DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
DevSecOps Pipeline
Demo Refactoring Jenkins
In this tutorial, we'll streamline a Jenkins Declarative Pipeline by moving multiple post { always { … } } blocks from individual stages into a single, pipeline-level post section. This approach enhances readability, reduces duplication, and makes future maintenance simpler.
Why Consolidate post { always } Blocks?
When you have several stages that each publish reports or perform cleanup, repeating the same post block can clutter your Jenkinsfile. Instead, you can leverage the pipeline-level post block to handle all “always” actions in one place.
Original Jenkinsfile with Repeated Post Sections
Below is a snippet of the existing pipeline. Notice the three stages that each contain their own post { always { … } } block:
stage('Unit Tests - JUnit and JaCoCo') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
post {
always {
junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml'
jacoco execPattern: 'target/jacoco.exec'
}
}
}
stage('Mutation Tests - PIT') {
steps {
sh 'mvn org.pitest:pitest-maven:mutationCoverage'
}
post {
always {
pitmutation mutationStatsFile: '**/target/pit-reports/**/mutations.xml'
}
}
}
stage('SonarQube') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('SonarQube') {
sh 'mvn sonar:sonar \
-Dsonar.projectKey=numeric-application \
-Dsonar.host.url=http://devsecops-demo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com:9000'
}
}
timeout(time: 2, unit: 'MINUTES') {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: true
}
}
}
stage('Vulnerability Scan - Docker') {
steps {
sh 'mvn dependency-check:check'
}
post {
always {
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: 'target/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
}
We’re duplicating the same “always” publishing logic in three places. Let’s consolidate.
Consolidating Post Actions
Jenkins Declarative Pipeline allows a post section at the root of the pipeline block. All specified actions run after every stage completes.
For reference, check the official Jenkins Pipeline Syntax documentation.
Note
A pipeline-level post block can contain always, success, failure, and unstable directives.
Post Actions Summary
| Report Type | Original Location | New Location |
|---|---|---|
| JUnit & JaCoCo | Unit Tests stage post.always | Pipeline-level post.always |
| PIT Mutation Reports | Mutation Tests stage post.always | Pipeline-level post.always |
| Dependency-Check Publisher | Vulnerability Scan stage post.always | Pipeline-level post.always |
Refactored Jenkinsfile
- Remove all individual
post { always { … } }sections. - Add one
postblock under thepipelineroot. - Copy each
alwaysstep into that block.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Unit Tests - JUnit and JaCoCo') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
stage('Mutation Tests - PIT') {
steps {
sh 'mvn org.pitest:pitest-maven:mutationCoverage'
}
}
stage('SonarQube - SAST') {
steps {
withSonarQubeEnv('SonarQube') {
sh 'mvn sonar:sonar \
-Dsonar.projectKey=numeric-application \
-Dsonar.host.url=http://devsecops-demo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com:9000'
}
timeout(time: 2, unit: 'MINUTES') {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: true
}
}
}
}
stage('Vulnerability Scan - Docker') {
steps {
sh 'mvn dependency-check:check'
}
}
stage('Docker Build and Push') {
steps {
withDockerRegistry([credentialsId: 'docker-hub', url: '']) {
sh 'printenv'
sh 'docker build -t siddharth67/numeric-app:${GIT_COMMIT} .'
sh 'docker push siddharth67/numeric-app:${GIT_COMMIT}'
}
}
}
stage('Kubernetes Deployment - DEV') {
steps {
withKubeConfig([credentialsId: 'kubeconfig']) {
sh 'sed -i "s/#replace#siddharth67\\/numeric-app:${GIT_COMMIT}/g" k8s_deployment_service.yaml'
sh 'kubectl apply -f k8s_deployment_service.yaml'
}
}
}
}
post {
always {
junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml'
jacoco execPattern: 'target/jacoco.exec'
pitmutation mutationStatsFile: '**/target/pit-reports/**/mutations.xml'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: 'target/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
}
Verifying the Refactor
After updating your Jenkinsfile, commit and push to trigger a new build:
git add Jenkinsfile
git commit -m "Refactor: consolidate all post.always actions to pipeline level"
git push
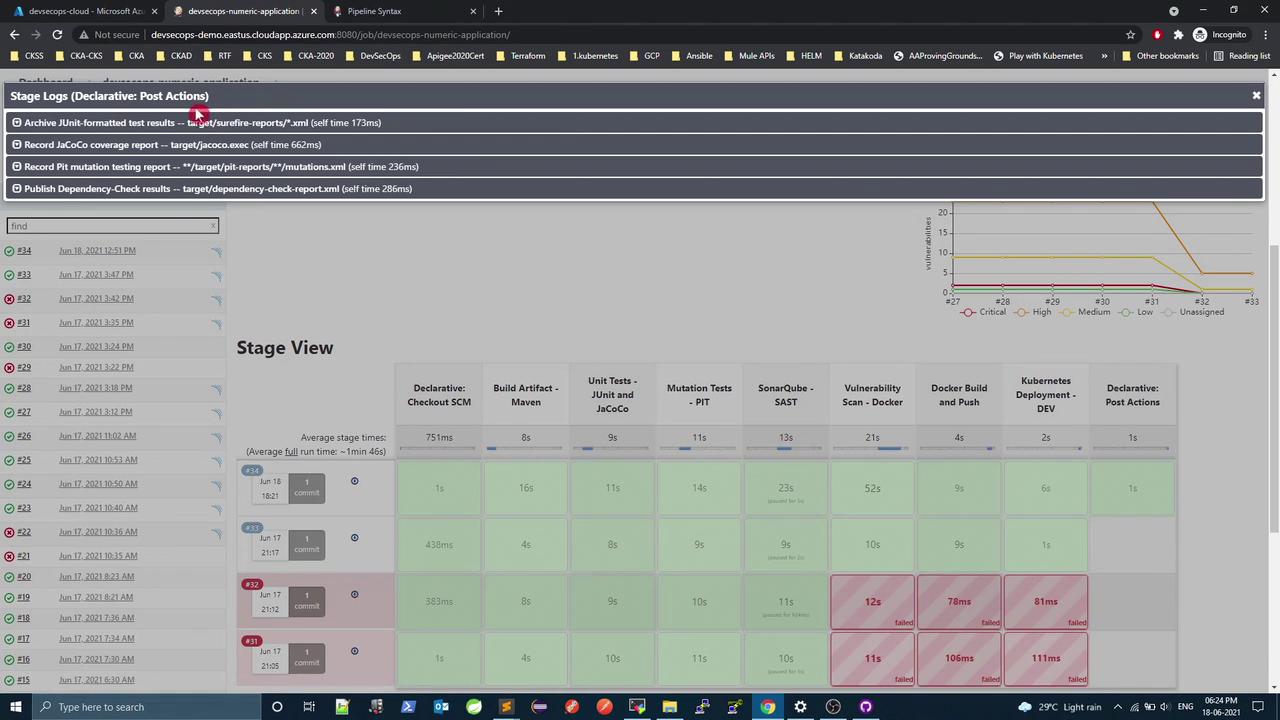
In the Jenkins dashboard, you should see all post actions executed at the end of the pipeline:

Next Steps
Jenkins pipelines can also leverage:
- Environment directives for global variables
- Parallel stages with
failFastto optimize runtime - Embedded scripted logic (
script { … }) for loops, conditionals, and error handling
Here’s a brief example showcasing parallel execution and a script block:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Initial Stage') {
steps {
echo 'Executing first stage.'
}
}
stage('Parallel Stage') {
when { branch 'master' }
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Branch A') {
agent { label 'for-branch-a' }
steps { echo 'Running on Branch A' }
}
stage('Branch B') {
agent { label 'for-branch-b' }
steps { echo 'Running on Branch B' }
}
}
}
stage('Browser Tests') {
steps {
script {
def browsers = ['chrome', 'firefox']
browsers.each { browser ->
echo "Testing in ${browser}"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab