DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
Kubernetes Operations and Security
Demo Prometheus Grafana
In this guide, you’ll learn how to integrate Prometheus, Grafana, and Alertmanager to monitor Kubernetes resources and push alerts to external services like Slack. We’ll cover:
- Exposing Grafana & Prometheus via NodePort
- Querying metrics with Prometheus (PromQL)
- Visualizing Istio data in Grafana dashboards
- Configuring alerting channels in Grafana
- Defining Prometheus alert rules and using Alertmanager
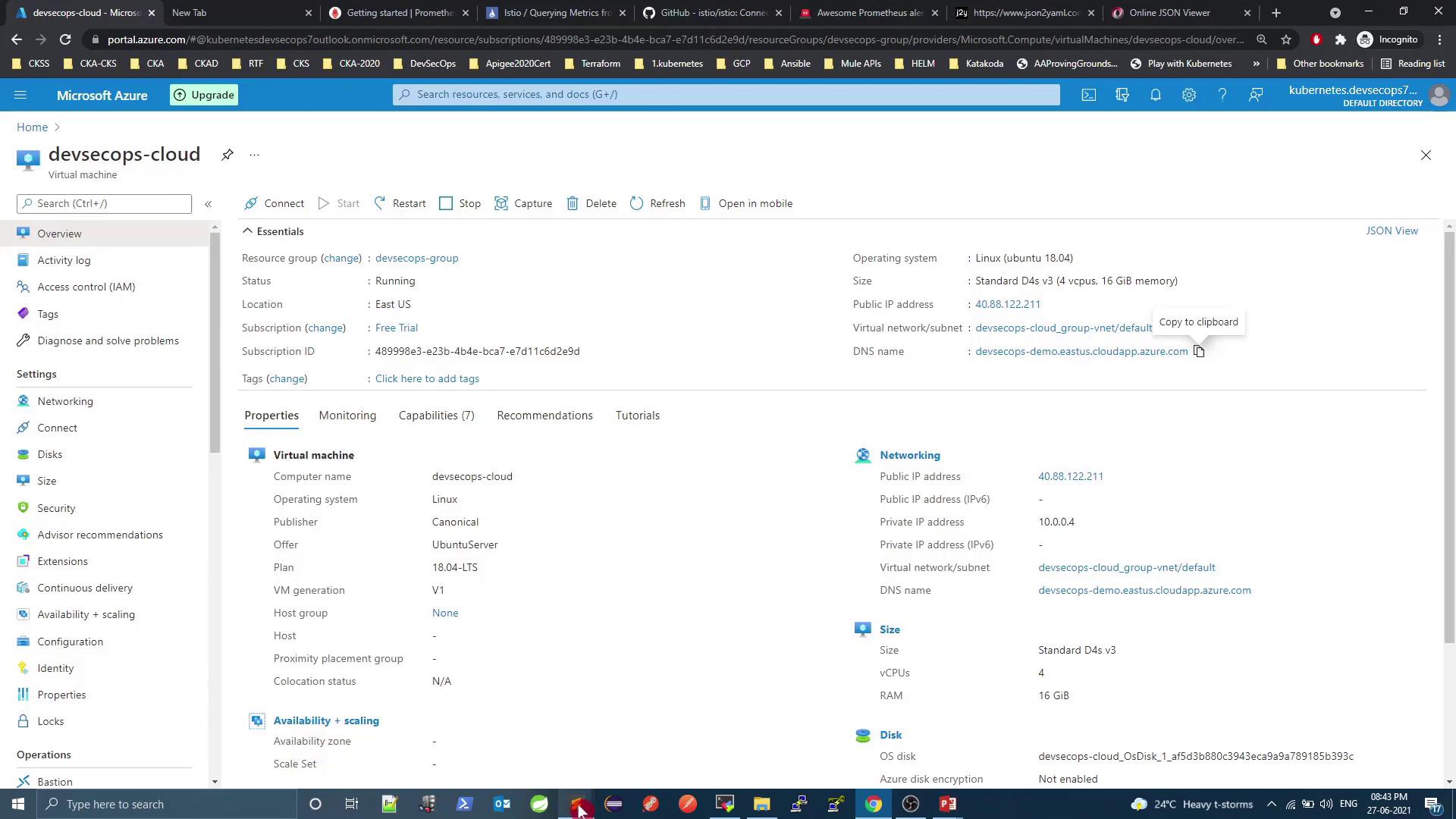
1. Exposing Grafana & Prometheus
By default, both services are deployed as ClusterIP, which prevents external access. To view dashboards from outside the cluster, change the Service type to NodePort.
| Service | Default Type | NodePort Port | Access URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grafana | ClusterIP | 3000:32556 | http://<VM_PUBLIC_DNS>:32556 |
| Prometheus | NodePort | 9090:32690 | http://<VM_PUBLIC_DNS>:32690 |
Why NodePort?
A NodePort service maps a port on each node’s IP to your service, allowing external HTTP/S access without an Ingress.
1.1 Expose Grafana
Check current services:
kubectl -n istio-system get svc
# NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP PORT(S)
# grafana ClusterIP 10.106.90.144 3000/TCP
# prometheus NodePort 10.108.8.197 9090:32458/TCP,20001:13086/TCP
Edit the Grafana Service and set type: NodePort:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: grafana
namespace: istio-system
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: grafana
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
name: service
Apply and verify:
kubectl -n istio-system apply -f grafana-service.yaml
kubectl -n istio-system get svc grafana
# NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP PORT(S)
# grafana NodePort 10.106.90.144 3000:32556/TCP
Access Grafana at http://<VM_PUBLIC_DNS>:32556.
Prometheus is already listening on http://<VM_PUBLIC_DNS>:32690.
2. Exploring Metrics with Prometheus
Prometheus scrapes metrics at intervals defined in prometheus.yml:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # scrape every 15 seconds
Since Istio injects service metrics automatically, you can use built-in dashboards or craft PromQL queries. For example:
istio_requests_total
2.1 Generating Traffic
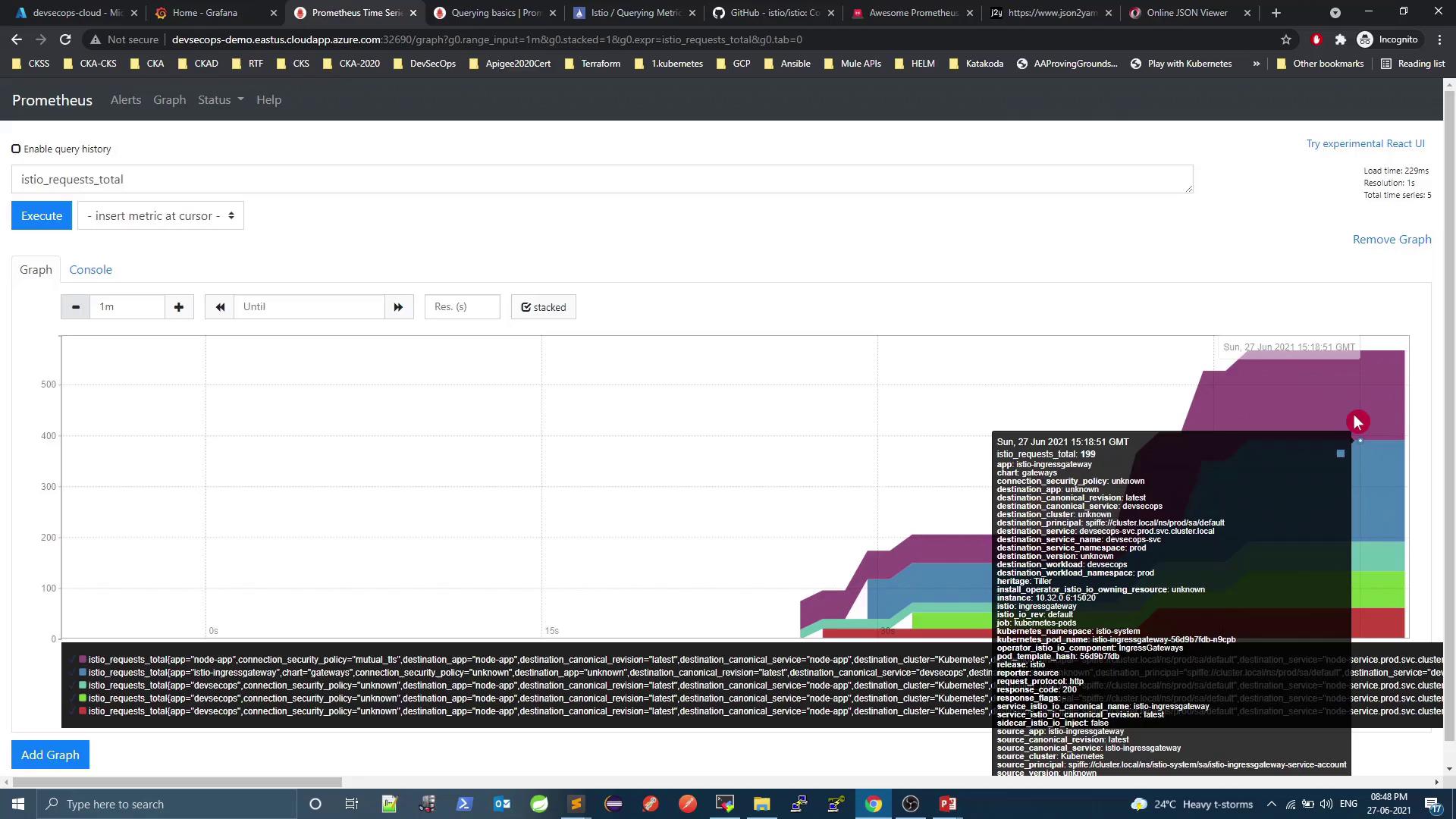
To populate metrics, send continuous HTTP requests via the Istio Ingress Gateway:
Traffic Generator Loop
This loop will run indefinitely until you stop it (Ctrl+C). Ensure you target the correct host and port to avoid unintended load.
while true; do
curl -s http://<INGRESS_HOST>:<INGRESS_PORT>/increment/99
sleep 0.1
done
After a few seconds, refresh Prometheus and switch to Graph view. You should see:
3. Visualizing Data in Grafana
Grafana provides prebuilt dashboards for Istio monitoring. Log in at http://<VM_PUBLIC_DNS>:32556, then configure your data source (Prometheus) and explore:
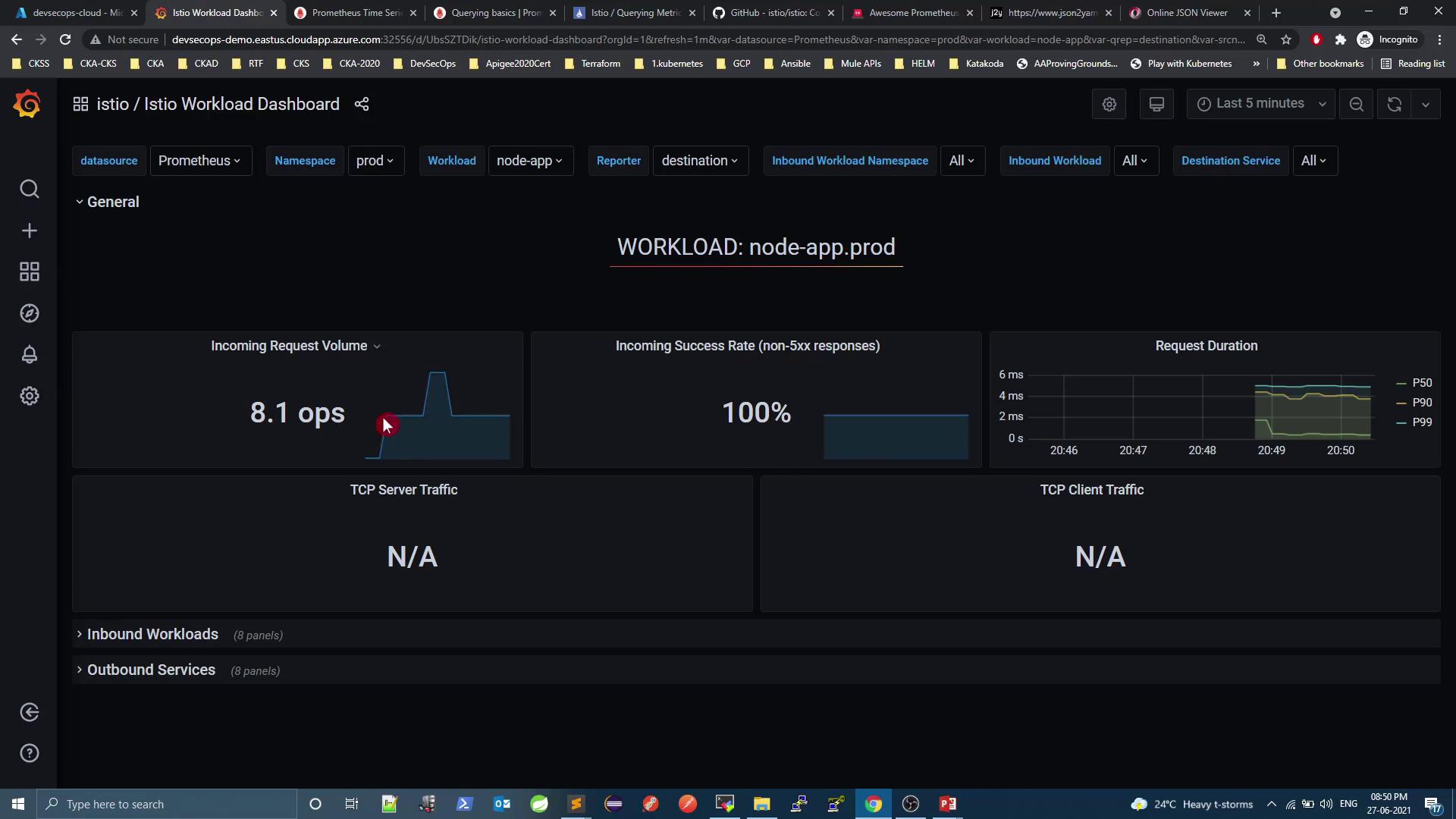
3.1 Istio Workload Dashboard
Shows per‐workload metrics (request rate, success rate, latency). Example for node-app.prod:
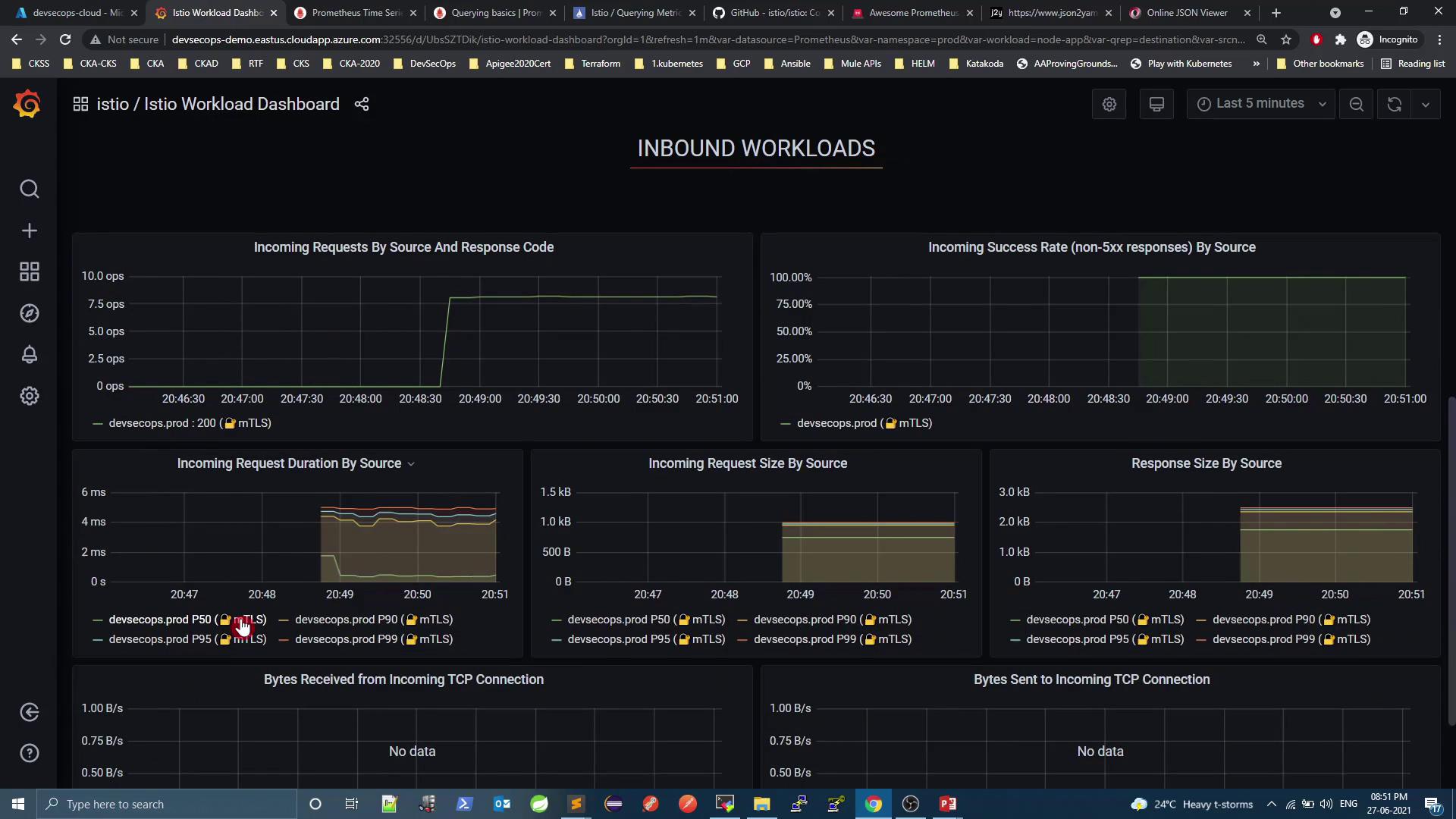
3.2 Inbound Workloads
Detailed inbound metrics: request/response sizes, mTLS usage, error rates:
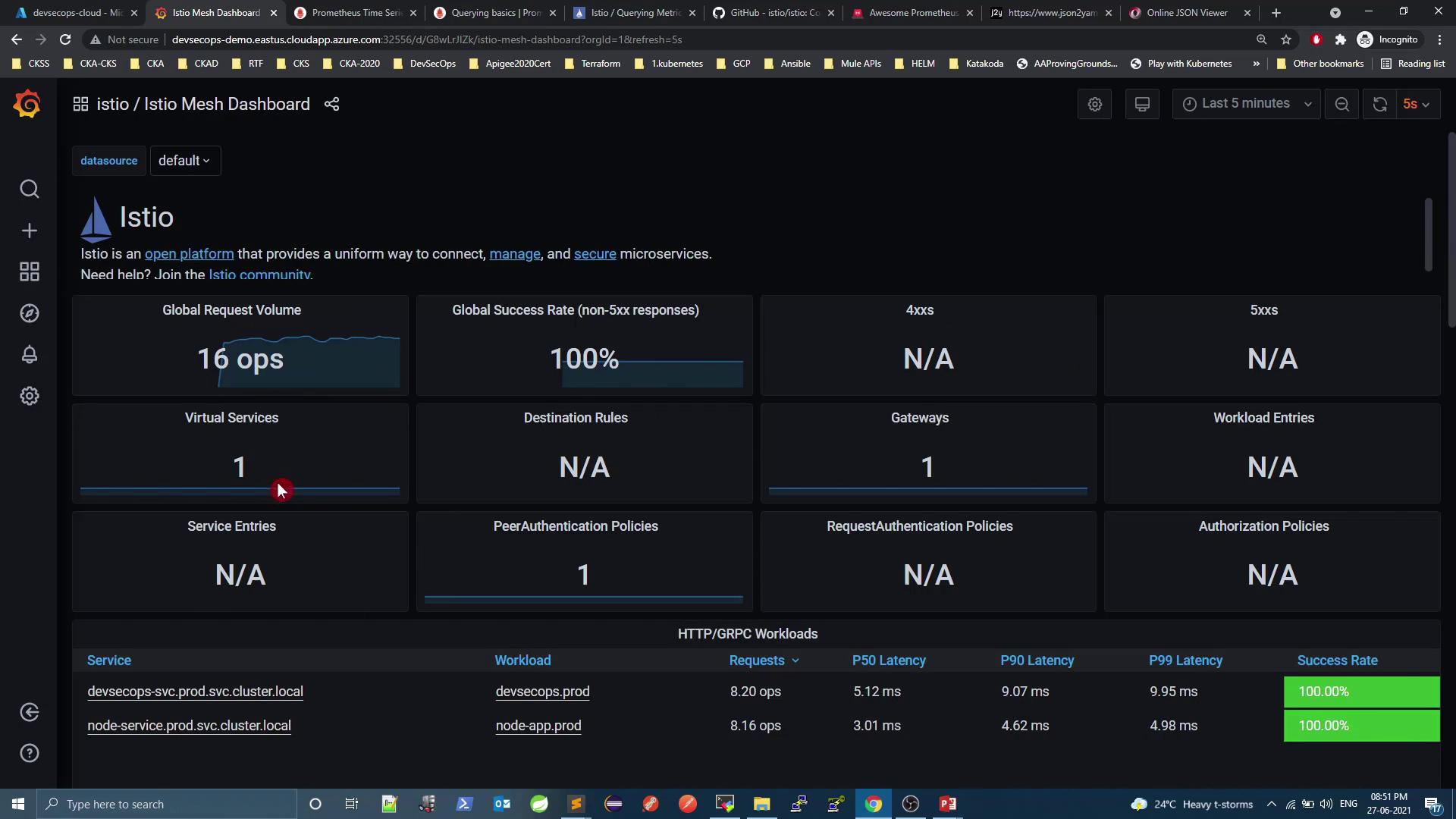
3.3 Mesh Dashboard
Get global insights: overall request volume, success rate, virtual services, gateways:
4. Alerting with Grafana
Grafana supports built-in alert rules and notification channels (Slack, email, PagerDuty, etc.). To create a Slack channel:
Notification channel → New channel
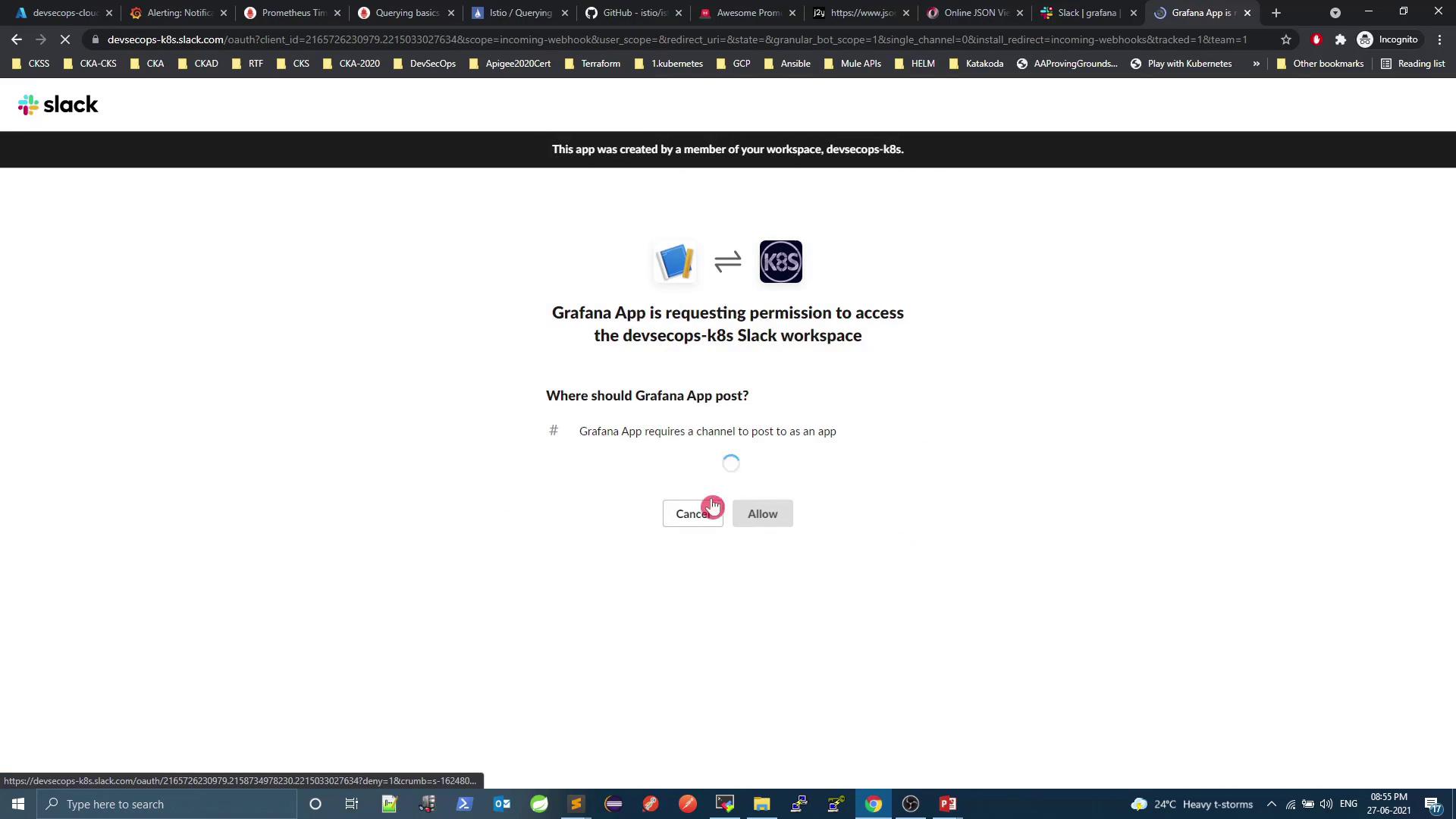
Select Slack and add your webhook URL.
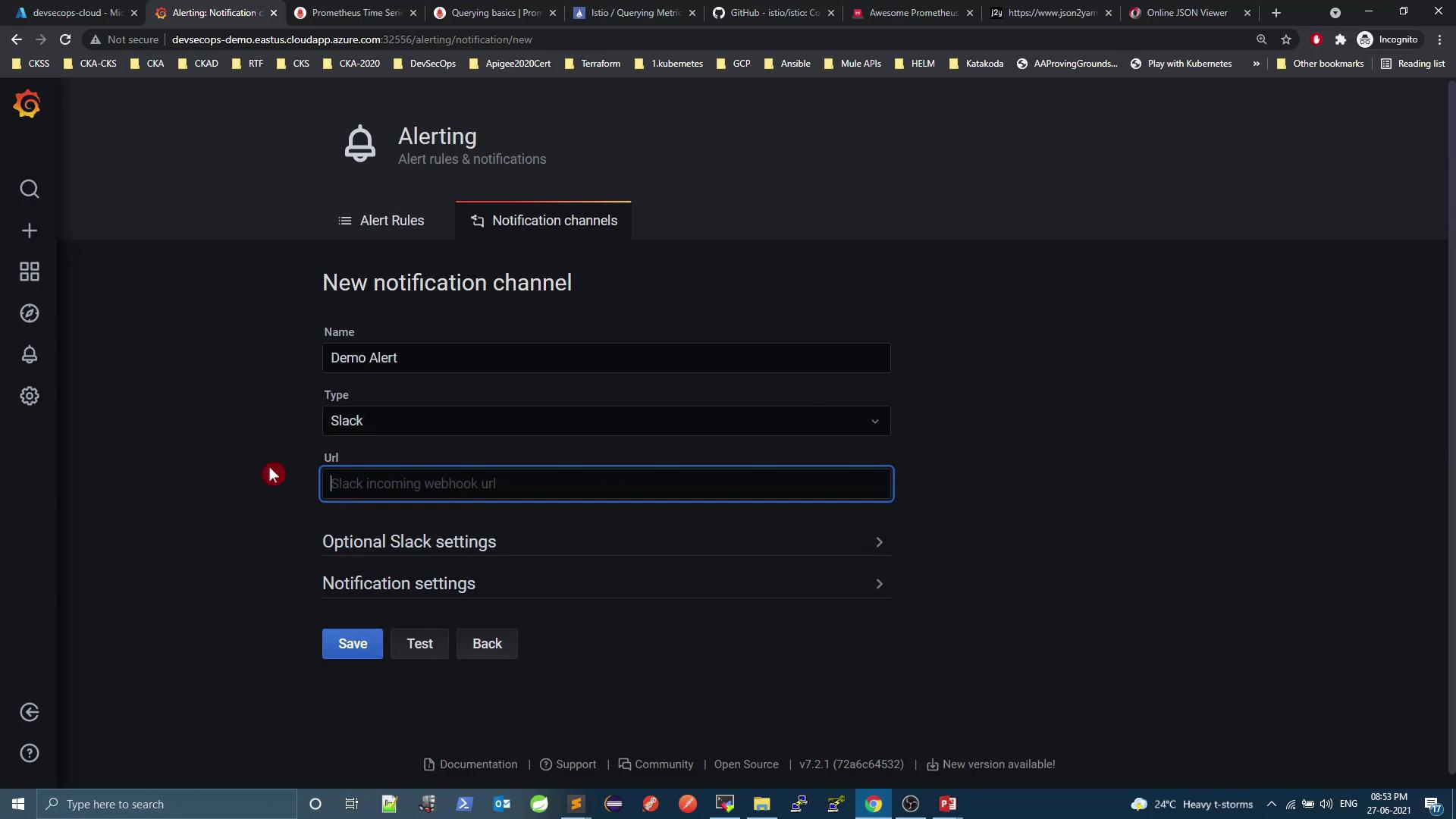
Approve the Grafana app in Slack.
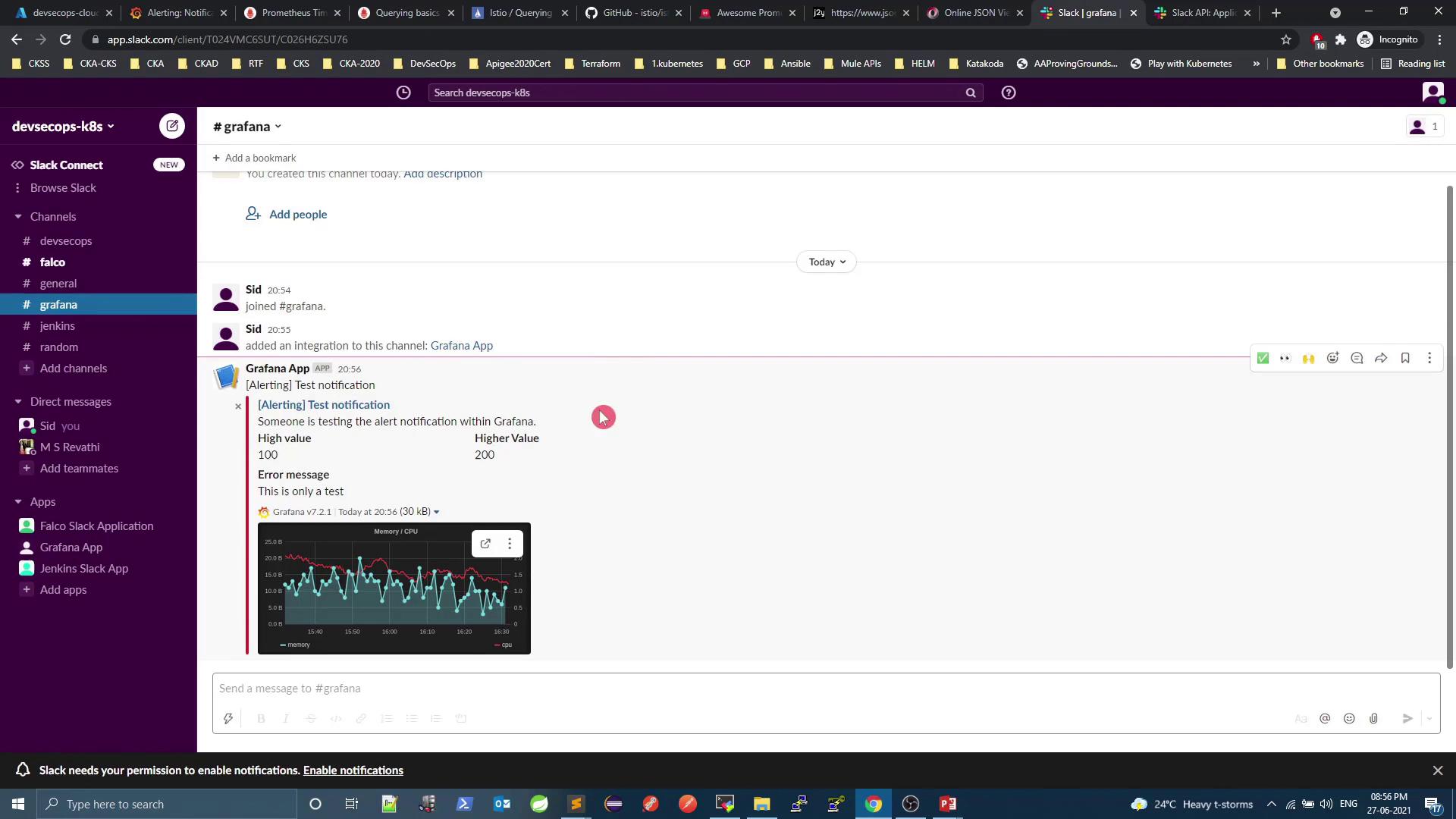
Test the channel and watch alerts roll in:
5. Prometheus Alerts & Alertmanager
Out of the box, Prometheus doesn’t ship with alert rules. Let’s integrate Alertmanager and define rules:
Verify current state
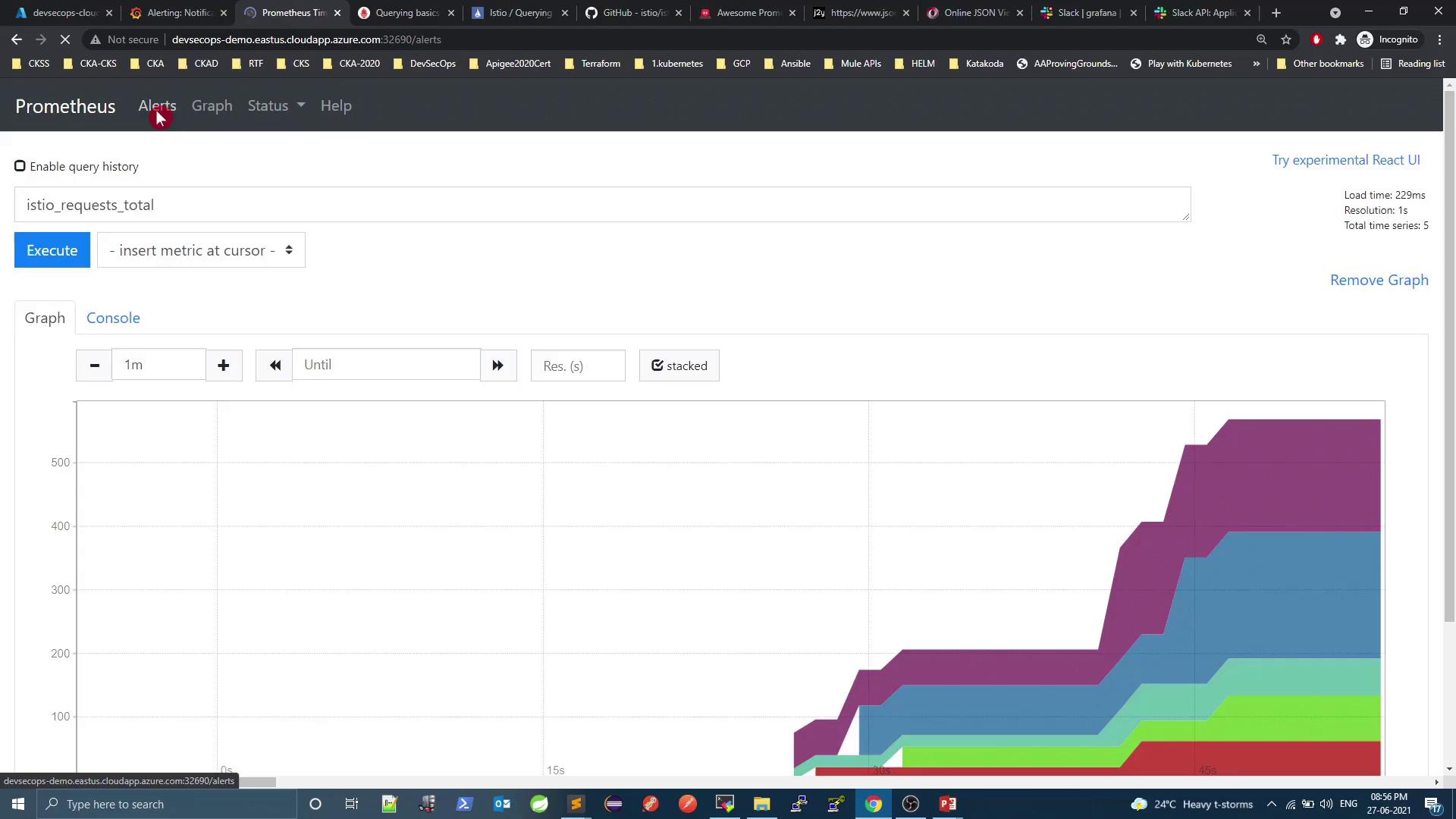
Check Alertmanager integration
Next, install Alertmanager, create custom alert rules, and configure routing (Slack, email, etc.) in alertmanager.yml and your Prometheus rules files.
Links & References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab