Docker Certified Associate Exam Course
Docker Compose
Example Voting Application with Docker Compose
In this step-by-step tutorial, you’ll learn how to orchestrate a multi-service voting application using Docker Compose. By the end, you’ll have a running stack that includes Redis, PostgreSQL, a voting frontend, a worker processor, and a results dashboard.
Prerequisites
- Docker Engine installed (version ≥ 19.03)
- Basic familiarity with
dockerCLI - A terminal/SSH session on Linux, macOS, or Windows WSL
Step 1: Install Docker Compose
Docker Compose isn’t bundled with Docker Engine by default. Install it on Linux with:
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.16.1/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" \
-o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
docker-compose --version
Expected output:
docker-compose version 1.16.1, build 1719ceb
Note
Replace 1.16.1 with the latest stable release. See the Compose releases on GitHub for details.
Step 2: Clean Up Existing Containers
Before deploying, stop any previous demo containers:
# List running containers
docker ps
# Stop containers by ID or prefix
docker stop 69 54 5b 2f 0b
# Verify all relevant containers are stopped
docker ps
Warning
Stopping containers will terminate running services. Ensure you don’t have unsaved data in those containers.
Step 3: Define Services in docker-compose.yml
Create a file named docker-compose.yml with the following content. It leverages Compose file format version 3.
version: '3'
services:
redis:
image: redis
db:
image: postgres:9.4
vote:
image: voting-app
ports:
- "5000:80"
depends_on:
- redis
worker:
image: worker-app
depends_on:
- db
- redis
result:
image: result-app
ports:
- "5001:80"
depends_on:
- db
Service Overview
| Service | Image | Ports | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| redis | redis | – | In-memory queue for incoming votes |
| db | postgres:9.4 | – | Persistent storage for vote records |
| vote | voting-app | 5000→80 | Frontend where users cast their vote |
| worker | worker-app | – | Processes queued votes into the PostgreSQL DB |
| result | result-app | 5001→80 | Displays aggregated vote results |
Note
The depends_on key ensures containers start in the correct order, but it doesn’t wait for health checks. Consider adding healthchecks for production workloads.
See the Compose file reference for advanced options.
Step 4: Deploy the Stack
From the directory containing docker-compose.yml, run:
docker-compose up -d
This command will pull images, create a default network, and start all five containers. Container names are prefixed by your folder name (e.g., root_redis_1).
Verify everything is up:
docker ps
You should see containers for Redis, PostgreSQL, vote, worker, and result.
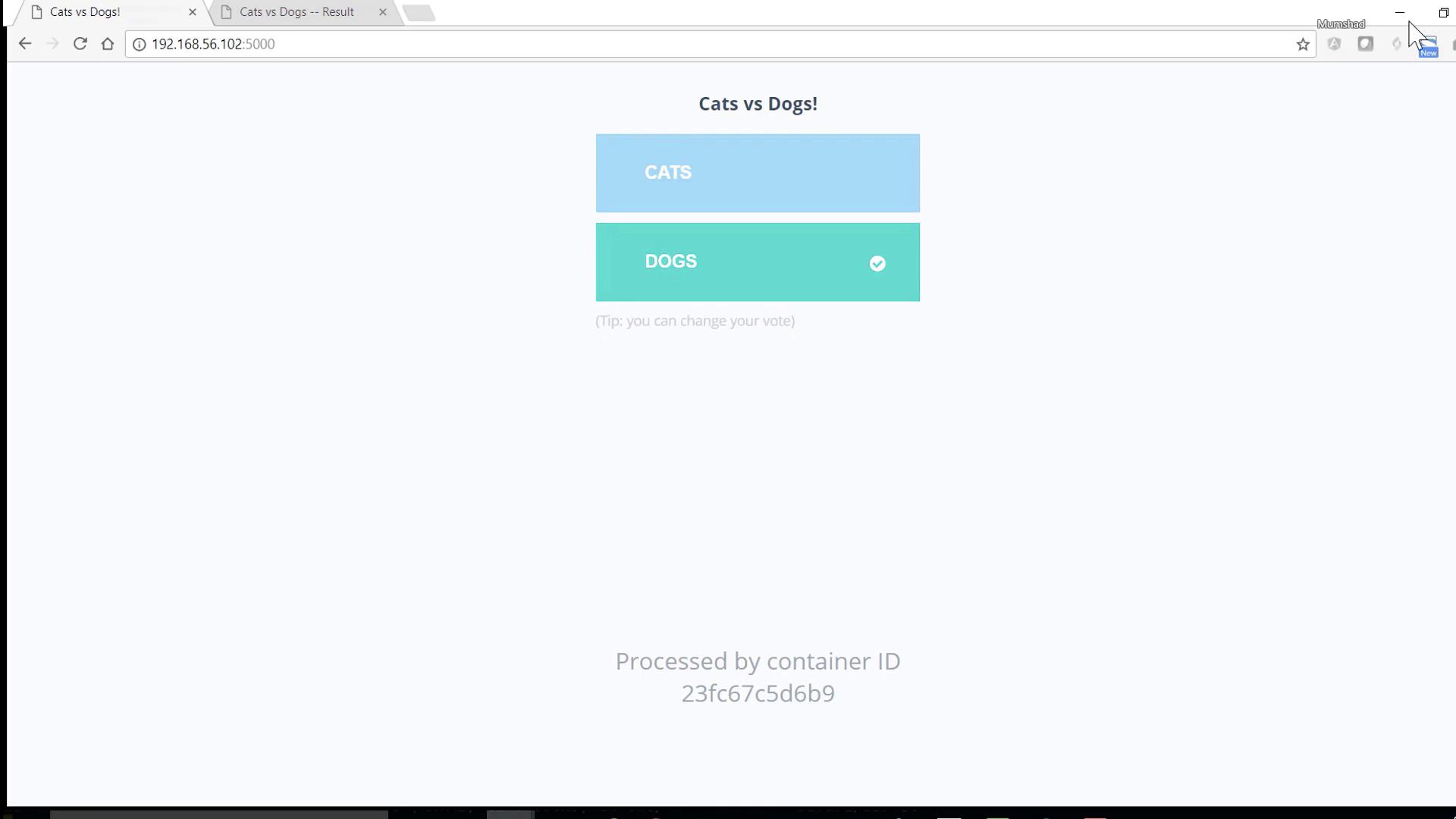
Step 5: Access the Application
- Voting interface: http://localhost:5000
- Results dashboard: http://localhost:5001
Cast a vote on the first page, then switch to the results page to see real-time counts.
Clean Up
When you’re done testing, stop and remove all services with:
docker-compose down
This command stops containers and removes the network. Volumes and images remain unless you add the --volumes or --rmi all flags.
References and Further Reading
Watch Video
Watch video content