DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
Kubernetes Operations and Security
Demo Kube bench
In this lesson, we’ll use kube-bench to run the CIS Kubernetes Benchmark tests against your cluster. We’ll cover:
- Overview of the CIS Benchmark PDF
- Manual Kubelet anonymous-auth check
- Installing and running kube-bench
- Parsing JSON output with
jq - CI/CD integration with Jenkins
CIS Kubernetes Benchmark PDF
Download the official CIS Kubernetes Benchmark from the CIS website:
CIS Kubernetes Benchmark requires an email to access the PDF.
Note
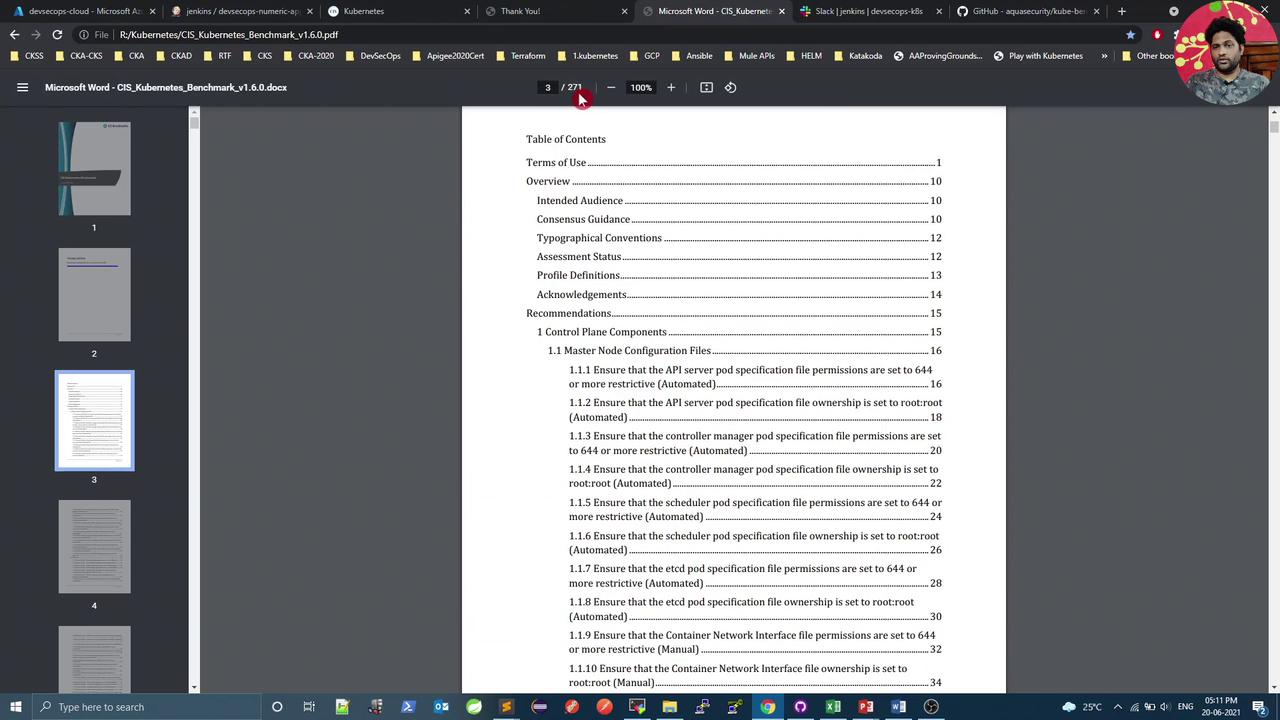
The PDF contains ~270 pages of guidelines, organized by test IDs per component. For instance, 4.2.1 in Worker Node Security Configuration verifies --anonymous-auth=false.
After downloading, open the PDF to review sections such as Terms of Use, Overview, and Recommendations.
Manual Check: Kubelet Anonymous Auth
On a kubeadm-provisioned node, verify the running Kubelet process and its config file:
# Identify the kubelet process
ps -ef | grep kubelet
# Display the Kubelet configuration
cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
In config.yaml, confirm anonymous auth is disabled:
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: false
Warning
If anonymous auth is set to true, update the YAML, then reload and restart the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart kubelet
Installing kube-bench
kube-bench on GitHub is a Go-based tool from Aqua Security that automates CIS checks. To install on Ubuntu:
# Download the latest .deb package (version may vary)
curl -L -O https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/releases/download/v0.3.1/kube-bench_0.3.1_linux_amd64.deb
# Install kube-bench
sudo apt install ./kube-bench_0.3.1_linux_amd64.deb -y
Running kube-bench
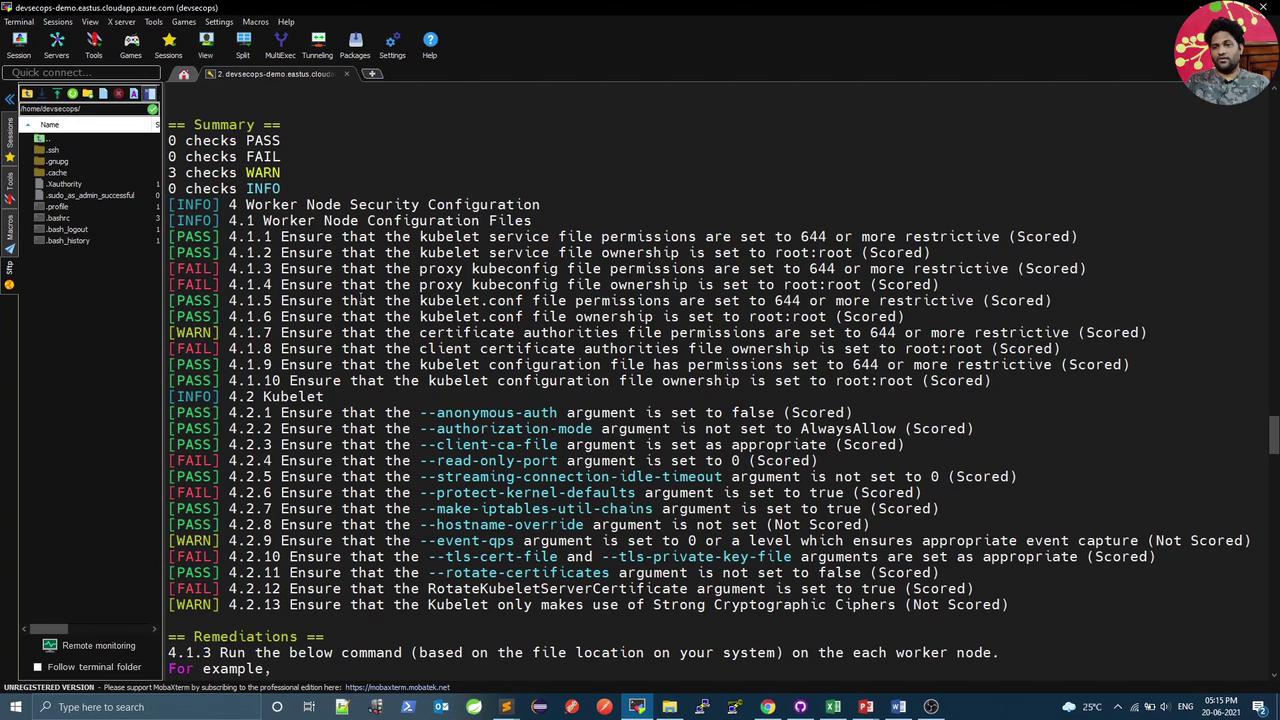
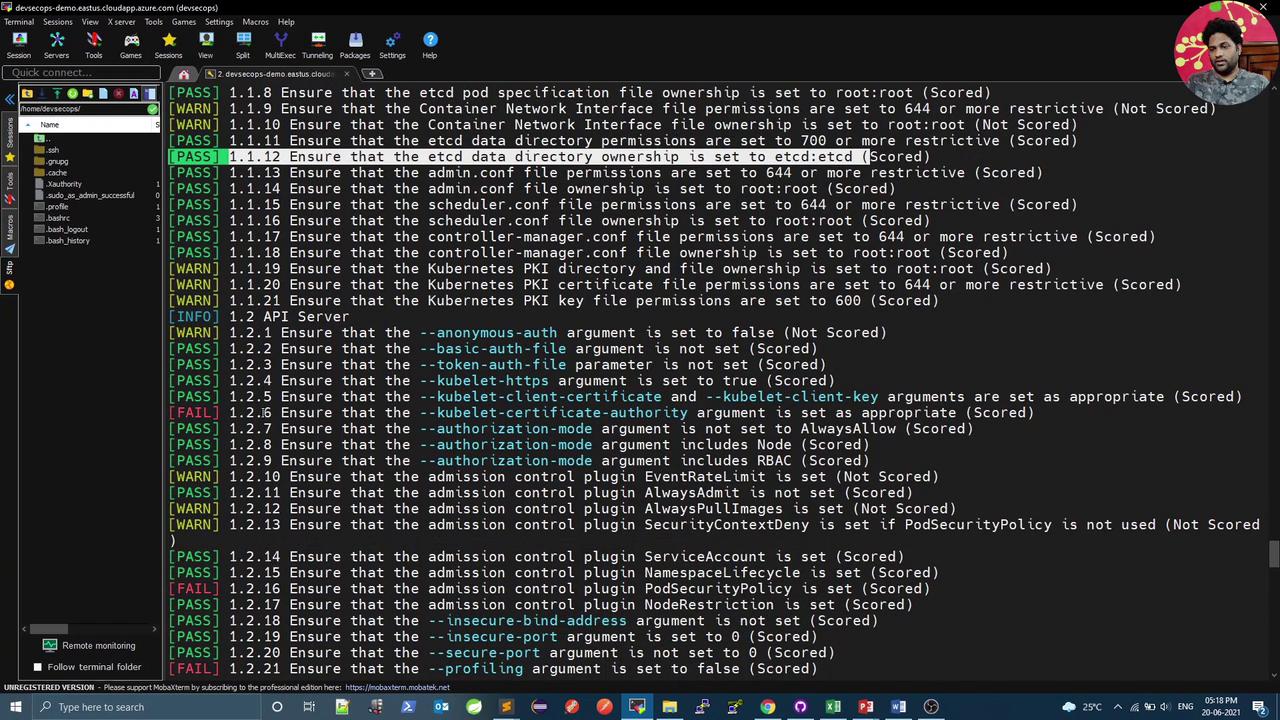
Execute all CIS checks (master, node, etcd, control plane):
kube-bench
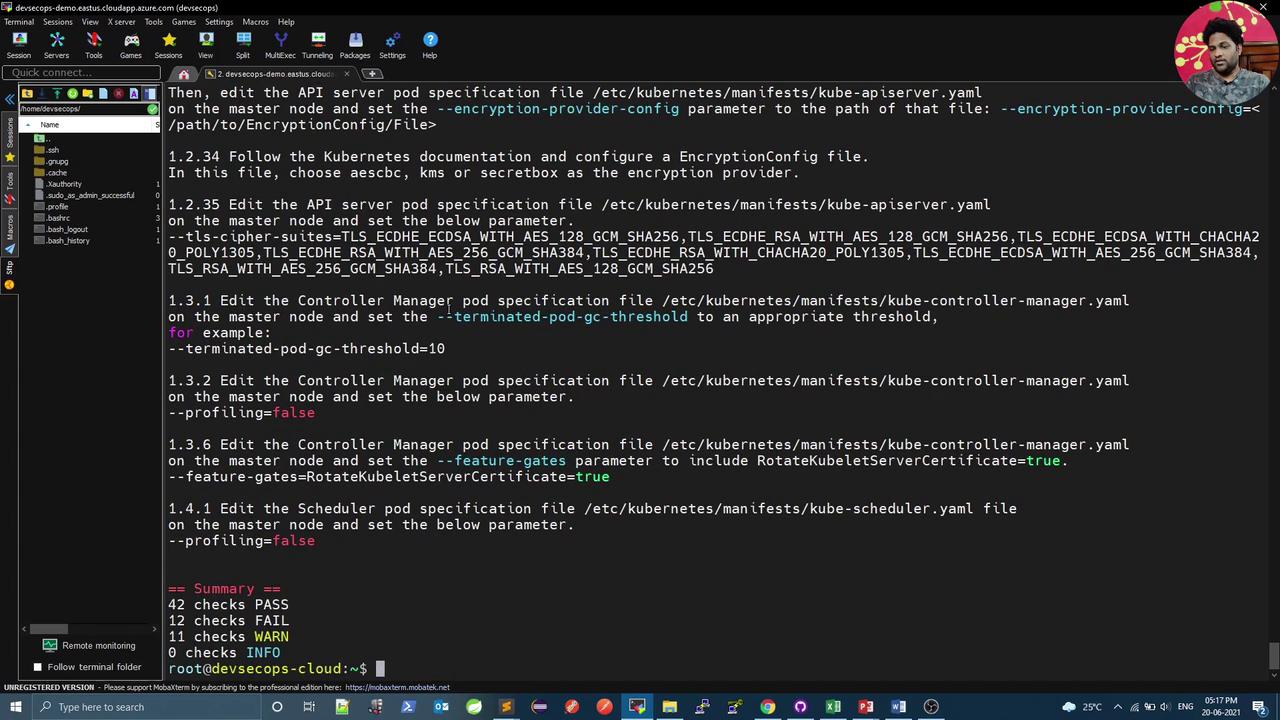
Example summary:
== Summary ==
42 checks PASS
3 checks FAIL
24 checks WARN
0 checks INFO
You can target specific components:
| Component | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| All | kube-bench | Run all CIS checks |
| Master | kube-bench master | Validate control plane configurations |
| Node | kube-bench node | Inspect worker node settings |
| Etcd | kube-bench etcd | Check etcd data store security |
# Run checks on the master node
kube-bench master
# Run checks on worker nodes
kube-bench node
JSON Output and Filtering
For CI automation, output results in JSON and use jq to filter:
kube-bench node --check 4.2.1 --json | jq
{
"id": "4",
"version": "1.5",
"text": "Worker Node Security Configuration",
"node_type": "node",
"tests": [
{
"section": "4.2",
"pass": 1,
"fail": 0,
"info": 0,
"desc": "Kubelet",
"results": [
{
"test_number": "4.2.1",
"test_desc": "Ensure that the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false (Scored)",
"status": "PASS",
"remediation": "If using a Kubelet config file, edit the file to set authentication: anonymous: enabled to false..."
}
]
}
]
}
To extract failure count:
total_fail=$(kube-bench node --check 4.2.1 --json | jq '.[].total_fail')
echo "Total fails: $total_fail"
Note
Ensure jq is installed (sudo apt install jq) to parse JSON output.
Jenkins Integration
Integrate kube-bench into a Jenkins pipeline to enforce CIS compliance:
stage('K8S CIS Benchmark') {
steps {
script {
parallel(
'Master': {
sh 'bash cis-master.sh'
},
'Etcd': {
sh 'bash cis-etcd.sh'
},
'Kubelet': {
sh 'bash cis-kubelet.sh'
}
)
}
}
}
Each script runs targeted checks, parses JSON, and exits with code 1 on failures. Example cis-kubelet.sh:
#!/bin/bash
# Run specific Kubelet tests
total_fail=$(kube-bench node \
--version 1.15 \
--check 4.2.1,4.2.2 \
--json | jq -r '.[].total_fail')
if [[ "$total_fail" -ne 0 ]]; then
echo "CIS Benchmark Failed: Kubelet checks 4.2.1,4.2.2"
exit 1
else
echo "CIS Benchmark Passed: Kubelet checks 4.2.1,4.2.2"
fi
Repeat similar scripts for cis-master.sh (e.g., checks 1.1.12, 1.2.1) and cis-etcd.sh (e.g., check 2.2).
Warning
Failing any CIS test will mark the Jenkins stage as failed. Adjust thresholds as needed.
Conclusion
By combining kube-bench with JSON output and jq filters, you can automate CIS Kubernetes Benchmark checks in your CI/CD pipeline. These scans help ensure your cluster adheres to security best practices before production deployment.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab