In this guide, you’ll learn how to deploy OctarineSec KubeScan to continuously assess and monitor Kubernetes workloads. KubeScan computes a risk score between 0 (no risk) and 10 (high risk) for each workload based on configurable runtime rules.
Prerequisites
A Kubernetes cluster (v1.16+)
kubectl configured for your clusterDocker CLI for building and pushing images
Git for cloning the repository
1. Clone & Build Since the official images might not be publicly pullable, clone the source and build both UI and server components:
git clone https://github.com/octarinesec/kube-scan.git cd kube-scan # Build the UI client cd client docker build -t < YOUR_CLIENT_IMAG E > . docker push < YOUR_CLIENT_IMAG E > # Build the server cd ../server docker build -t < YOUR_SERVER_IMAG E > . docker push < YOUR_SERVER_IMAG E >
Open kube-scan.yaml and locate the ConfigMap under the kube-scan namespace. Adjust thresholds or add rules to match your security policy:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Namespace metadata : name : kube-scan --- apiVersion : v1 kind : ConfigMap metadata : name : kube-scan namespace : kube-scan data : risk-config.yaml : | expConst: 9 # Exploitability weight impactConst: 3 # Impact weight low: 3 # Low risk threshold medium: 5 # Medium risk threshold max: 10 # Maximum score basic: - name: "privileged" title: "Workload is privileged" shortDescription: "Privileged containers get full host access" description: "Privileged containers can compromise host confidentiality." integrity: "Low" availability: "Low" exploitability: "Moderate" attackVector: "Local" scope: "Host" handler: "IsPrivileged"
You can extend basic or create new rule sets for network, resource limits, or Pod security policies.
3. Deploy KubeScan Update the Deployment spec in kube-scan.yaml to use your built images:
apiVersion : apps/v1 kind : Deployment metadata : name : kube-scan namespace : kube-scan spec : template : spec : containers : - name : kube-scan-ui image : <YOUR_CLIENT_IMAGE> env : - name : API_SERVER_PORT value : "80" - name : kube-scan image : <YOUR_SERVER_IMAGE> env : - name : KUBESCAN_RISK_CONFIG_FILE_PATH value : "/etc/kubescan/risk-config.yaml" volumeMounts : - name : config mountPath : /etc/kubescan volumes : - name : config configMap : name : kube-scan
Apply the complete manifest:
kubectl apply -f kube-scan.yaml kubectl -n kube-scan get all
4. Expose the UI Service By default, the UI Service is ClusterIP. To access it externally, switch to LoadBalancer or NodePort:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Service metadata : name : kube-scan-ui namespace : kube-scan spec : type : LoadBalancer selector : app : kube-scan ports : - port : 80 targetPort : 80 protocol : TCP
Reapply and get the external endpoint:
kubectl apply -f kube-scan.yaml kubectl -n kube-scan get svc kube-scan-ui
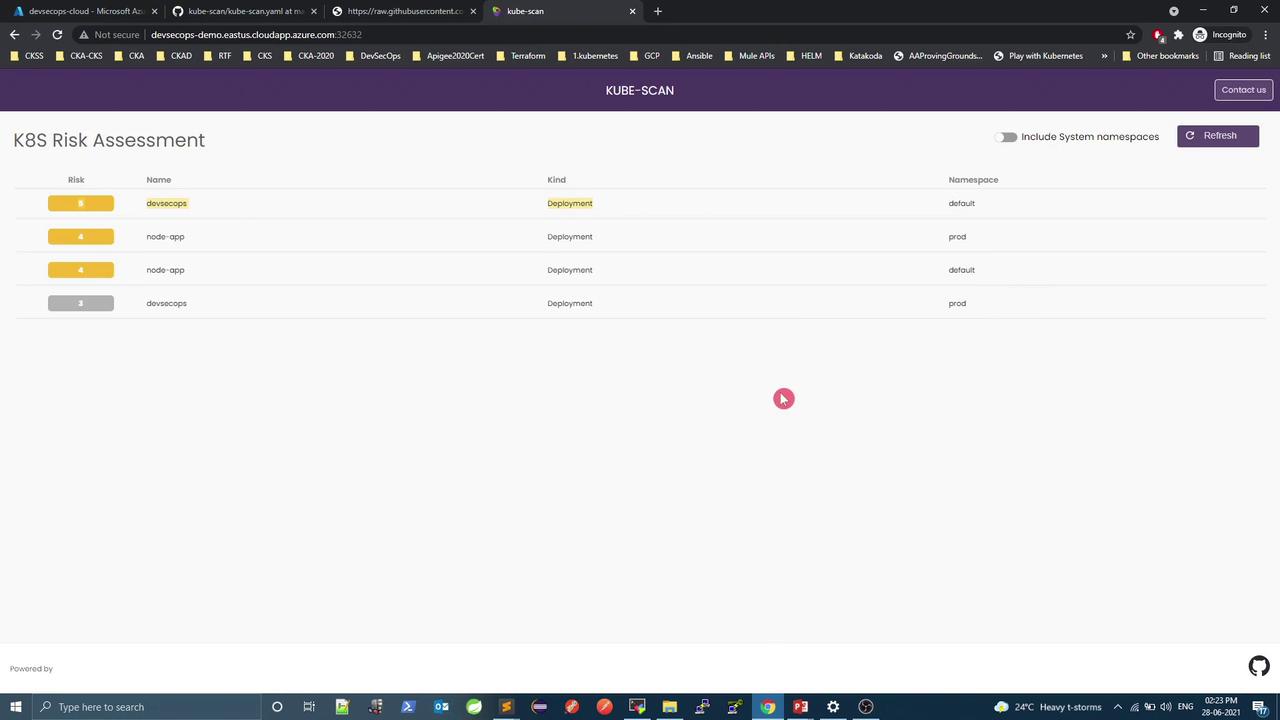
5. Access the Dashboard Open your browser at http://<HOST>:<PORT>. The K8S Risk Assessment dashboard displays all workloads with their risk scores.
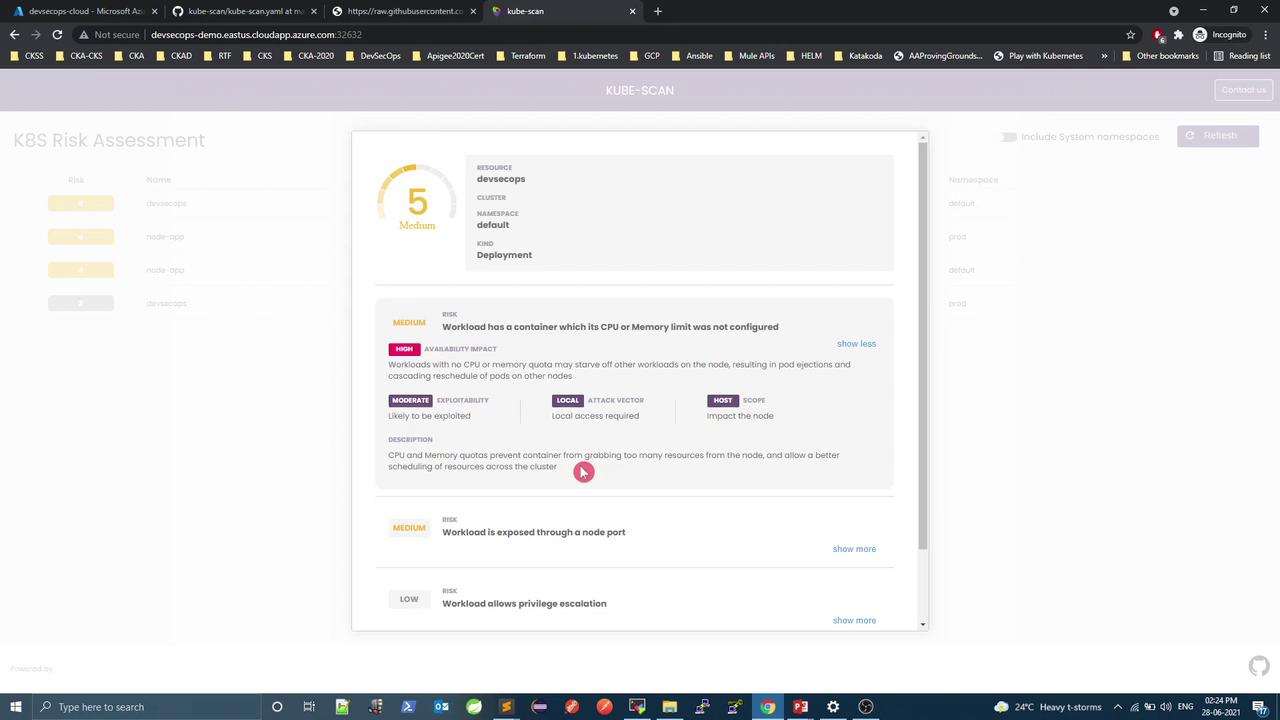
6. Workload Risk Comparison Compare two deployments of the same DevSecOps application:
Environment Risk Score Security Context Resource Limits Default 5 (Medium) None None Production 3 (Low) runAsNonRoot, noPrivilegeEscalation, readOnlyRootFilesystem requests: cpu=200m, memory=256Mi
Default Deployment (Higher Risk) apiVersion : apps/v1 kind : Deployment metadata : name : devsecops spec : template : spec : containers : - name : devsecops-container image : replace
Production Deployment (Lower Risk) apiVersion : apps/v1 kind : Deployment metadata : name : devsecops namespace : prod spec : template : spec : containers : - name : devsecops-container image : replace securityContext : runAsNonRoot : true allowPrivilegeEscalation : false readOnlyRootFilesystem : true resources : requests : cpu : "200m" memory : "256Mi" limits : cpu : "500m" memory : "512Mi"
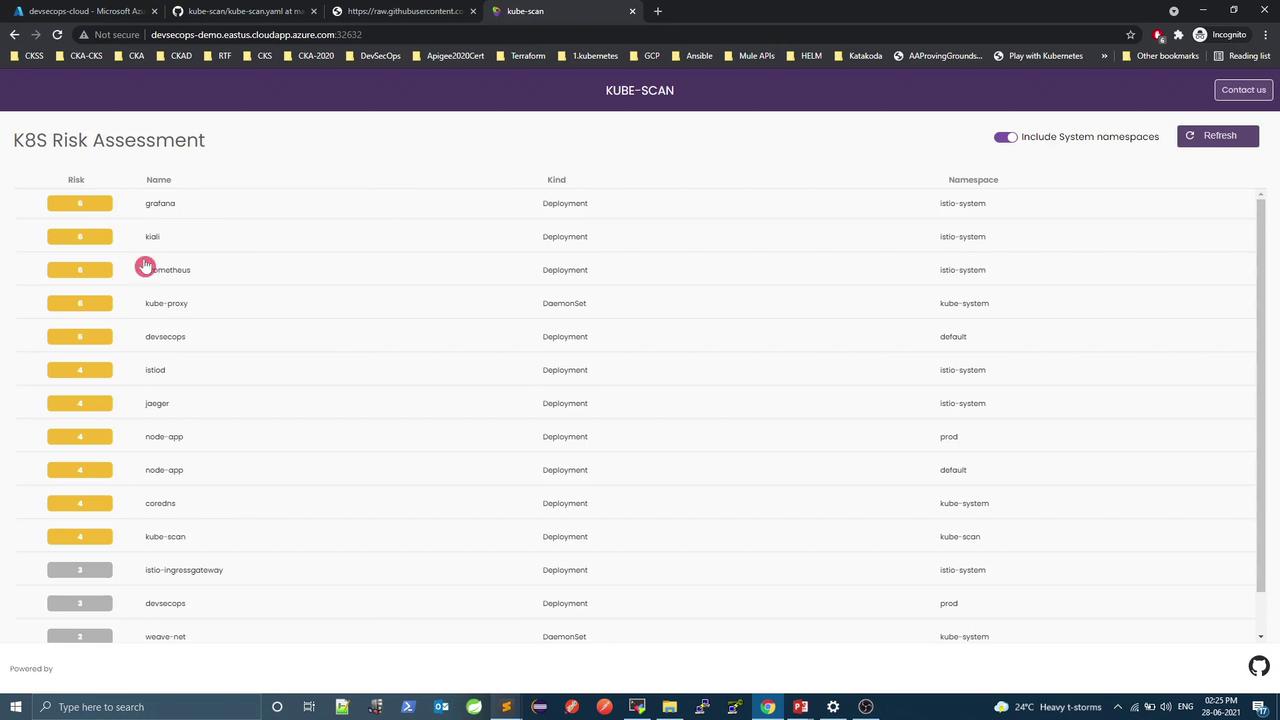
7. System Namespace Pods Enable “Show system pods” to include core components (e.g., grafana, prometheus) in the assessment.
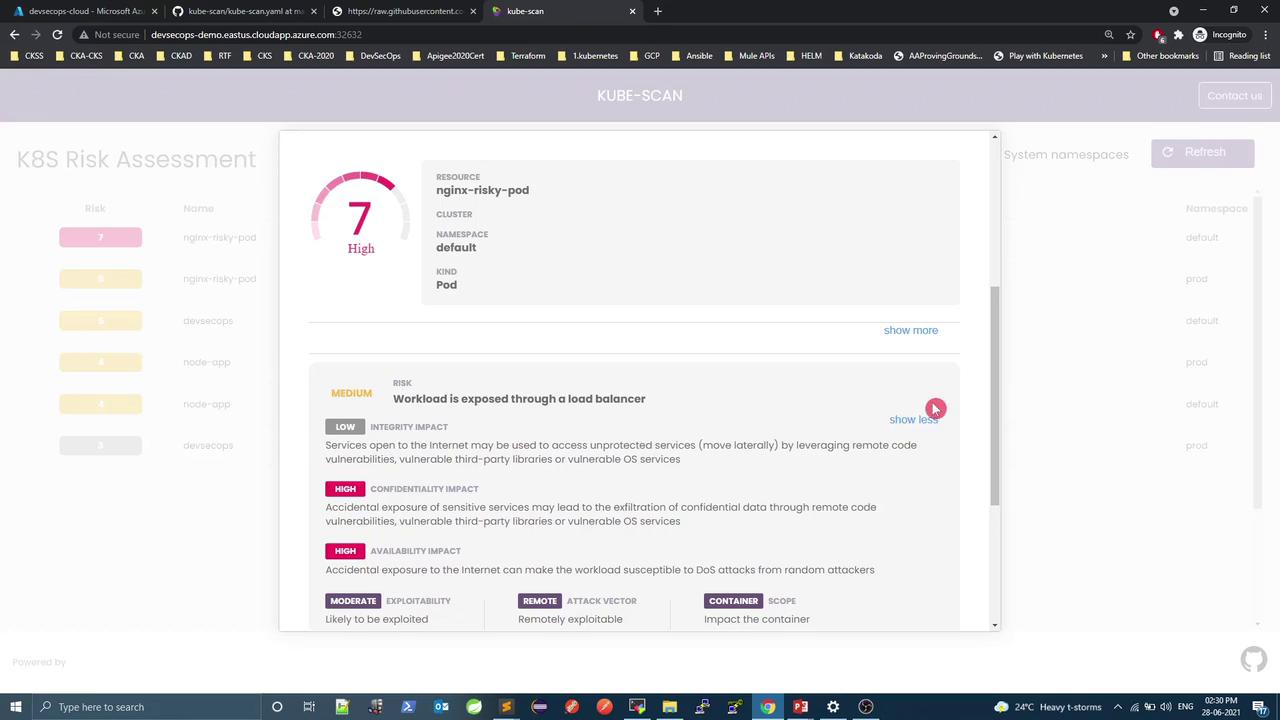
8. Risky Nginx Pod Demo Create a deliberately risky Pod and Service in both default and prod namespaces:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Pod metadata : name : nginx-risky-pod labels : run : nginx-risky-pod spec : shareProcessNamespace : true volumes : - name : vol hostPath : path : /etc containers : - name : nginx-risky-pod image : nginx securityContext : allowPrivilegeEscalation : true readOnlyRootFilesystem : false capabilities : add : [ "ALL" ] volumeMounts : - name : vol mountPath : /opt --- apiVersion : v1 kind : Service metadata : name : risky-pod-svc spec : selector : run : nginx-risky-pod ports : - port : 80 targetPort : 80 protocol : TCP
Apply and force an immediate scan:
kubectl apply -f risk-pod.yaml kubectl apply -f risk-pod.yaml -n prod kubectl -n kube-scan delete pod -l app=kube-scan
In default , nginx-risky-pod scores 7 (High) due to hostPath, ALL capabilities, missing limits, and LoadBalancer exposure.
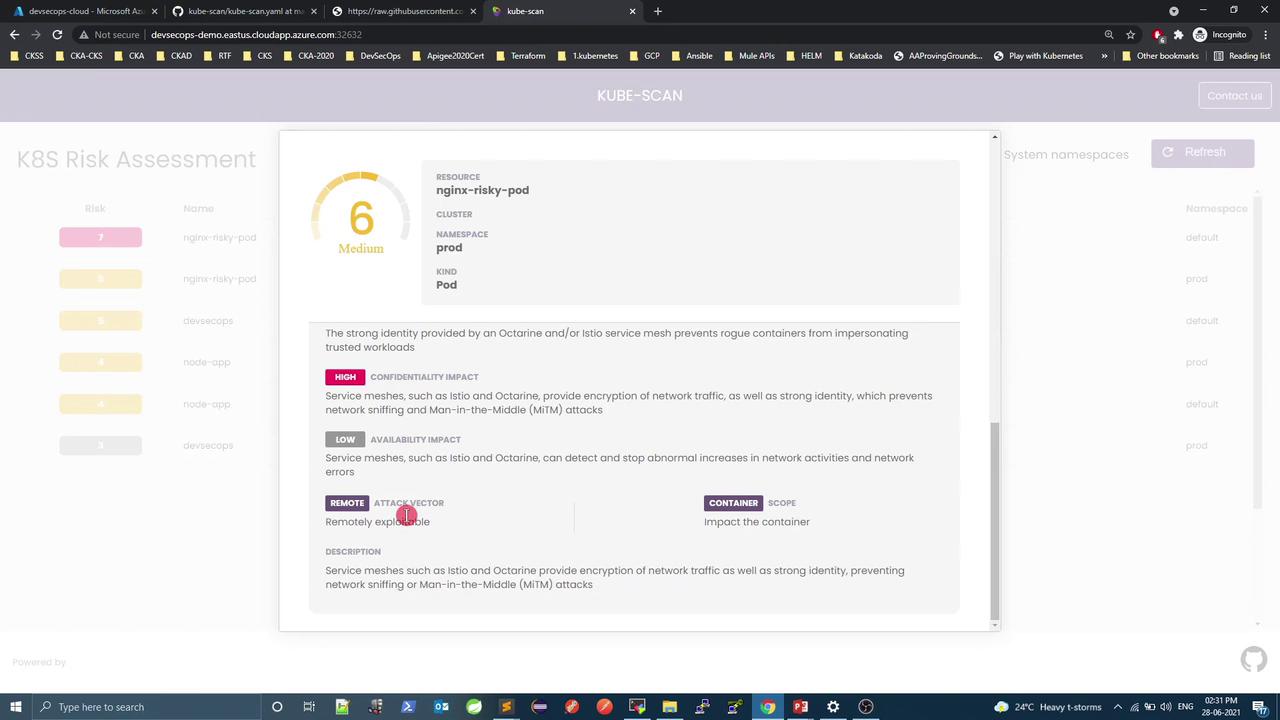
In prod with an Istio sidecar, the score drops to 6 (Medium) thanks to service-mesh encryption and identity features.
Conclusion KubeScan provides an automated scoring engine to surface misconfigurations and risk hotspots. By reviewing scores and iteratively adding Pod security contexts, resource constraints, or service meshes, you can drive your cluster toward a more secure posture.
Links and References