1. Enable the Kubernetes Engine API
- Sign in to the GCP Console and search for GKE, then click Kubernetes Engine.
If you’re on a managed learning environment (e.g., KodeKloud), the Kubernetes Engine API is often pre-enabled.
- If prompted, click Enable to activate the Kubernetes Engine API.

- After enabling, you’ll be redirected to the Kubernetes clusters dashboard.
2. Choose Cluster Type
Click Create on the Kubernetes clusters page. You’ll see two modes: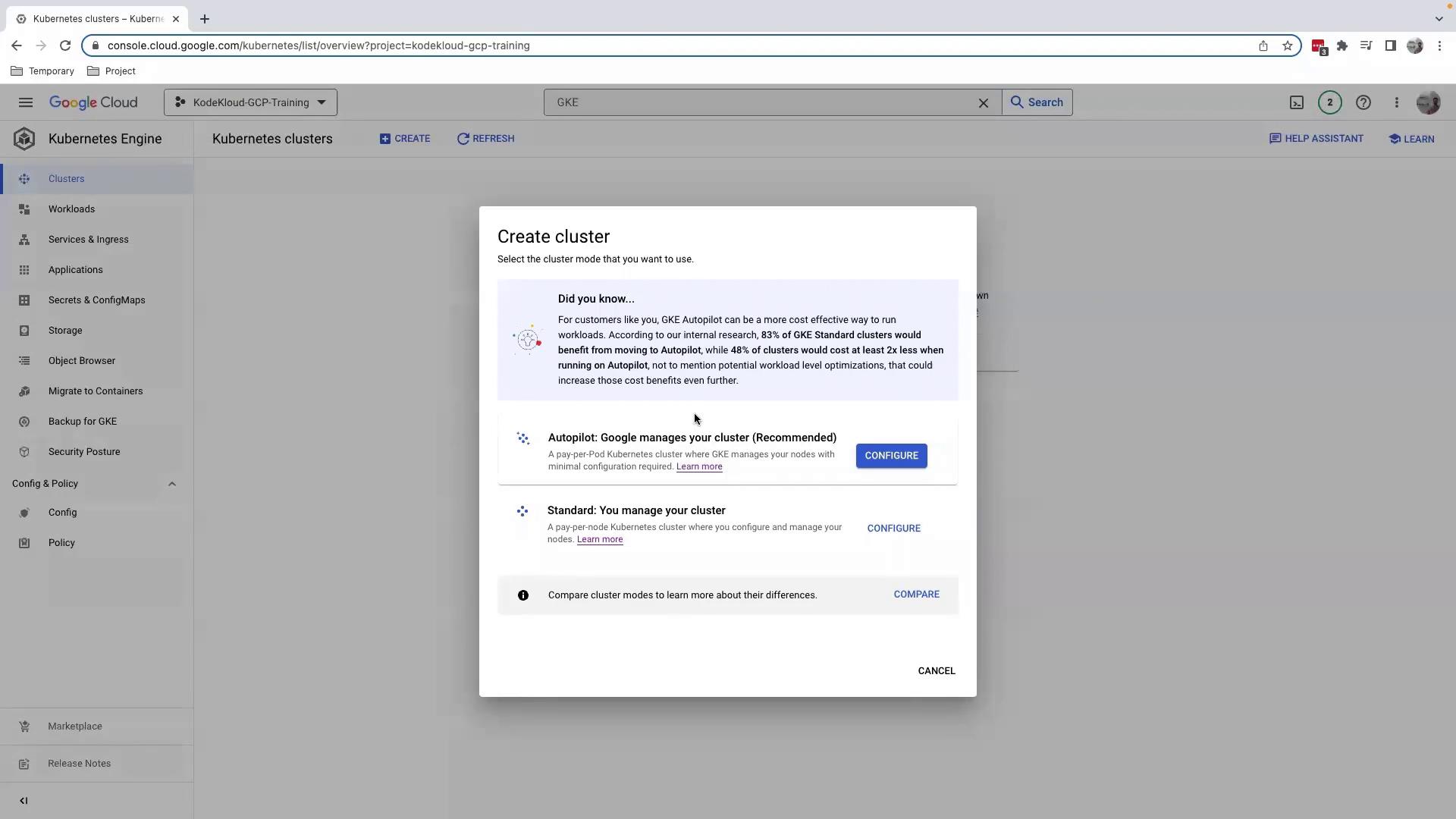
| Cluster Mode | Management Responsibility | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Autopilot | GCP manages nodes, upgrades, and scaling | Minimal ops overhead and quick start |
| Standard | You manage node pools, upgrades, and autoscaling | Custom machine types & security |
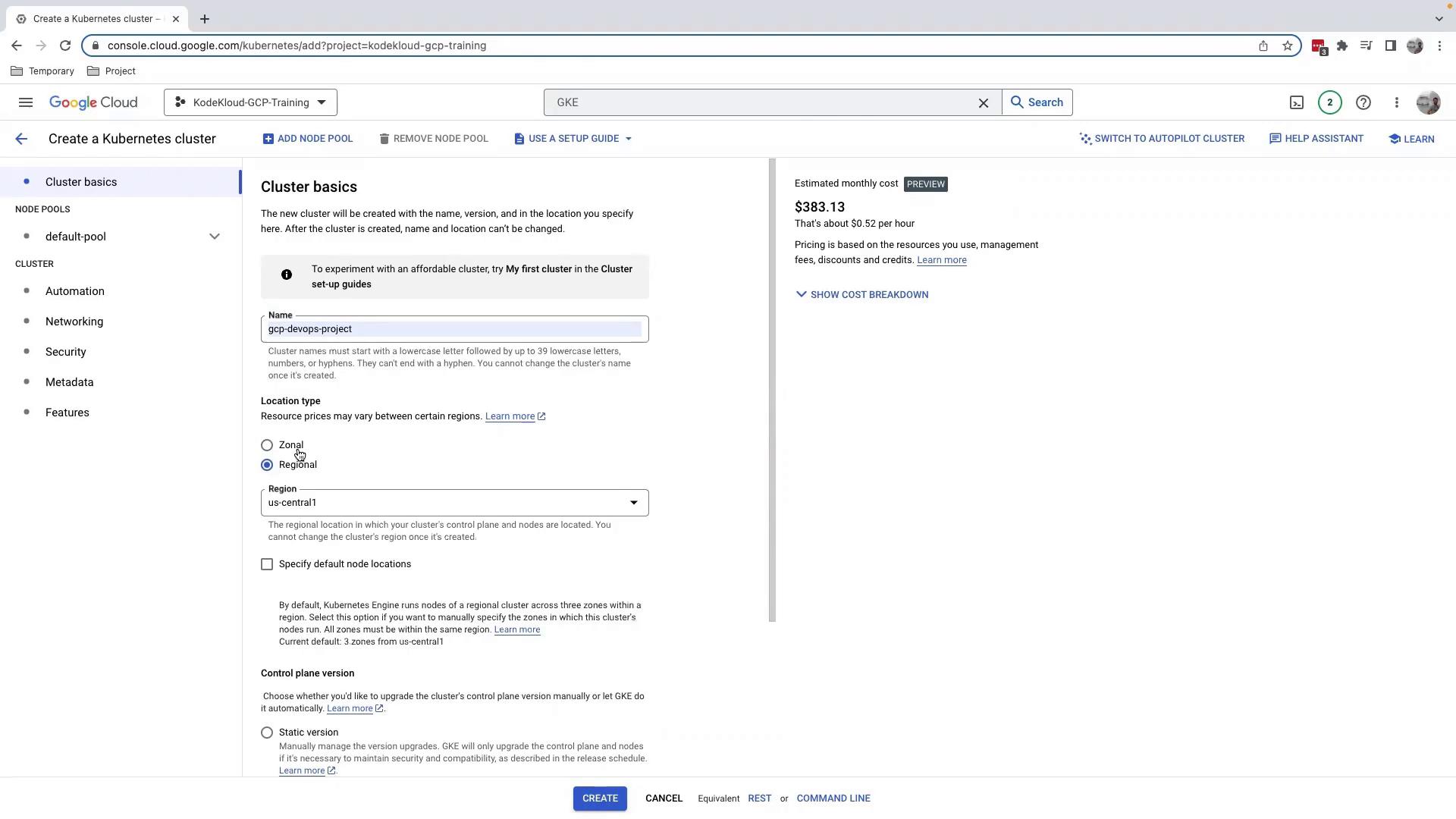
3. Configure Your Standard Cluster
- Name your cluster (e.g.,
gcp-devops-project). - Choose a Location type:
- Regional spans multiple zones.
- Zonal resides in a single zone (we’ll use Zonal here).
3.1 Node Pools
A node pool is a set of VM instances with the same configuration. By default, you get one node pool—expand Node pools to adjust settings.
3.1.1 Select Image Type
Under Nodes, choose your node image: Container-Optimized OS, Ubuntu, or Windows. We’ll keep the default.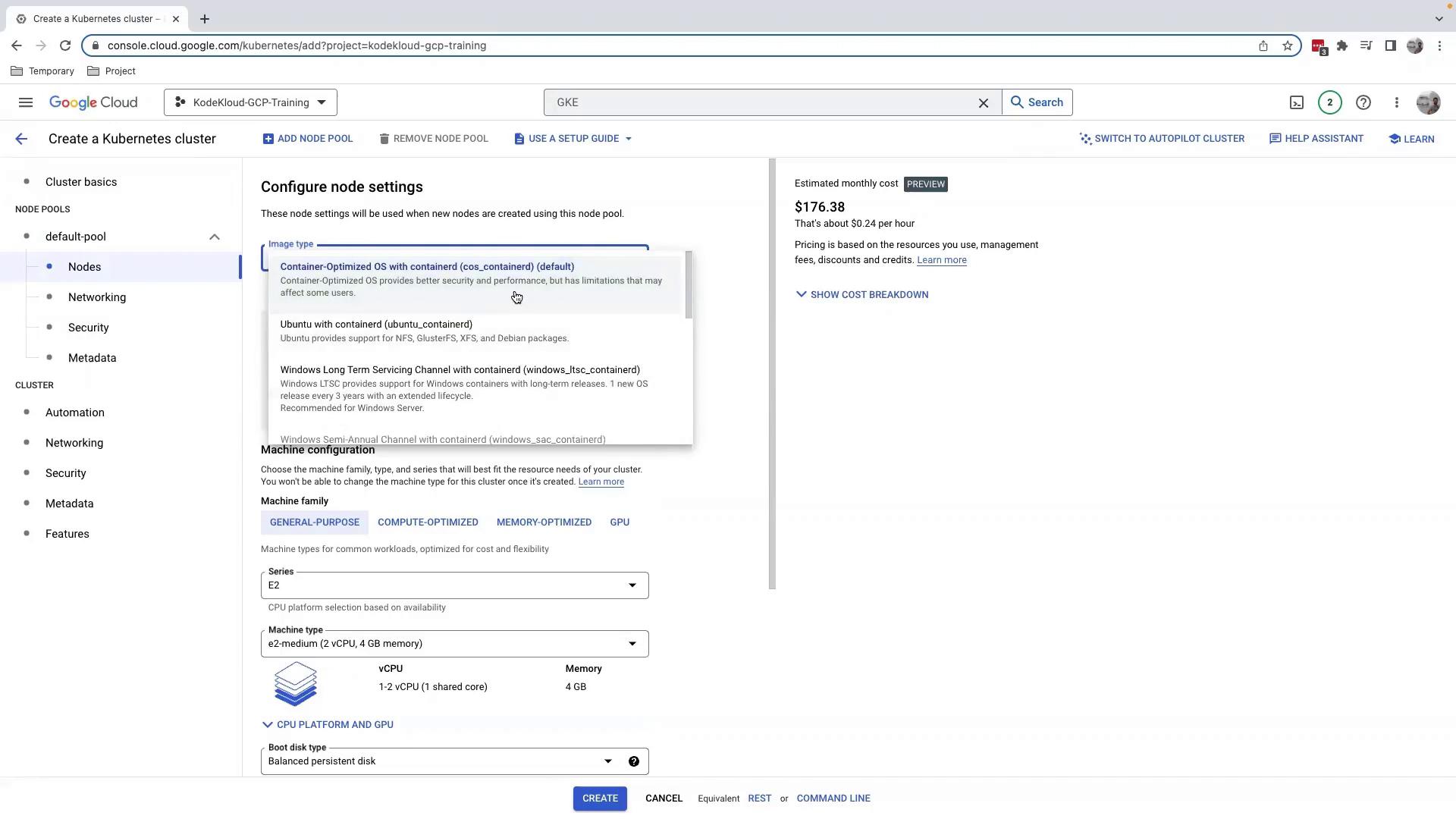
3.1.2 Machine Type & Boot Disk
- Machine type defaults to
e2-medium; adjust CPU and memory if needed. - Reduce the Boot disk to 16 GB for cost savings.
3.2 Networking
Leave the network defaults. Note that Maximum pods per node is set to 110 by default.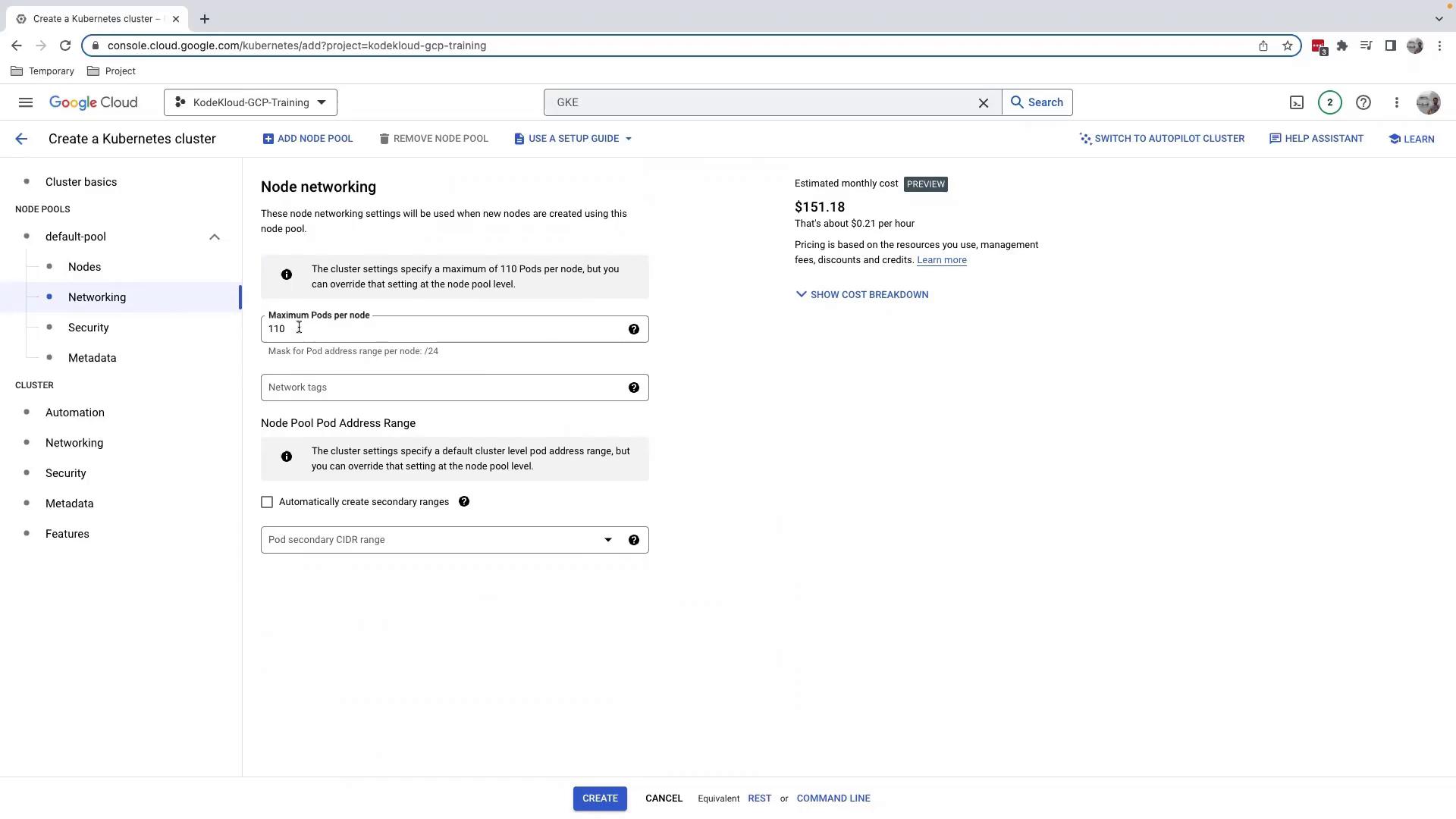
3.3 Security & Metadata
Add Kubernetes labels, taints, or custom GCE instance metadata. Enforce security policies here.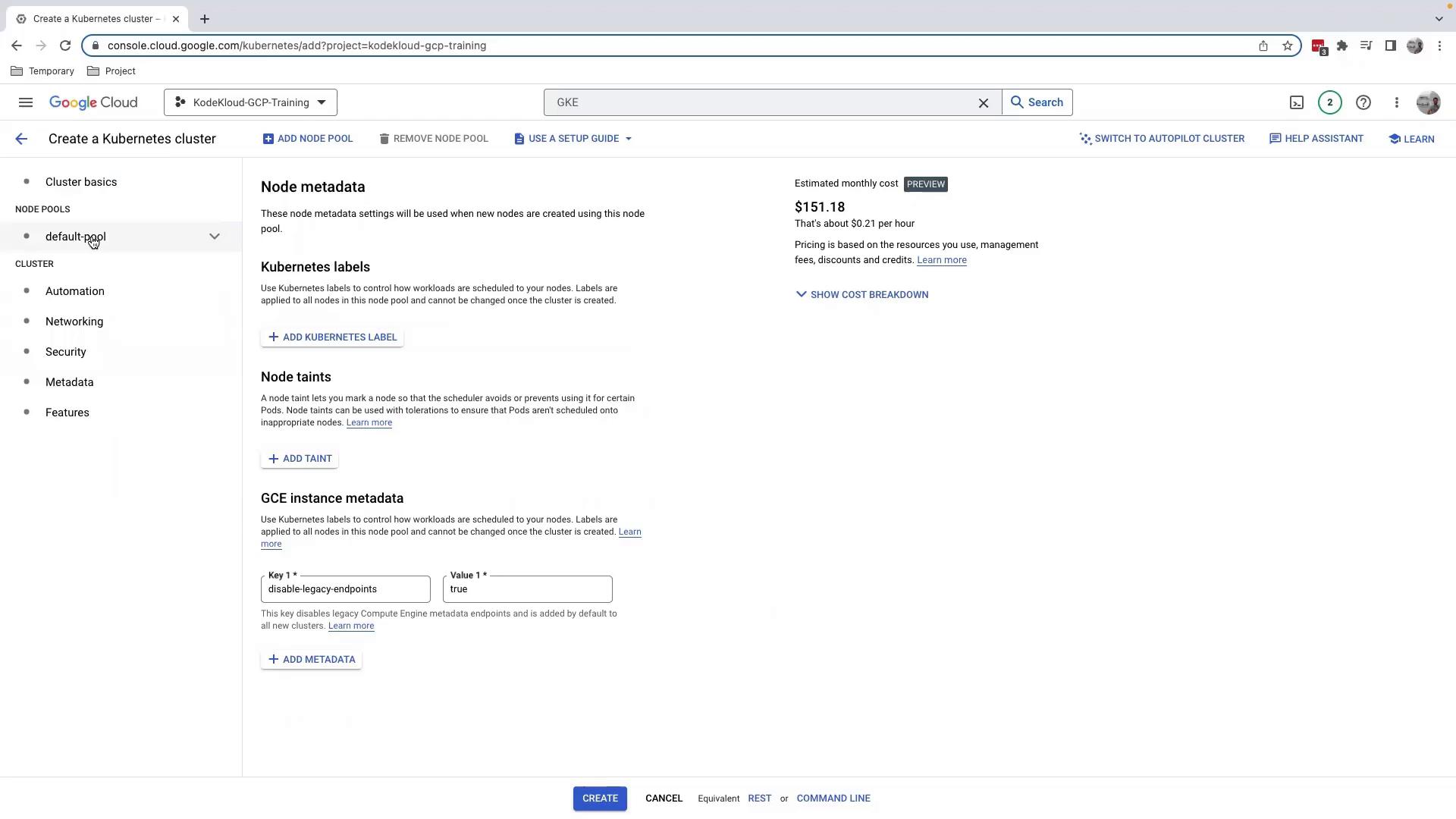
3.4 Autoscaling & Resource Management
Enable Node Pool Autoscaling or the Vertical Pod Autoscaler for dynamic scaling. The balanced policy distributes pods evenly across nodes.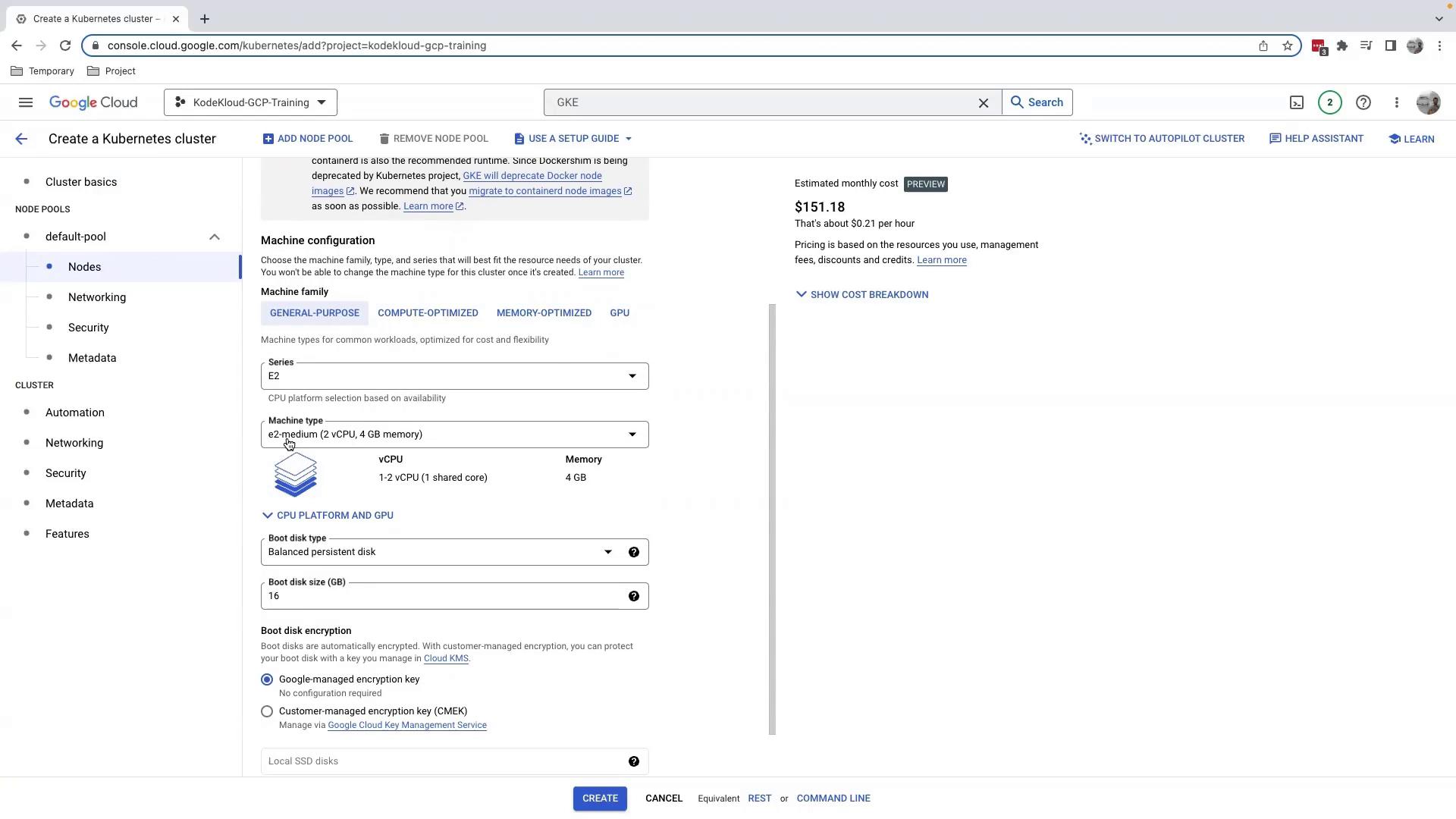
Provisioning GKE clusters incurs charges. Review GKE pricing and delete unused clusters to avoid surprise costs.
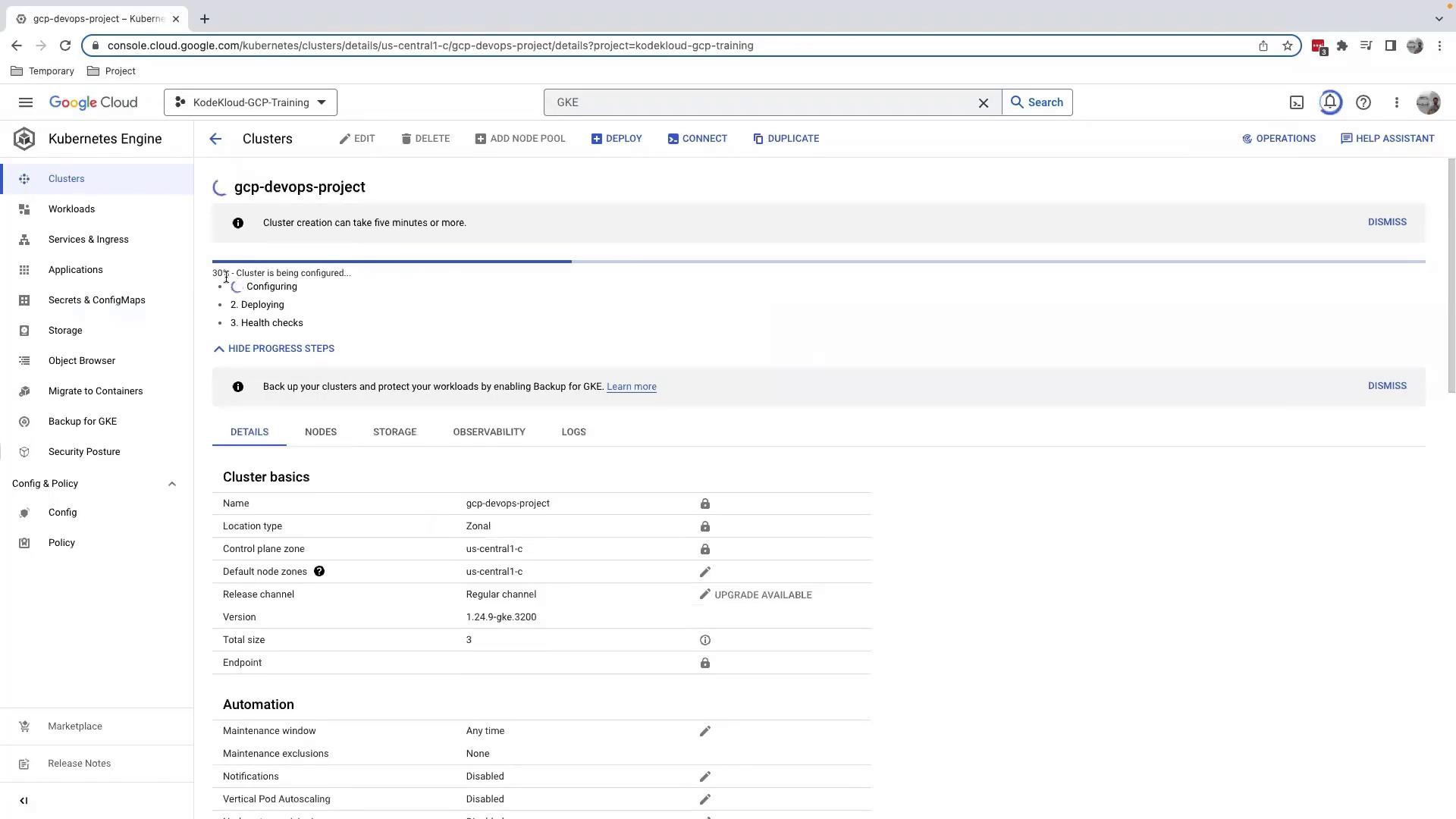
4. Inspect Your Cluster
After provisioning completes (~10 minutes), click your cluster name to open the details page:
- Add Node Pool: Create pools with different machine types or sizes.
- Workloads: View running pods and deployments.
- Maintenance: Set maintenance windows and policies (avoid “Any time” for production).
5. Cleaning Up
To remove your cluster:- Click Delete on the cluster details page.
- Confirm the cluster name.