- Build a Docker image and push it to Docker Hub.
- Scan Kubernetes manifests with OPA and Kubescape.
- Perform image vulnerability scans using Trivy.
- Upgrade a vulnerable dependency (Tomcat) and verify the fix.
- Deploy the hardened image to a Kubernetes cluster.
1. Jenkins Pipeline Configuration
Define your pipeline with a reusableimageName environment variable:
| Stage | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Build Artifact - Maven | Compile code & package JAR |
| Unit Tests - JUnit & JaCoCo | Validate functionality & track code coverage |
| Mutation Tests - PIT | Assess test suite robustness |
| SonarQube - SAST | Static code analysis |
| Docker Build & Push | Build Docker image & push to registry |
| Vulnerability Scan - Kubernetes | Lint & security test K8s manifests (OPA, Kubescape) |
| Trivy Scan | Container image vulnerability scan |
| Kubernetes Deployment | Deploy to target cluster |
1.1 Docker Build & Push
1.2 Kubernetes Manifest Scans
1.3 Trivy Scan Stage
2. Trivy Scan Script
Createtrivy-k8s-scan.sh at the root of your repo:
--lightmode skips non-OS packages for faster scans.- Cache volume is mapped to reuse vulnerability data between runs.
3. Initial Trivy Scan Results
Running the scan for the first time may reveal CVEs in embedded libraries: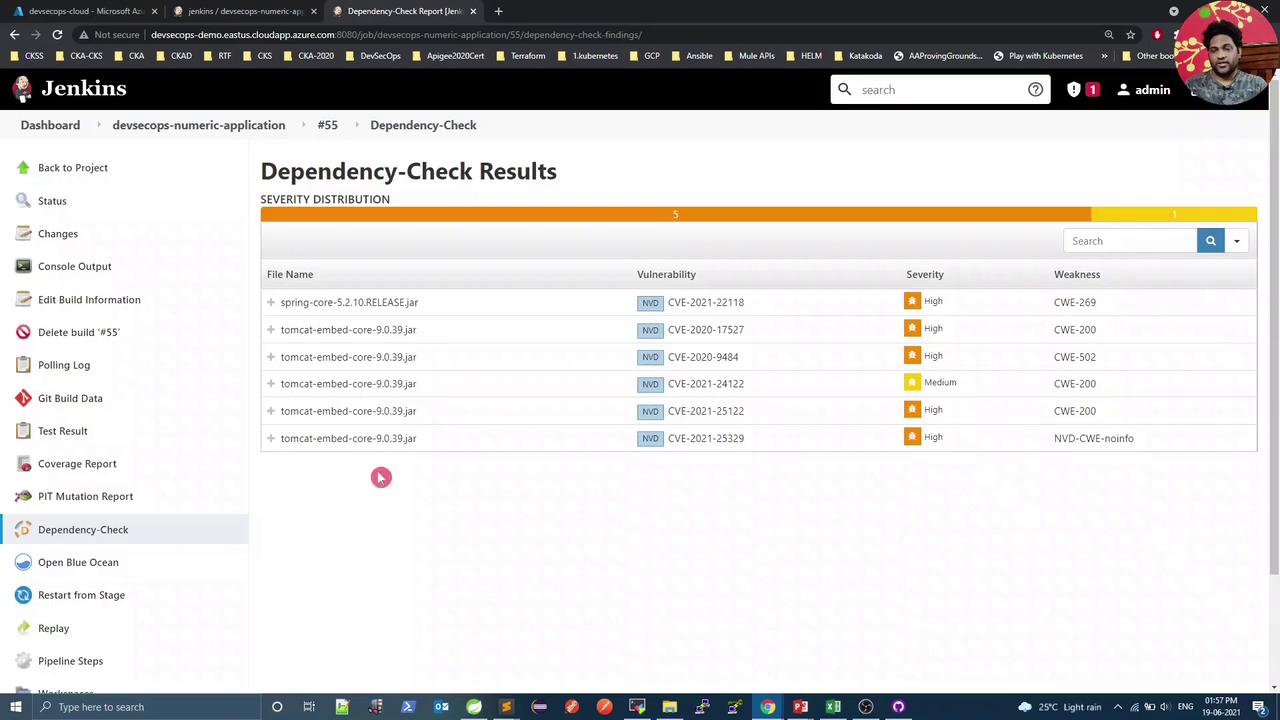
pom.xml.
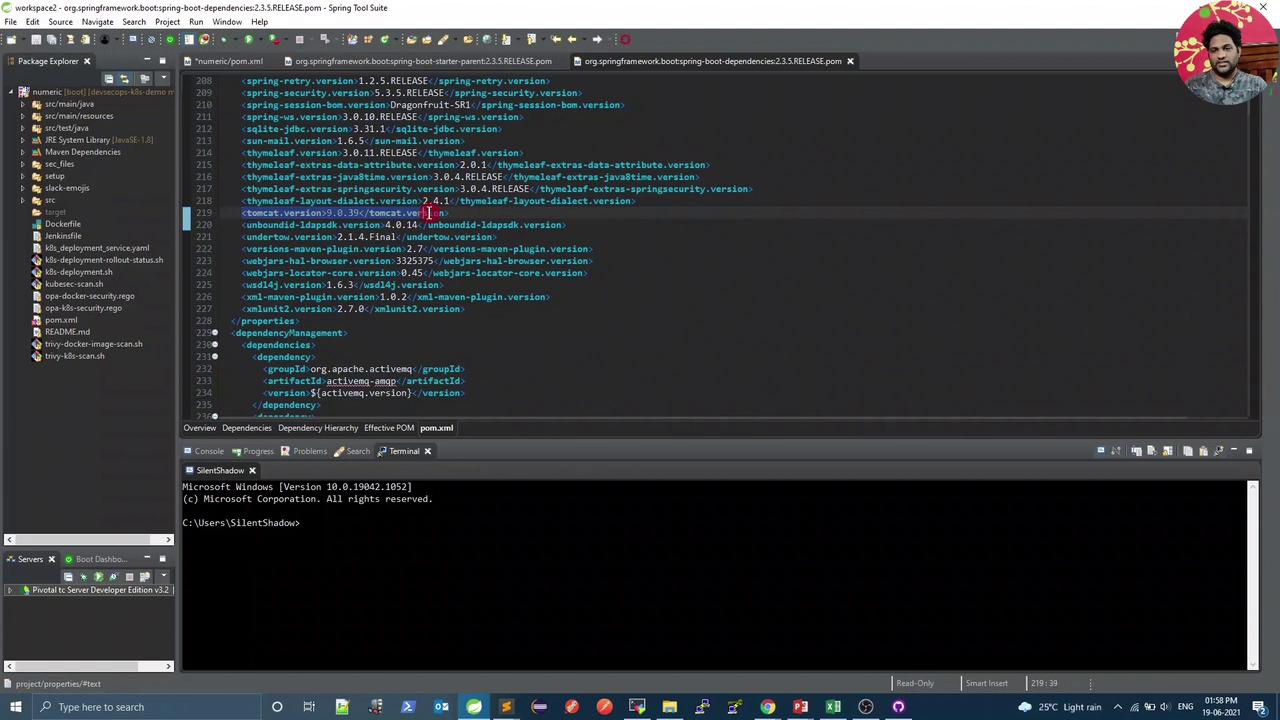
4. Update Tomcat Version in pom.xml
Open your Maven POM in Spring Tool Suite and override the tomcat.version property:
5. Post-Upgrade Scan
After the Tomcat upgrade, rerun Trivy to confirm no vulnerabilities remain:That’s it for this lesson—your CI/CD pipeline now enforces both manifest and image security checks before deploying to production.