DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
DevSecOps Pipeline
Demo Dependency Check
In this hands-on tutorial, we’ll integrate the OWASP Dependency-Check Maven plugin into a Spring Boot project and automate vulnerability scanning in Jenkins. You will:
- Configure the Dependency-Check plugin in
pom.xml. - Verify documentation and install required Jenkins plugins.
- Update the
Jenkinsfileto run the scan and publish reports. - Analyze results, upgrade dependencies, or adjust CVSS thresholds.
1. Add the OWASP Dependency-Check Plugin
Open your pom.xml and register the plugin alongside existing ones (JaCoCo, PIT, etc.):
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- Other build plugins (JaCoCo, PIT) -->
<!-- OWASP Dependency-Check -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.owasp</groupId>
<artifactId>dependency-check-maven</artifactId>
<version>6.1.6</version>
<configuration>
<format>ALL</format>
<failBuildOnCVSS>9</failBuildOnCVSS>
<!-- You can add suppression files, proxy settings, internal CVE mirrors, etc. -->
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Here we generate JSON, CSV, XML, and HTML reports and fail builds for vulnerabilities with CVSS ≥ 9.
git add pom.xml
git commit -m "Add OWASP Dependency-Check Maven plugin"
git push
Note
Always align the plugin version with the latest stable release. Check Maven Central for updates.
Report Formats at a Glance
| Format | File Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HTML | .html | Human-readable web report |
| XML | .xml | Jenkins publisher input |
| JSON | .json | API consumption |
| CSV | .csv | Spreadsheet analysis |
2. Verify Plugin Docs & Jenkins Preparation
Refer to the official Dependency-Check Maven plugin guide for advanced configurations:
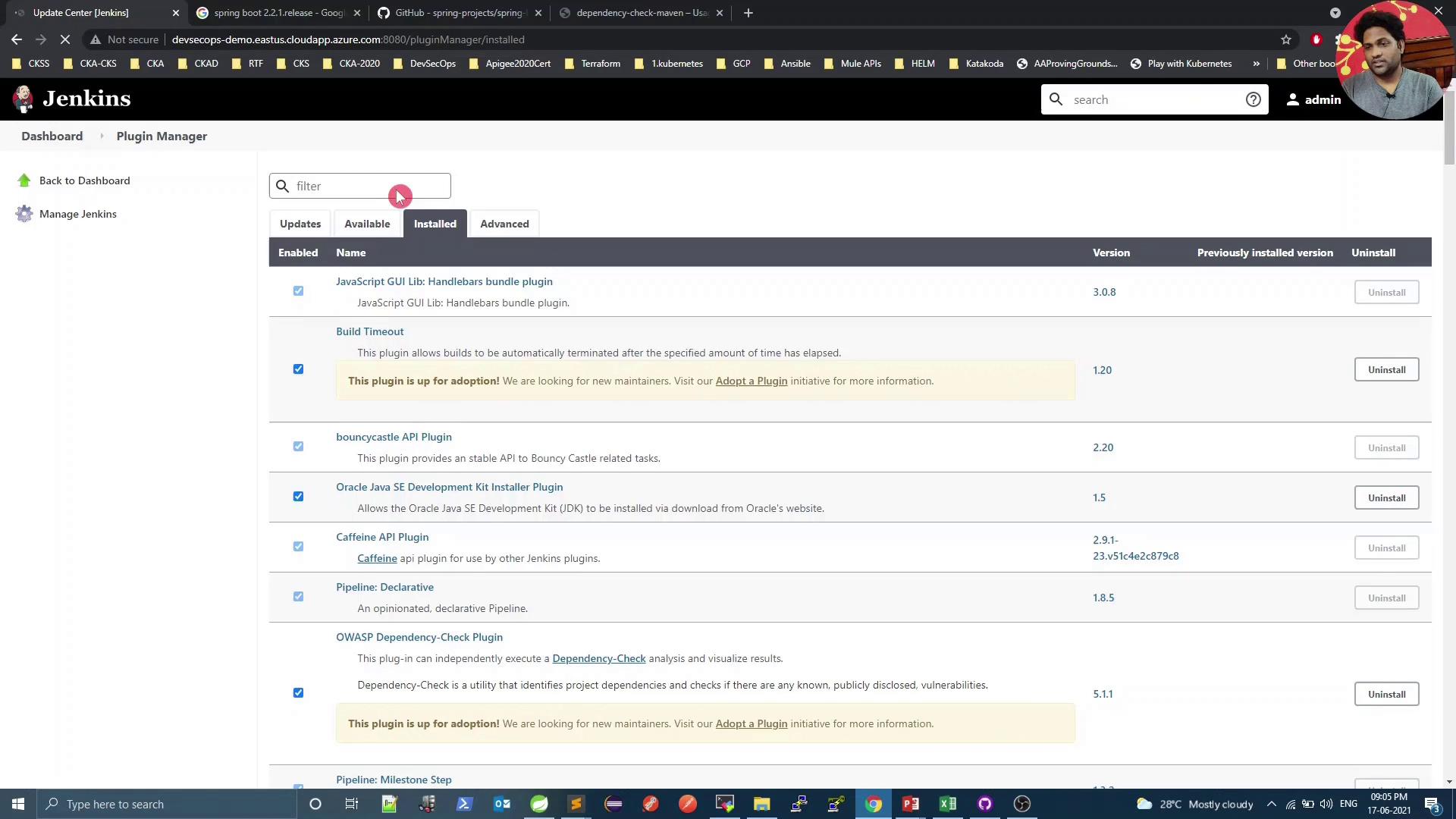
Ensure the Dependency-Check Publisher plugin is installed in Jenkins:
Warning
Without the Dependency-Check Publisher plugin, Jenkins cannot display the HTML or XML reports. Install or update it via Manage Jenkins → Plugin Manager.
3. Update Your Jenkins Pipeline
Insert a new stage in Jenkinsfile before pushing Docker images:
stage('Vulnerability Scan') {
steps {
sh 'mvn dependency-check:check'
}
post {
always {
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: 'target/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
}
Commit and push to trigger the updated pipeline.
4. Run the Pipeline and View Status
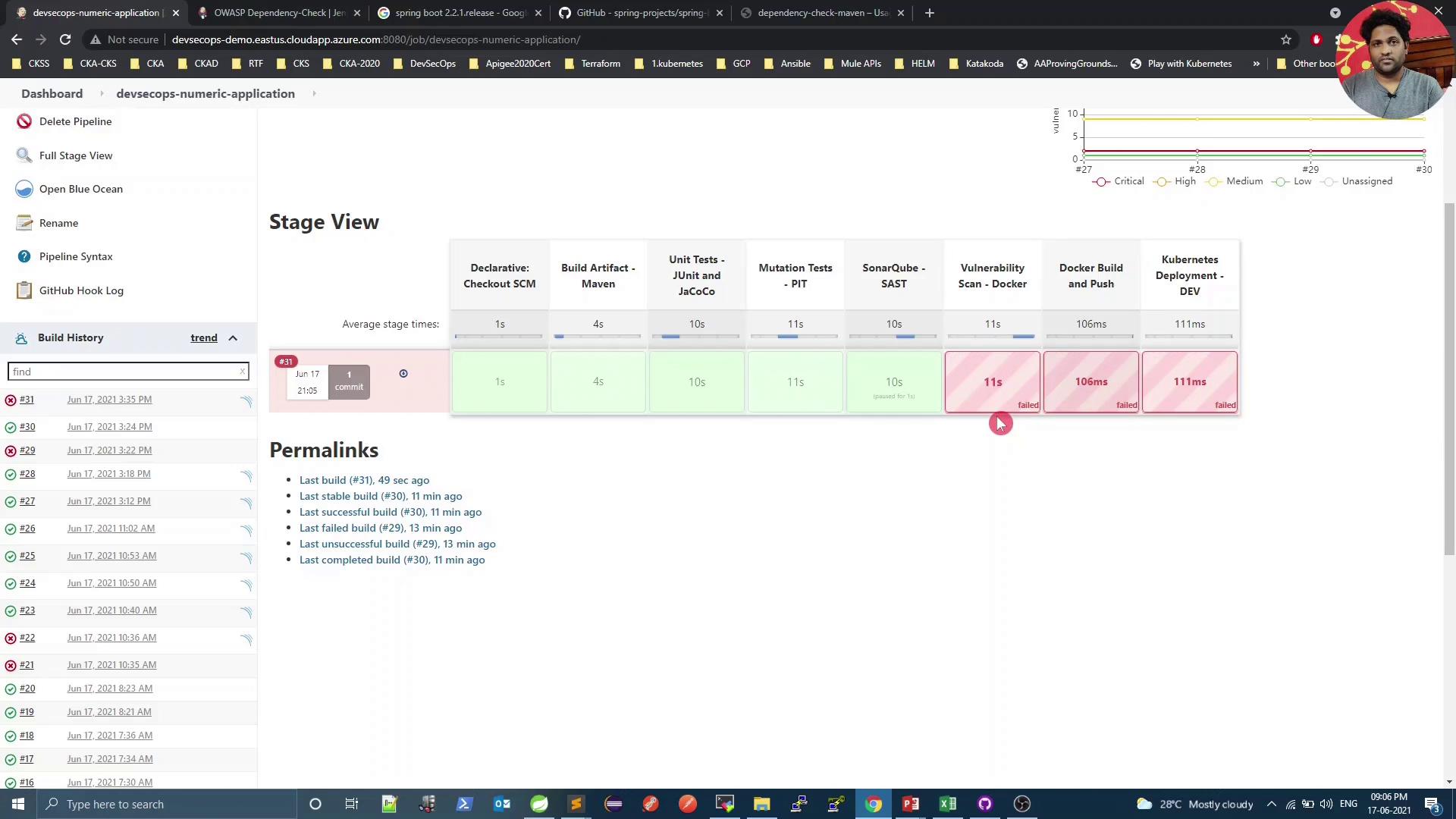
Kick off a new build in Jenkins. The scan downloads CVE data from NVD and examines all project dependencies.
5. Analyze the Scan Output
In the console logs, you’ll see entries like:
[INFO] Writing report to: .../target/dependency-check-report.sarif
[INFO] Writing report to: .../target/dependency-check-junit.xml
One or more dependencies were identified with known vulnerabilities:
- numeric:
hibernate-validator:6.0.18.Final ... : CVE-2020-10693
jackson-databind:2.12.1 ... : CVE-2020-25649
...
On the pipeline dashboard, click into the Dependency-Check results:
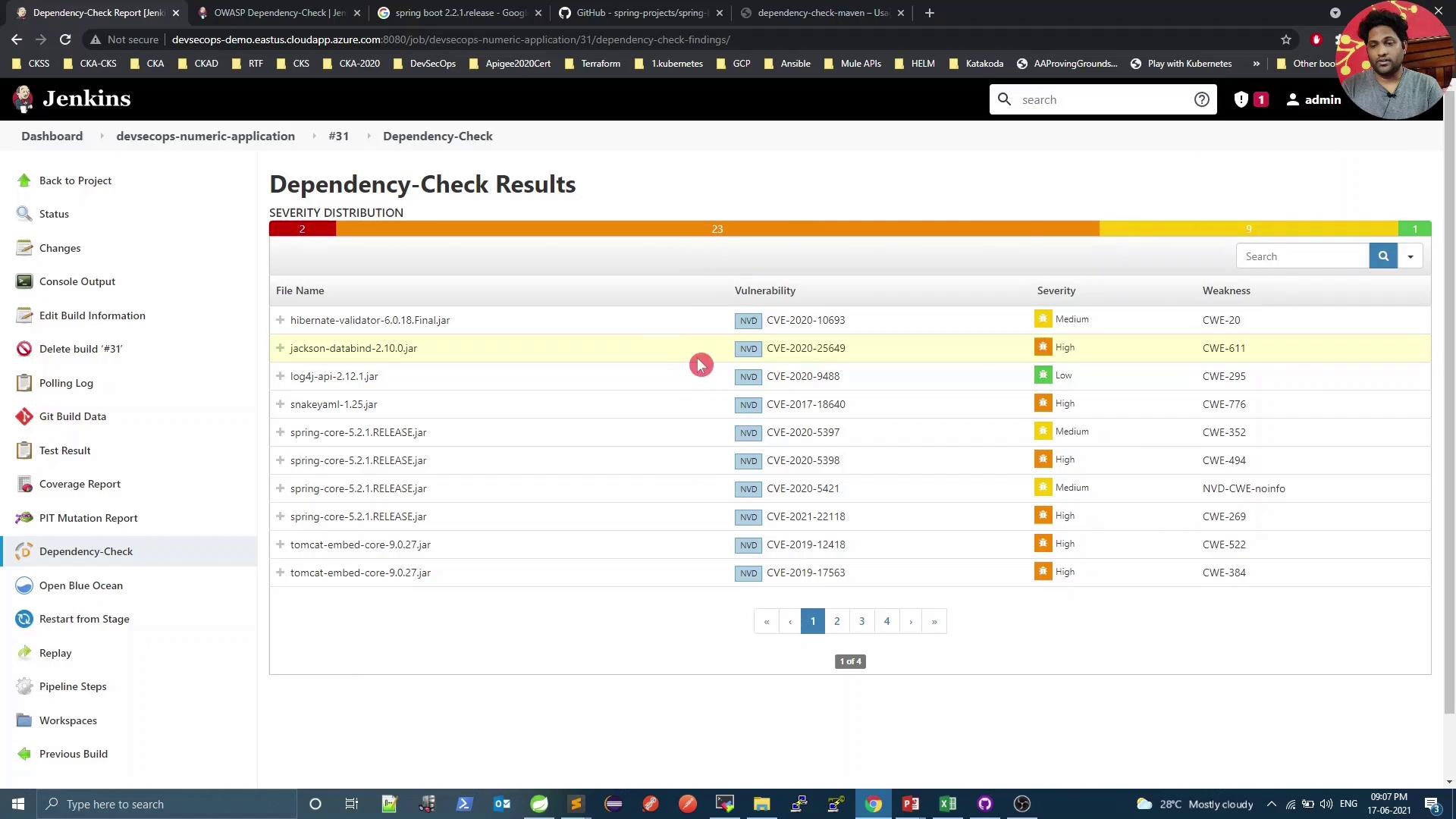
Select a specific dependency to inspect details:
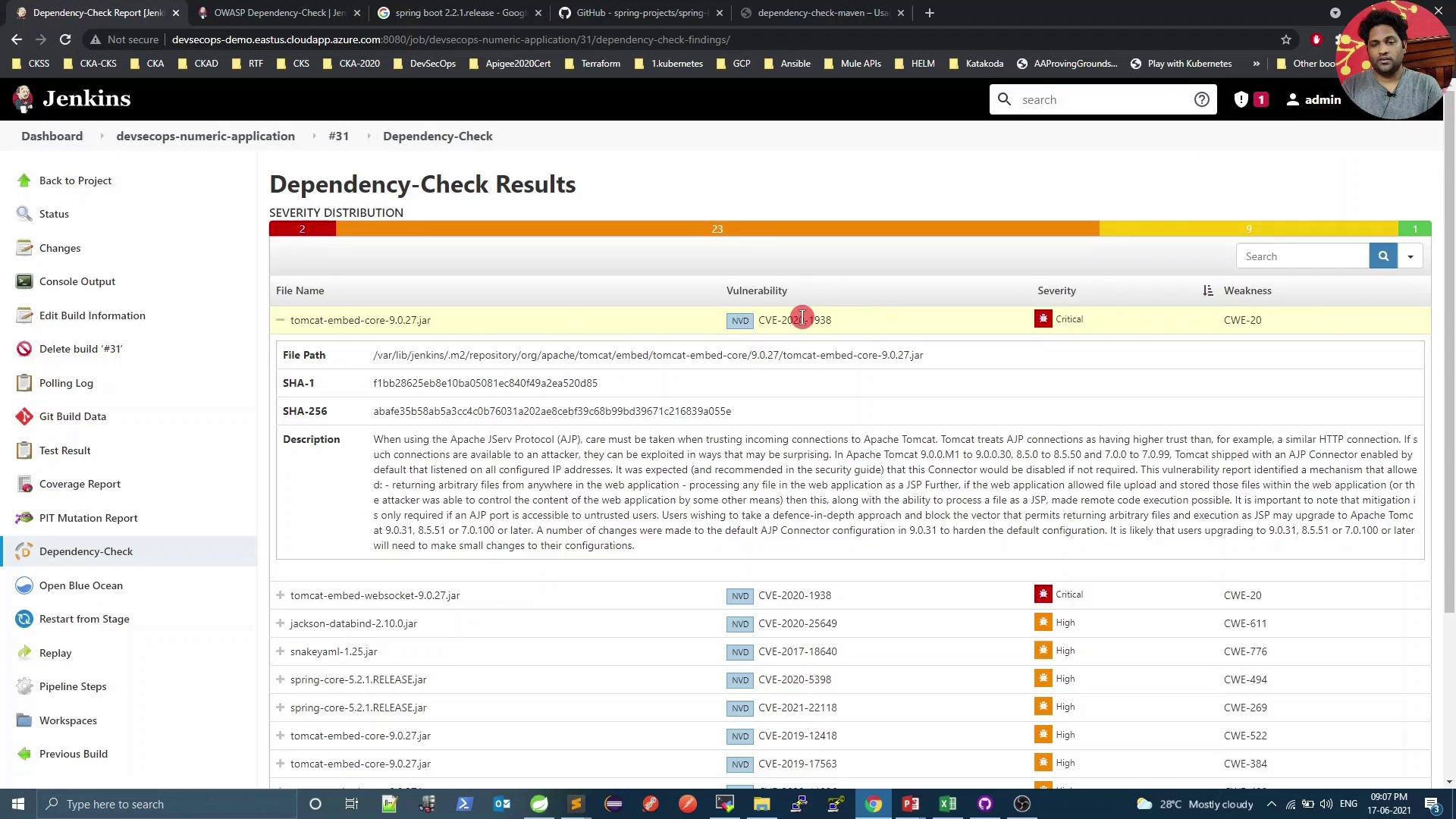
For instance, CVE-2020-1938 is rated 9.8 (critical):
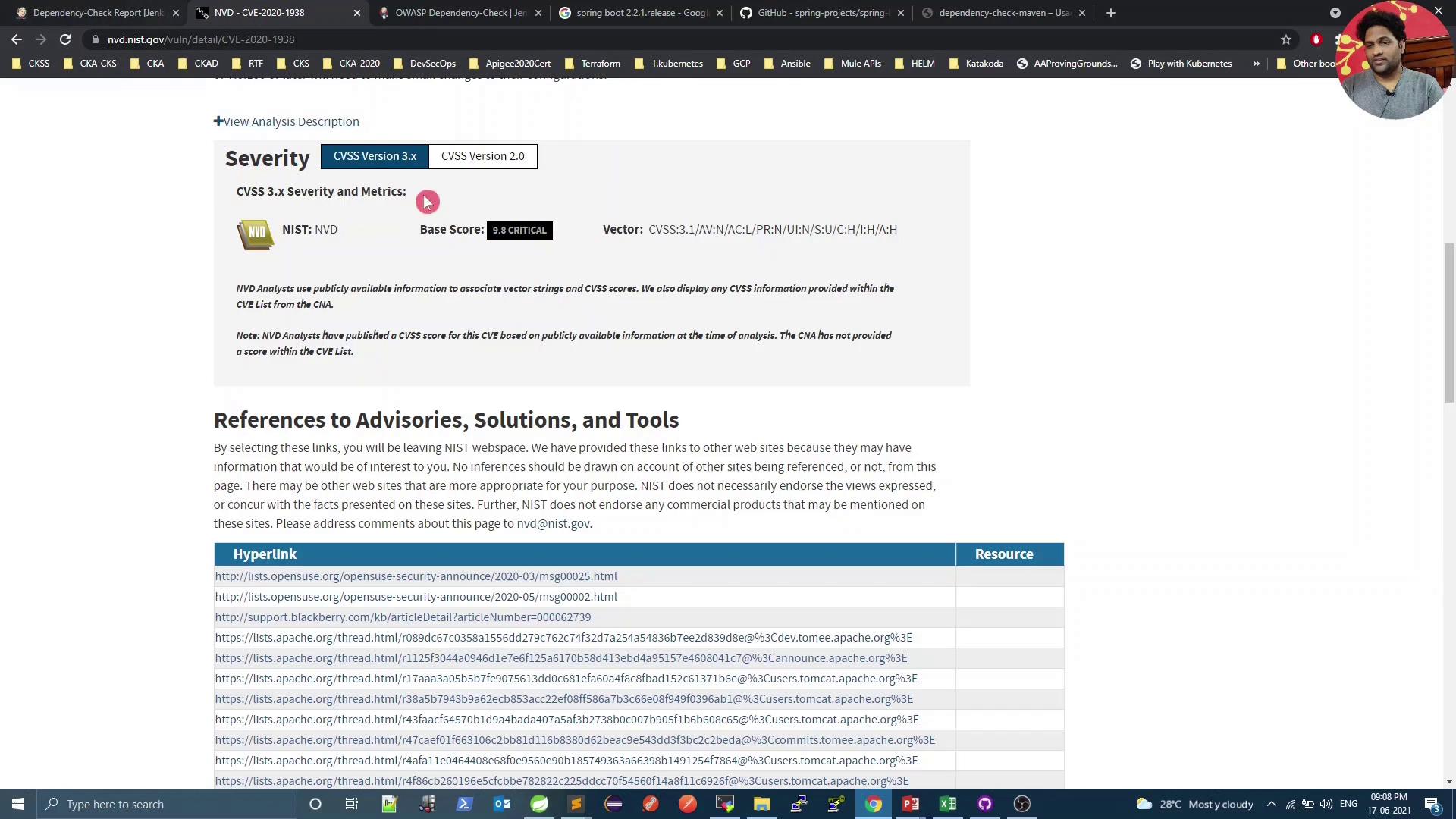
Because we set failBuildOnCVSS=9, the build fails on such high-severity findings. Next, we’ll explore mitigation.
6. Explore Transitive Dependencies
Spring Boot starters often introduce indirect (transitive) dependencies. Open your IDE’s dependency hierarchy to examine them:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
...
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- other starters -->
</dependencies>

7. Upgrade Spring Boot Version
Check the latest Spring Boot tags on GitHub to find patched releases:

After confirming compatibility, bump the parent version:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
Commit and push to trigger the pipeline again.
8. Re-run the Scan & Inspect Reports
The build and tests should now pass, but the Vulnerability Scan may still detect lower-severity issues.
Console summary:
[INFO] --- dependency-check-maven:6.1.6:check ---
[WARNING] One or more dependencies were identified with known vulnerabilities in numeric:
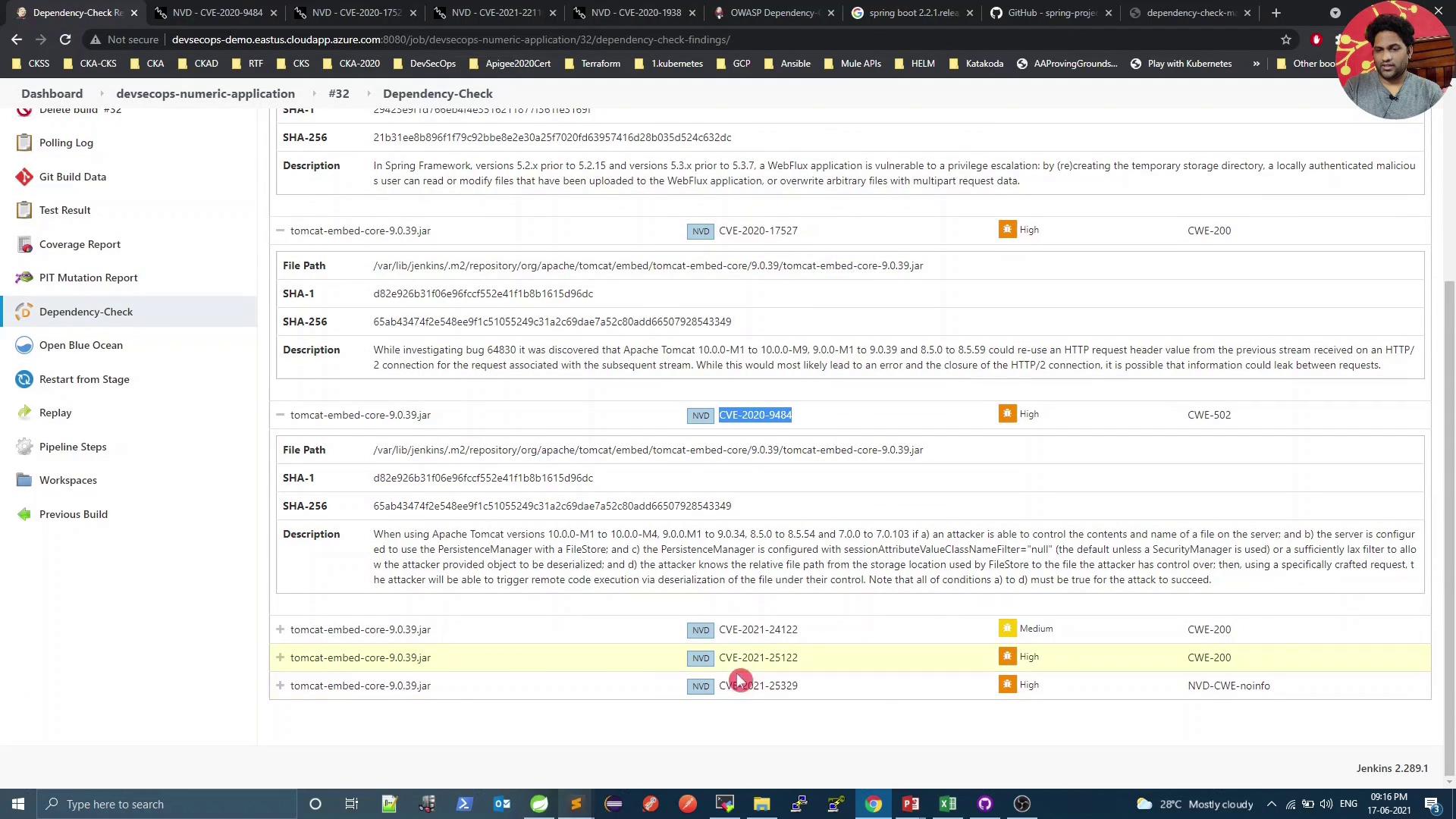
spring-core:5.2.10.RELEASE ... : CVE-2020-17527, CVE-2020-9484, CVE-2021-25112, CVE-2021-25239
Open the HTML report:
9. Adjust the CVSS Threshold
If you deem remaining vulnerabilities acceptable, lower the failure threshold in pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.owasp</groupId>
<artifactId>dependency-check-maven</artifactId>
<version>6.1.6</version>
<configuration>
<format>ALL</format>
<failBuildOnCVSS>8</failBuildOnCVSS>
</configuration>
</plugin>
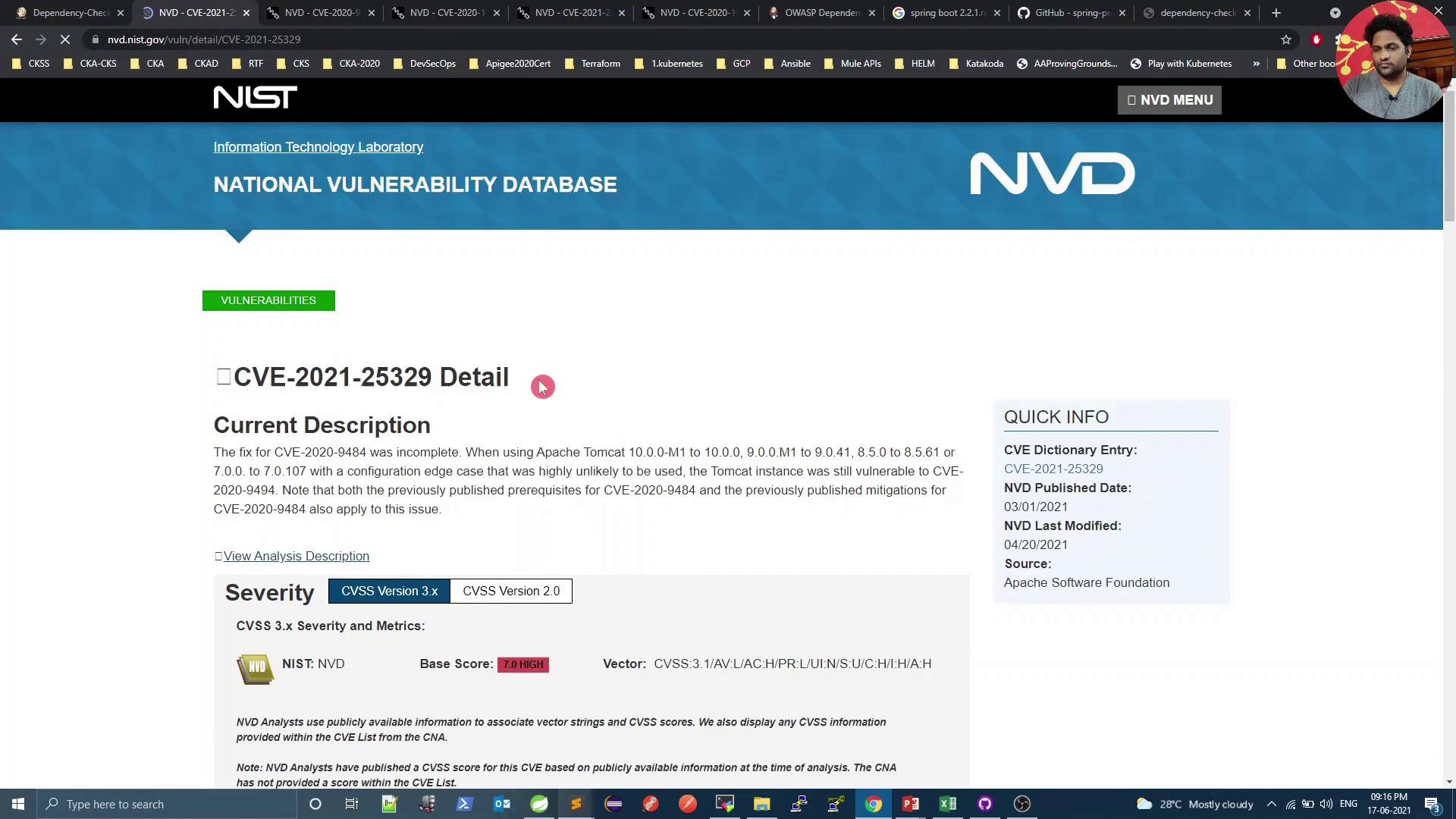
For example, CVE-2021-25329 has a score of 7.0:
Commit and push your changes. The pipeline will now pass the vulnerability stage for all CVSS < 8.
You’ve successfully integrated OWASP Dependency-Check into your CI pipeline. In our next lesson, we’ll explore container scanning with Trivy.
Watch Video
Watch video content