Key Concepts
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
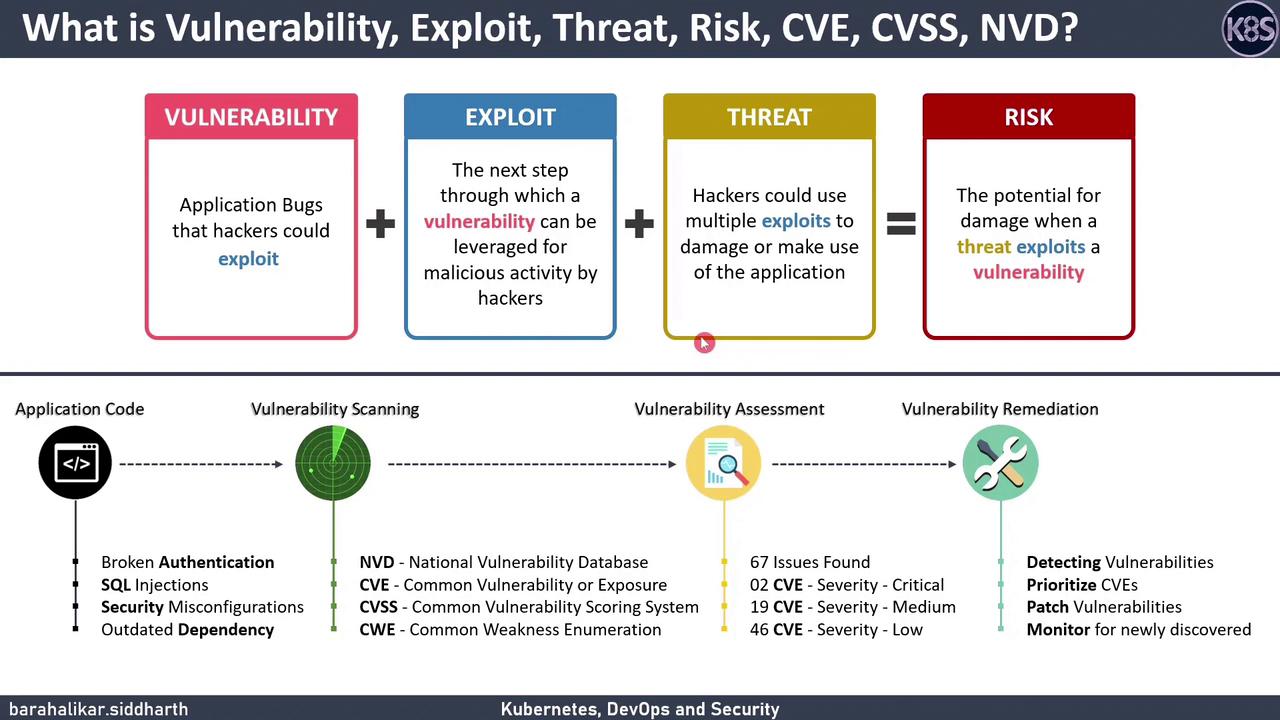
| Vulnerability | A flaw or bug in software that attackers can exploit. | SQL injection, broken authentication |
| Exploit | A script or technique that takes advantage of a vulnerability to perform malicious activity. | Remote code execution, unauthorized mining |
| Threat | Any potential cause of an unwanted security incident, such as an attacker or malware. | Phishing campaign, zero-day malware |
| Risk | The potential for loss or damage when a threat exploits a vulnerability. Calculated by severity and impact. | High-severity CVE in production environment |
A robust vulnerability management program reduces the window of exposure and lowers the overall security risk to your applications and infrastructure.
Vulnerability Scanning & Databases
Vulnerability scanners inspect code, container images, and configuration files, then compare findings against public vulnerability repositories. Once confirmed, issues are catalogued with unique identifiers.| Database / System | Description |
|---|---|
| NVD | The U.S. government’s repository of publicly disclosed vulnerabilities. |
| CVE | Unique IDs for known cybersecurity flaws (e.g., CVE-2021-34527). |
| CVSS | A scoring framework (0–10) that measures vulnerability severity and potential impact. |
| CWE | A taxonomy of software weaknesses, helping teams understand root causes and prevention strategies. |
Vulnerability Assessment
Once scanning completes, generate an assessment report that includes:- Severity: CVSS score or custom risk rating
- Vulnerability Age: Time since public disclosure
- Exploit Availability: Whether proof-of-concept code exists
- Remediation Guidance: Patching instructions or workarounds
Always address high-severity vulnerabilities with known exploits before lower-risk items. Automate prioritization using your CI/CD pipeline.
Remediation Workflow
- Prioritize
- Rank CVEs by CVSS score, exploitability, and business impact.
- Remediate
- Update or patch affected dependencies and configurations.
- Apply security fixes in code and container images.
- Verify & Monitor
- Re-scan to confirm fixes.
- Implement continuous monitoring and alerting for new vulnerabilities.
Next Steps
In the following lessons, you’ll perform real-world vulnerability scans and enforce security policies using:- Dependency Check for open-source libraries
- Trivy for container and filesystem scanning
- OPA Conftest to test your Kubernetes manifests
- Kubesec for policy checks in Kubernetes