What Is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes (or “K8s”) provides:- Automated container orchestration for microservices
- Declarative configuration to define desired state
- Self-healing to restart or replace failing containers
- Built-in service discovery and load balancing
- Secret and configuration management outside of code
Key Features
Automated Rollouts & Rollbacks
Kubernetes lets you perform rolling updates with zero downtime. Suppose you have version 4.4.1 of your Docker image running across 2,000 pods. After building and tagging version 4.8, you trigger a rolling update. Kubernetes gradually replaces the old pods, monitors health checks, and ensures continuity. If a critical bug appears in 4.8, a single rollback command reverts your deployment back to 4.4.1—fast and reliable.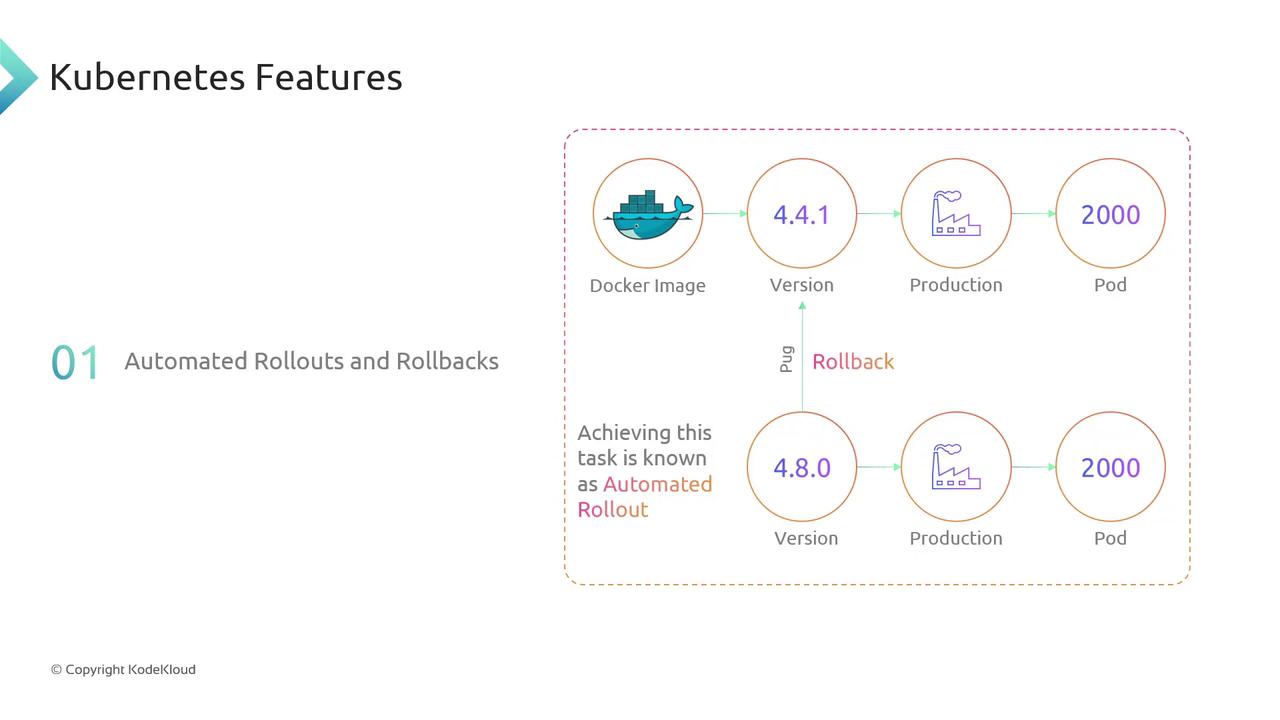
Self-Healing, Service Discovery & Load Balancing, and Security
- Self-Healing: Continuously monitors pod health. Crashed containers are automatically restarted or replaced.
- Service Discovery & Load Balancing: Kubernetes DNS and Services route traffic evenly across healthy pods.
- Security & Configuration Management: Use Secrets and ConfigMaps to store sensitive credentials and application configuration separately from your images.
Deployment Options
Kubernetes can be installed and managed in multiple environments:
Managed services free you from infrastructure maintenance, while on-premises clusters let you meet specific compliance or latency requirements.

In this course, we’ll deploy and manage a Kubernetes cluster on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Next Steps on GCP
Now that you’ve reviewed Kubernetes fundamentals, let’s dive into GKE setup:- Create a GKE cluster with
gcloud container clusters create - Configure
kubectlto point to your new cluster - Deploy sample workloads and explore scaling strategies