In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to enforce mutual TLS (mTLS) between your Kubernetes workloads using Istio’s PeerAuthentication API. We’ll cover:
Listing Istio Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)
Inspecting pods and services in the prod namespace
Observing traffic before and after mTLS
Applying DISABLE, PERMISSIVE, and STRICT mTLS modes
Verifying encryption with packet capture
Prerequisites
A running Kubernetes cluster with Istio installed
kubectl configured for your clusterKiali add-on for traffic visualization
1. List Istio CRDs Istio installs several CRDs, including PeerAuthentication. To view them:
Example output:
NAME CREATED AT authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z envoyfilters.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z gateways.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z istiooperators.install.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z monitoringdashboards.monitoring.kiali.io 2021-06-20T13:04:36Z peerauthentication.security.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z requestauthentications.security.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z services.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z sidecars.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z virtualservices.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z workloadentries.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:57Z workloadgroups.networking.istio.io 2021-06-20T13:04:56Z
By default, no PeerAuthentication resources are defined:
kubectl get peerauthentication -A # No resources found
2. Inspect the prod Namespace List pods and services running in prod:
kubectl -n prod get pods,svc
Pods:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/devsecops-769f696c95f7jq 2/2 Running 0 2m17s pod/devsecops-769f696c9f9f 2/2 Running 0 2m17s pod/node-app-597464649c-5x75q 2/2 Running 0 4d4h
Services:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP PORT ( S ) AGE service/devsecops-svc ClusterIP 10.101.121.127 8080/TCP 4d2h service/node-service ClusterIP 10.101.46.231 5000/TCP 4d4h
3. Observe Traffic Generate continuous requests to the devsecops-svc service:
while true ; do curl -s 10.101.121.127:8080/increment/99 sleep 1 done
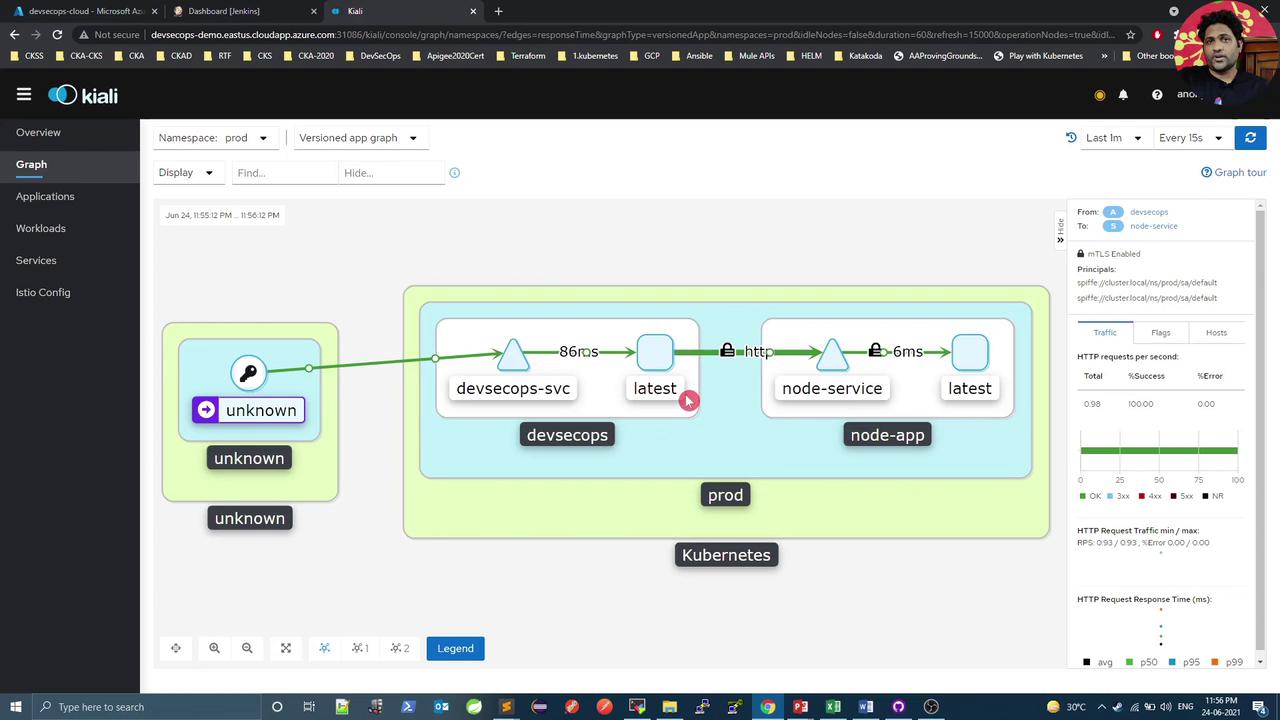
4. Visualize in Kiali Open Kiali’s Graph view for the prod namespace. By default, Istio uses PERMISSIVE mTLS, so you’ll see both plaintext and encrypted traffic between devsecops-svc and node-service.
Click the lock icon to confirm which connections are encrypted.
5. Disable mTLS Globally
Disabling mTLS will route all service-to-service traffic over plaintext HTTP, exposing your data in transit.
Create a PeerAuthentication in the istio-system namespace:
# peerauth-disable.yaml apiVersion : security.istio.io/v1beta1 kind : PeerAuthentication metadata : name : default namespace : istio-system spec : mtls : mode : DISABLE
Apply it:
kubectl apply -f peerauth-disable.yaml
Wait ~15 seconds and refresh Kiali. You’ll first see mixed traffic, then all connections drop the lock icon.
6. Switch to Permissive Mode
Permissive mode allows both mTLS and plaintext connections simultaneously—ideal for gradual rollout.
Edit the default PeerAuthentication:
kubectl edit peerauthentication default -n istio-system
Update the spec:
spec : mtls : mode : PERMISSIVE
Save and exit, then verify:
kubectl get peerauthentication default -n istio-system # NAME MODE AGE # default PERMISSIVE 2m36s
Refresh Kiali to observe a mix of encrypted and unencrypted traffic.
7. Enforce Strict mTLS Mode To require mTLS for all workloads:
kubectl edit peerauthentication default -n istio-system
Change to:
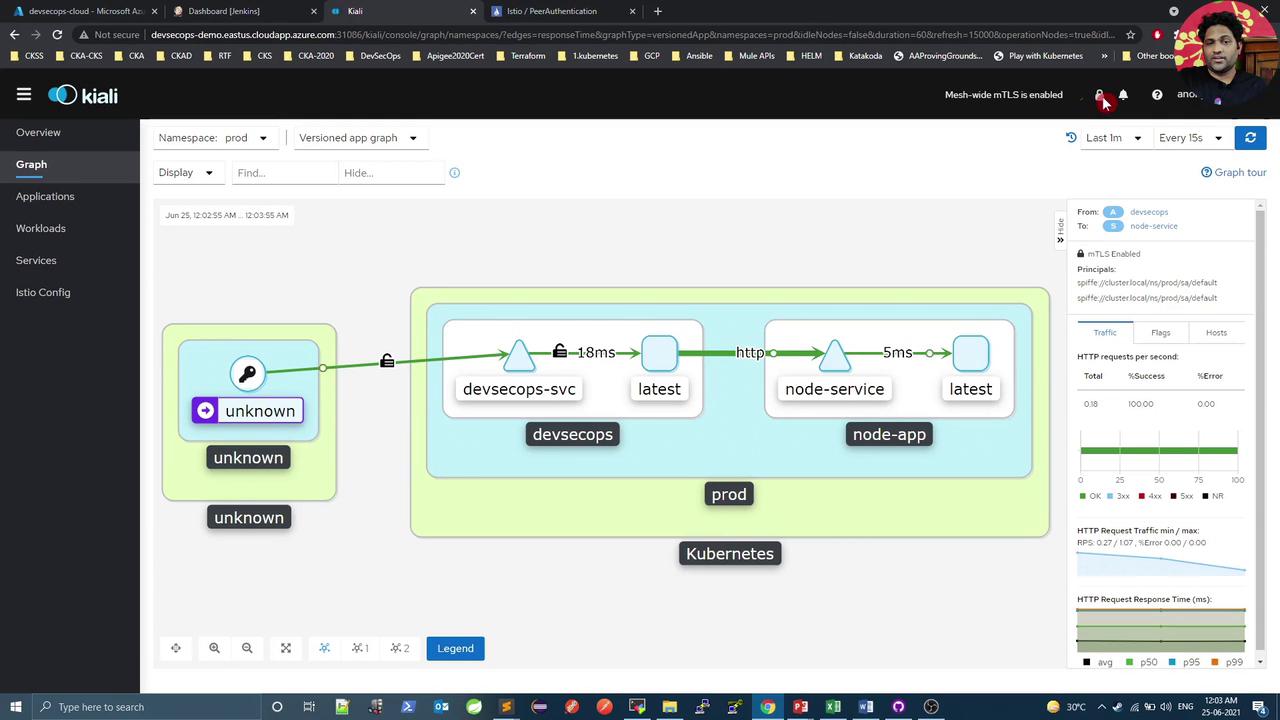
Save. The curl loop will now fail, as plaintext requests are blocked. Kiali will show a fully locked mesh:
Hover over the lock icon to see “Mesh-wide mTLS is enabled.”
8. Verify with Packet Capture Install the ksniff plugin and capture traffic to confirm encryption:
# Install ksniff kubectl krew install ksniff # Capture TCP traffic from a pod kubectl sniff < pod-nam e > -n prod --protocol tcp
Open the resulting PCAP in Wireshark and inspect TLS records on port 15001.
In this lesson, you learned how to manage mTLS modes with Istio’s PeerAuthentication API and verify traffic encryption. Next, explore securing ingress traffic using the Istio ingress gateway .
Links and References