3-linux-x64/python
jeremy 193886 0.0 0.0 4980 1936 pts/4 S 20:48 0:00 /usr/bin/python3 /home/jeremy/.cursor-server/cli/servers/Stable-82fe0f61c01d0791db7e5ab048849d5
6. Verify Remote OS Kernel
$ uname -r
6.5.12-arch1-1
7. Sample Python Function on the Remote Host
Here’s a quick Flask utility you might run remotely:
import os
import csv
import sqlite3
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, url_for, flash, session, g
from datetime import datetime
import hashlib
import logging
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = 'dev' # Change before production
app.config['DATABASE'] = os.path.join(app.instance_path, 'task_manager.sqlite')
def read_csv(file_path):
"""Read and print each row from a CSV file."""
with open(file_path, newline='') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
print(row)
Warning
Never use SECRET_KEY = 'dev' in production—generate a strong, random key instead.
8. Connecting to macOS or Windows Hosts
Repeat steps 2–4 with your other SSH targets:
- Add a new host entry, for example:
[email protected] - Select macOS (or Windows).
- Authenticate and open your project (e.g., a Pygame simulator).
By following these steps, Cursor AI transforms any client machine into a powerful remote development workstation, leveraging specialized hardware or unique OS environments without leaving your desk.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content