Prerequisites
- A running UCP cluster with at least one manager node.
kubectlconfigured to communicate with UCP’s Kubernetes API.- Access to a node’s external IP for Service testing.
1. Creating an NGINX Pod
- In the UCP console, go to Kubernetes → Pods and click Create.
- Select the default namespace.
Avoid using the
default namespace in production. Create a dedicated namespace for isolation and resource quotas.-
Paste the following Pod manifest to launch an NGINX container:
- Click Create and wait until the Pod status changes to Running.
- Click the newly created Pod to view its details:
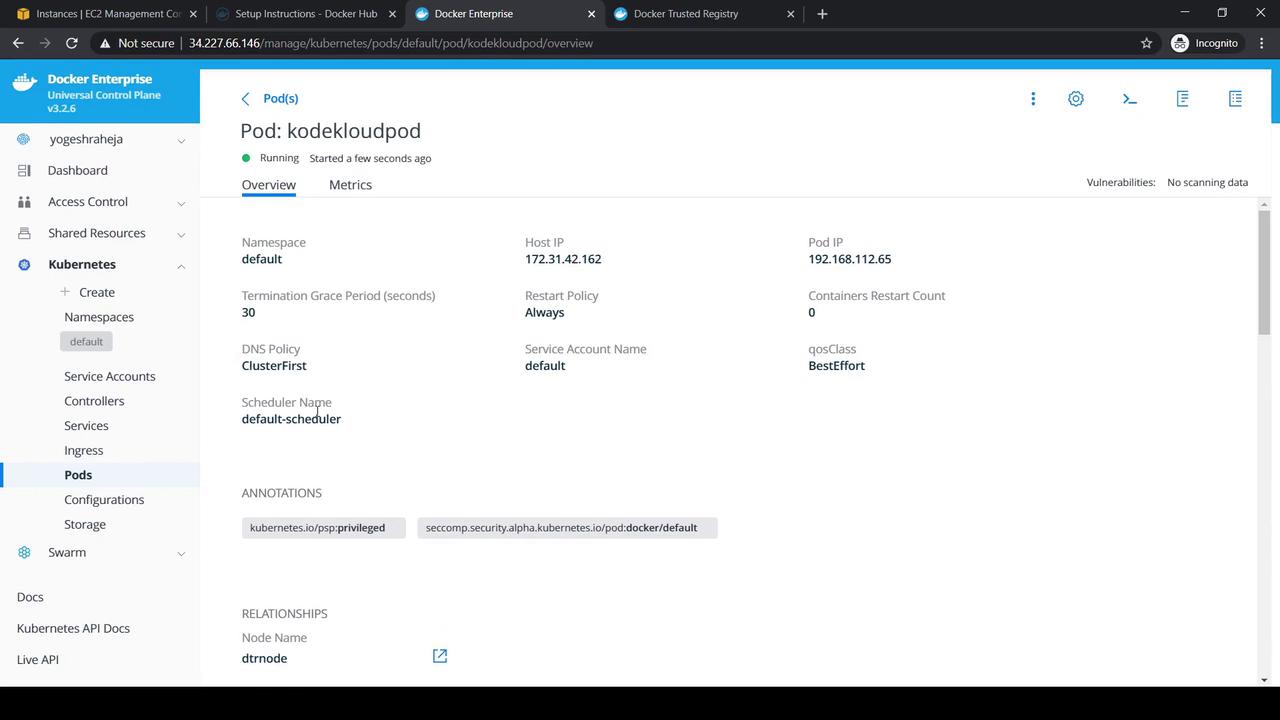
2. Exposing the Pod via a NodePort Service
To make the NGINX Pod reachable from outside the cluster:- Navigate to Kubernetes → Services and click Create.
- Keep the default namespace selected.
-
Enter this Service manifest, which maps port 80 on the Pod to port 30080 on each node:
- Click Create to provision the Service.
- Open the Service details to confirm the assigned ports:
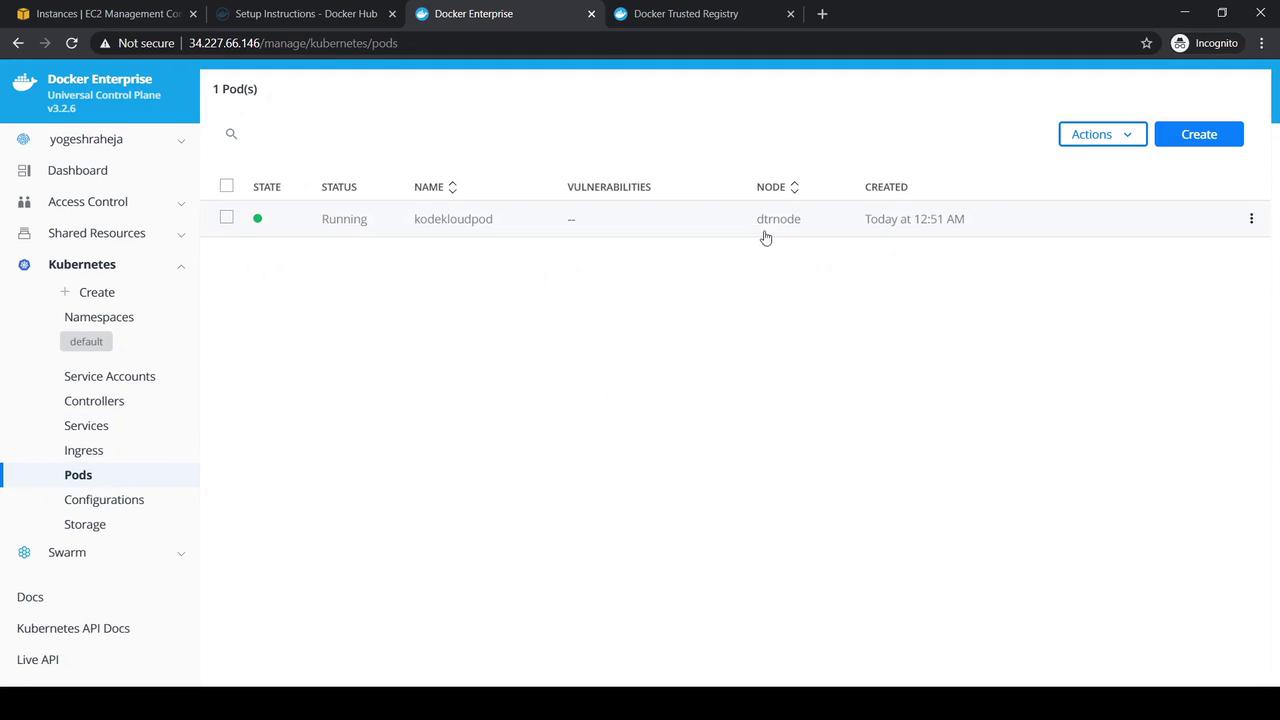
-
Retrieve the external IP of the node hosting the Pod:
-
In your browser, navigate to
http://<external-ip>:30080. You should see the default NGINX welcome page.
3. Cleaning Up Resources
Once testing is complete, remove the Pod and Service:- In the UCP console, select the nginx-nodeport-svc Service.
- Click Action → Remove, then confirm.
- Repeat for the nginx-pod Pod.
Follow the official Docker documentation for a safe and complete uninstallation process.
| Component | Documentation Link |
|---|---|
| Docker Trusted Registry (DTR) | https://docs.docker.com/ee/dtr/administration/install |
| Universal Control Plane (UCP) | https://docs.docker.com/ee/ucp/administration/install |
Uninstalling Docker Trusted Registry
- Open the DTR docs and scroll to Uninstall.
- Copy the provided command and execute it, supplying your UCP URL and credentials when prompted.
Uninstalling Universal Control Plane
- In the UCP docs, find the Uninstall section.
-
Run the interactive uninstall command on one manager node:
-
To clean up leftovers, execute:
-
Finally, delete any UCP-related secrets: