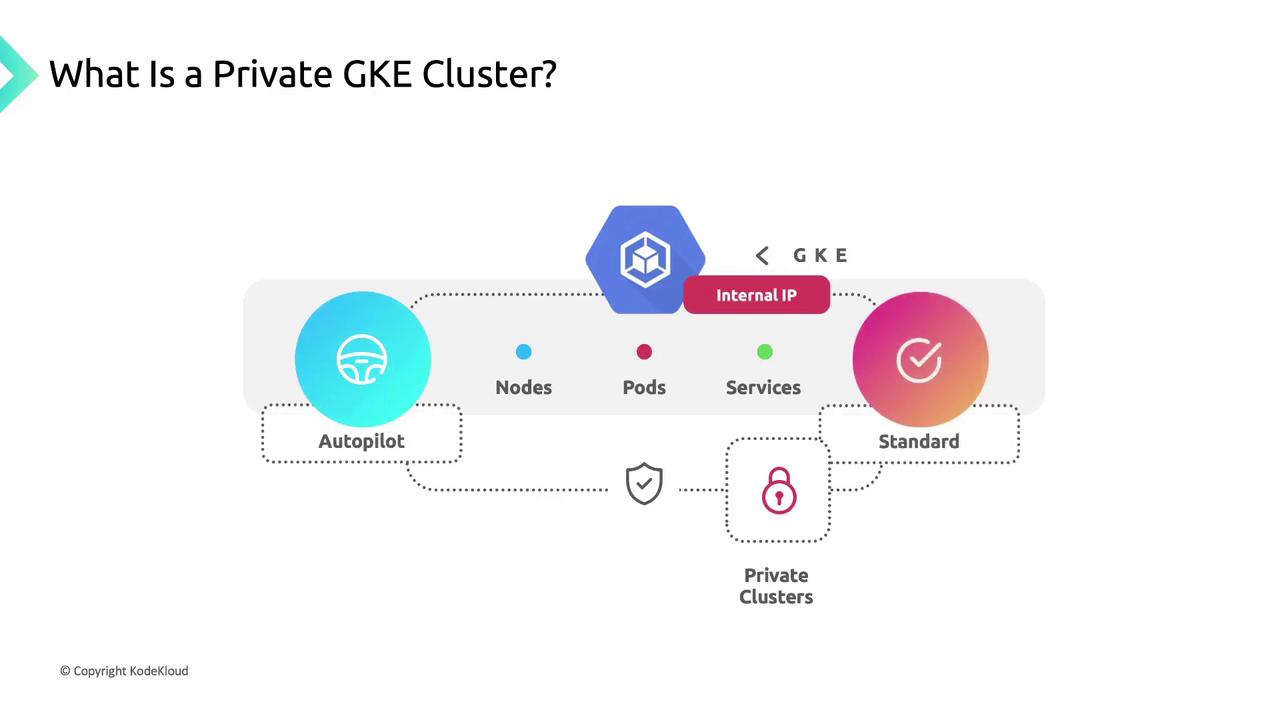
Default Network Isolation
By default, private clusters block all inbound internet traffic to nodes and pods. This isolation ensures your workloads remain hidden from the public internet.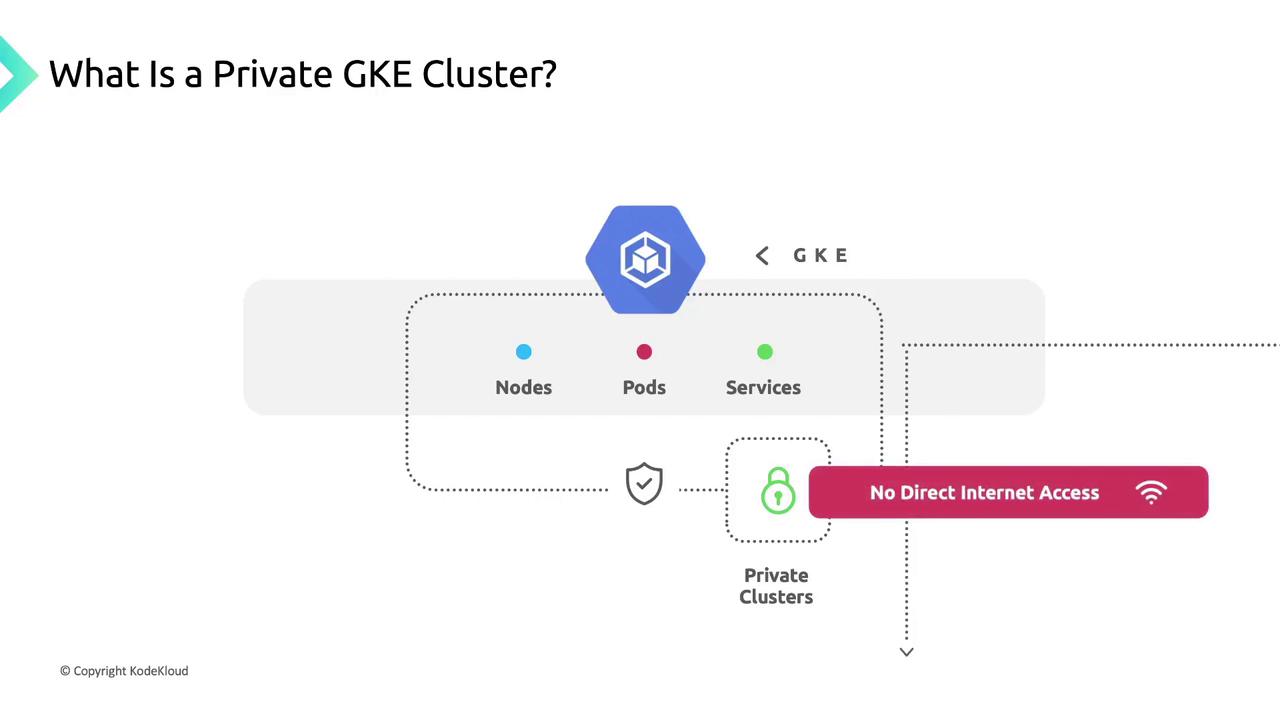
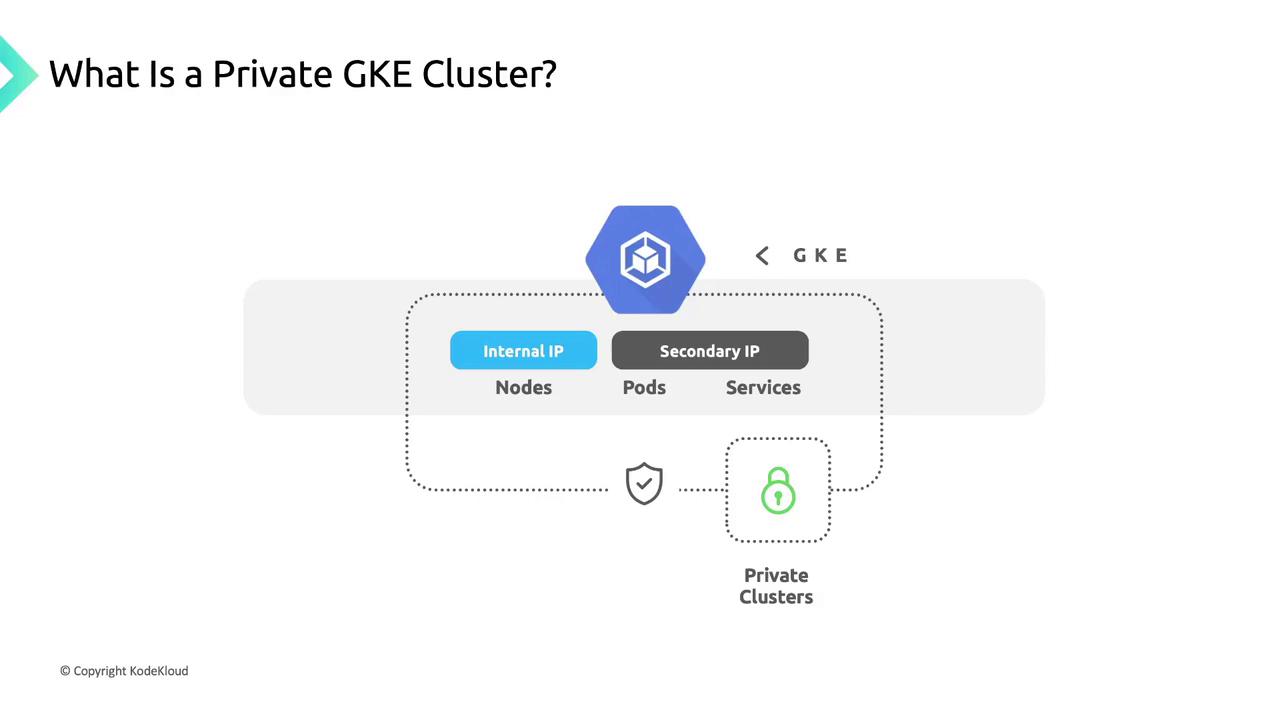
Internal IP Addressing
- Node IPs are allocated from the primary IP range of your chosen VPC subnet.
- Pod & Service IPs use secondary IP ranges within the same subnet.
Controlled Outbound Access with Cloud NAT
When your private cluster needs to reach the internet (for pulling container images or accessing external APIs), configure Cloud NAT. Cloud NAT provides secure, managed outbound connectivity while preserving your nodes’ internal IP addresses.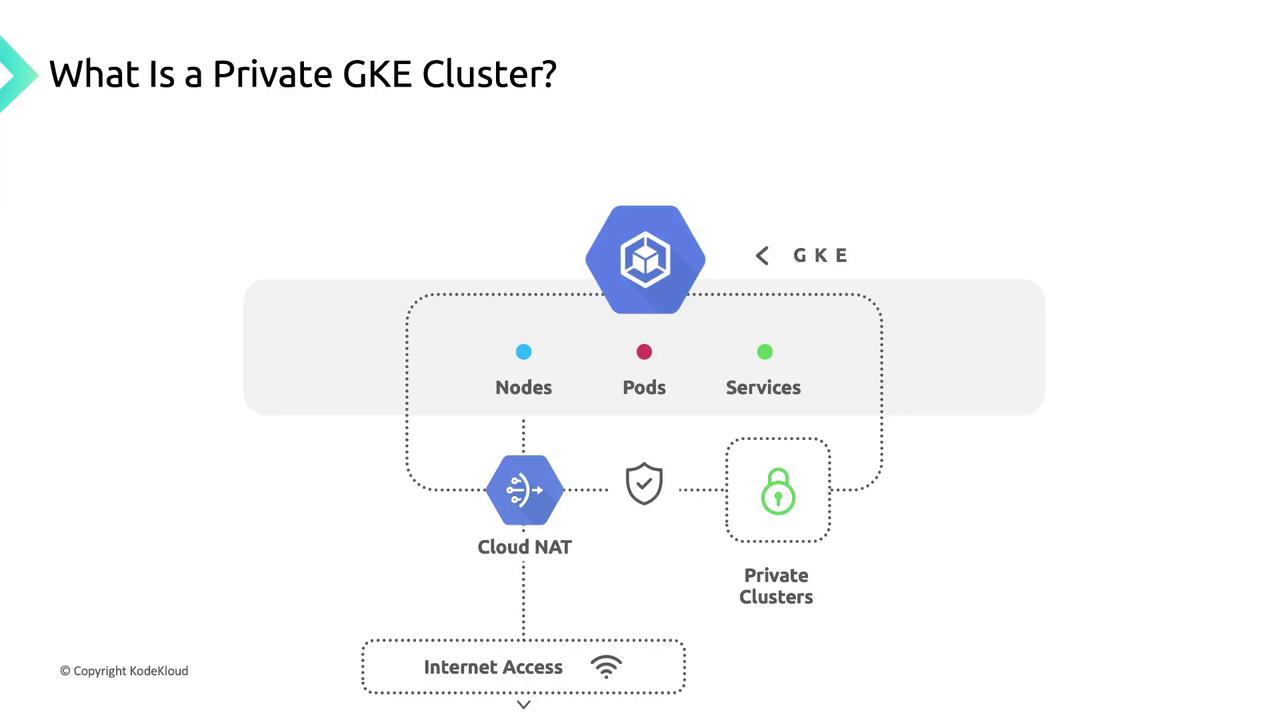
Flexible IP Range Support
As of GKE version 1.14.2, private clusters support multiple internal IP range types:- RFC 1918 private ranges (10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16)
- Privately used public IP blocks

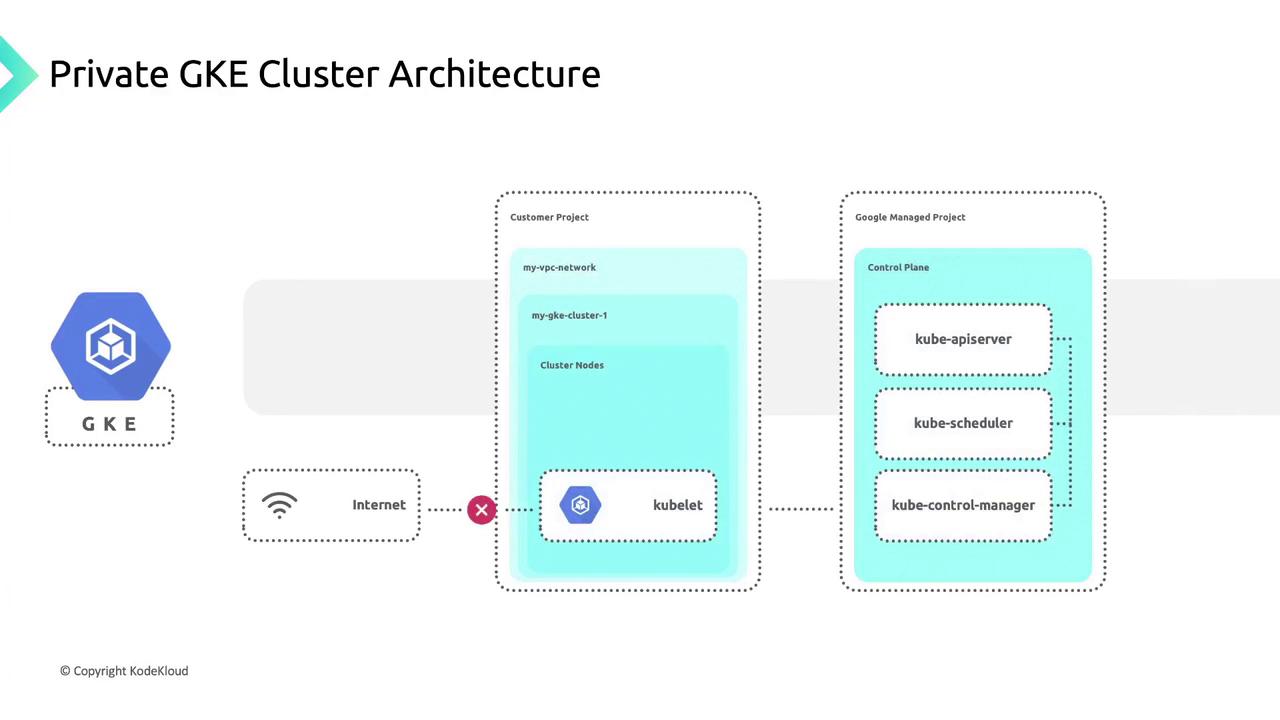
Shared Responsibility Architecture
Private GKE clusters split resources between two projects:| Project Type | Components | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Project | VPC network, cluster nodes, workloads | You secure nodes, containers, and applications. |
| Google-Managed Project | Control plane (API server, etcd, etc.) | Google secures and maintains control plane. |
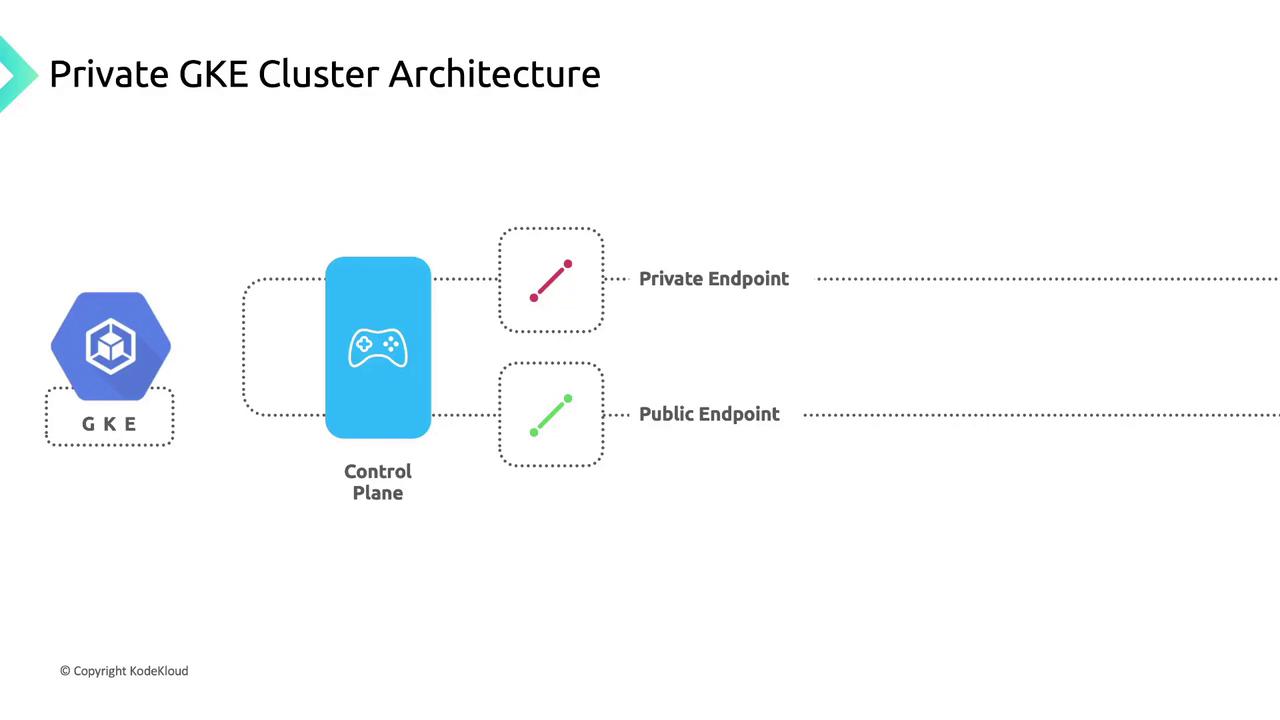
Control Plane Endpoints
The control plane exposes:- A private endpoint reachable only within your VPC network.
- An optional public endpoint, which you can disable for maximum isolation.
Node Connectivity and Isolation
Nodes in a private cluster obtain only internal IP addresses from your subnet. They cannot be accessed directly from the internet, ensuring strong workload isolation.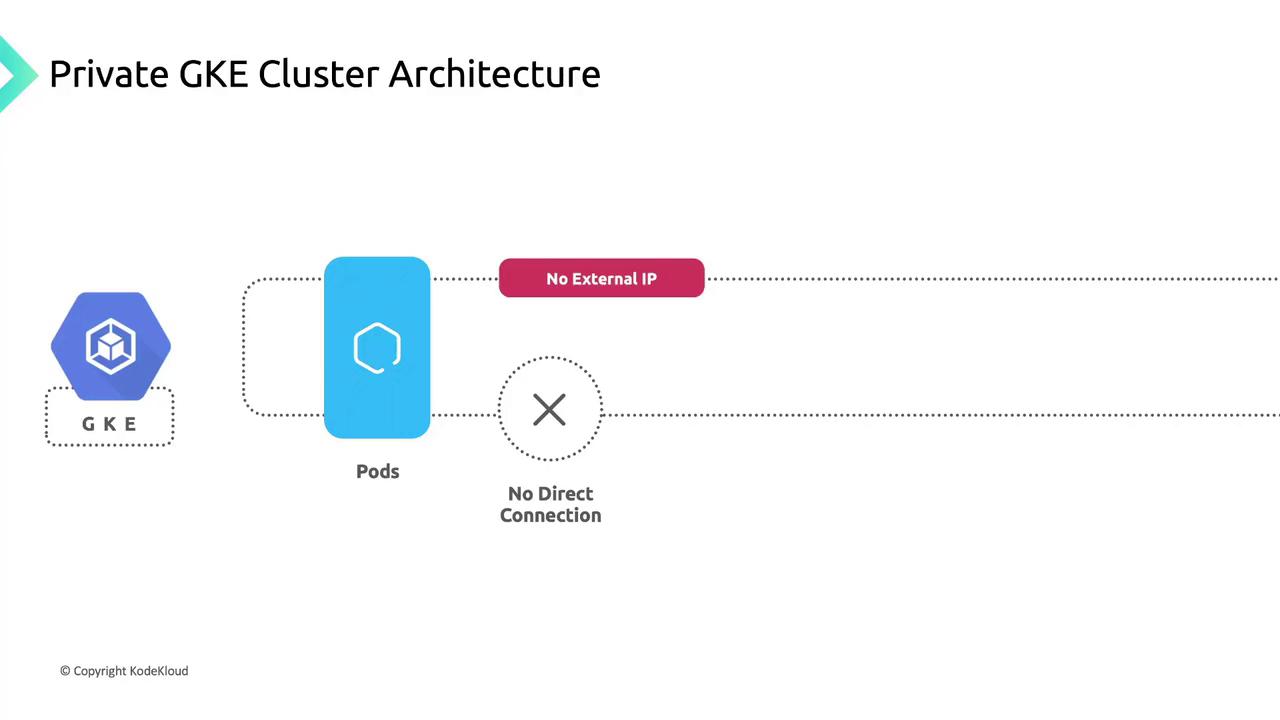
Service Exposure Options
To route external traffic into your private cluster, choose one of these Kubernetes service types:- LoadBalancer Service
Provisions a managed Google Cloud Load Balancer with a public IP. - NodePort Service
Opens a designated port on each node for direct access. - Ingress
Routes HTTP/HTTPS/TCP traffic by host and path rules through a shared load balancer.
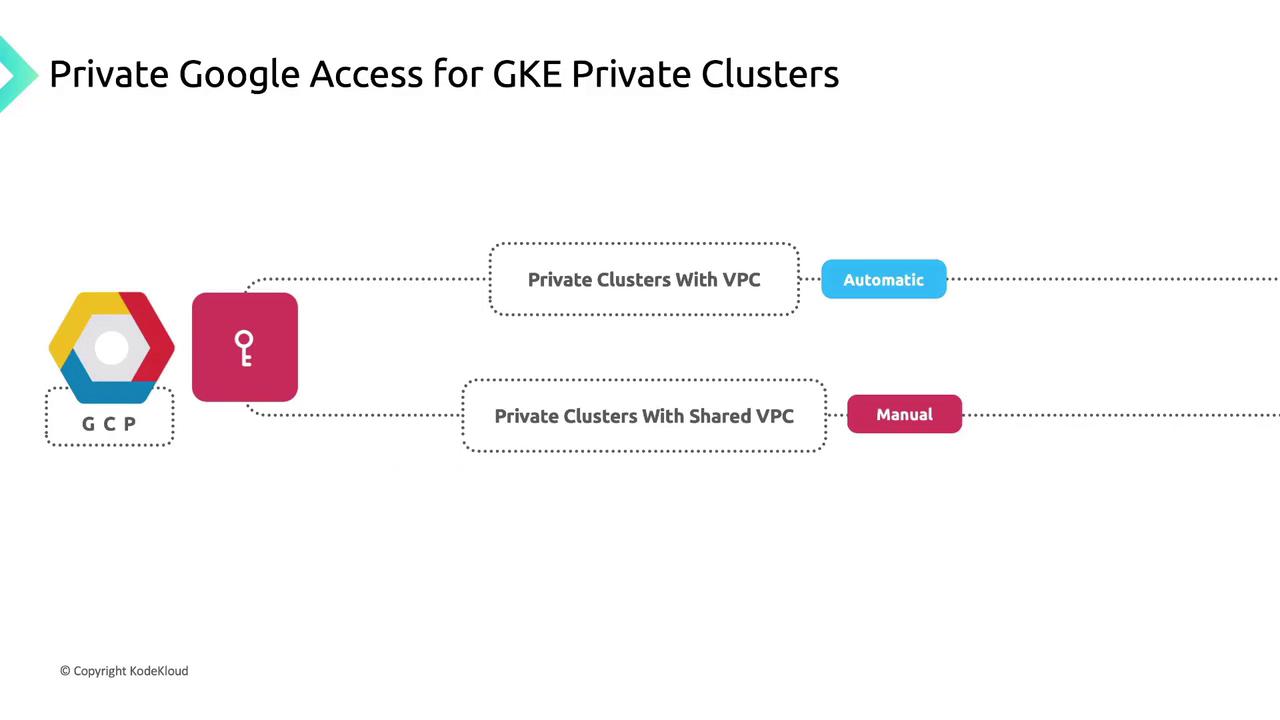
Private Google Access
Private Google Access lets VMs without external IPs call Google APIs and services over Google’s network:- Enabled: Subnet-bound instances can reach Artifact Registry, Cloud Storage, Pub/Sub, Cloud Logging, and more.
- Disabled: Instances are barred from Google APIs and managed services.
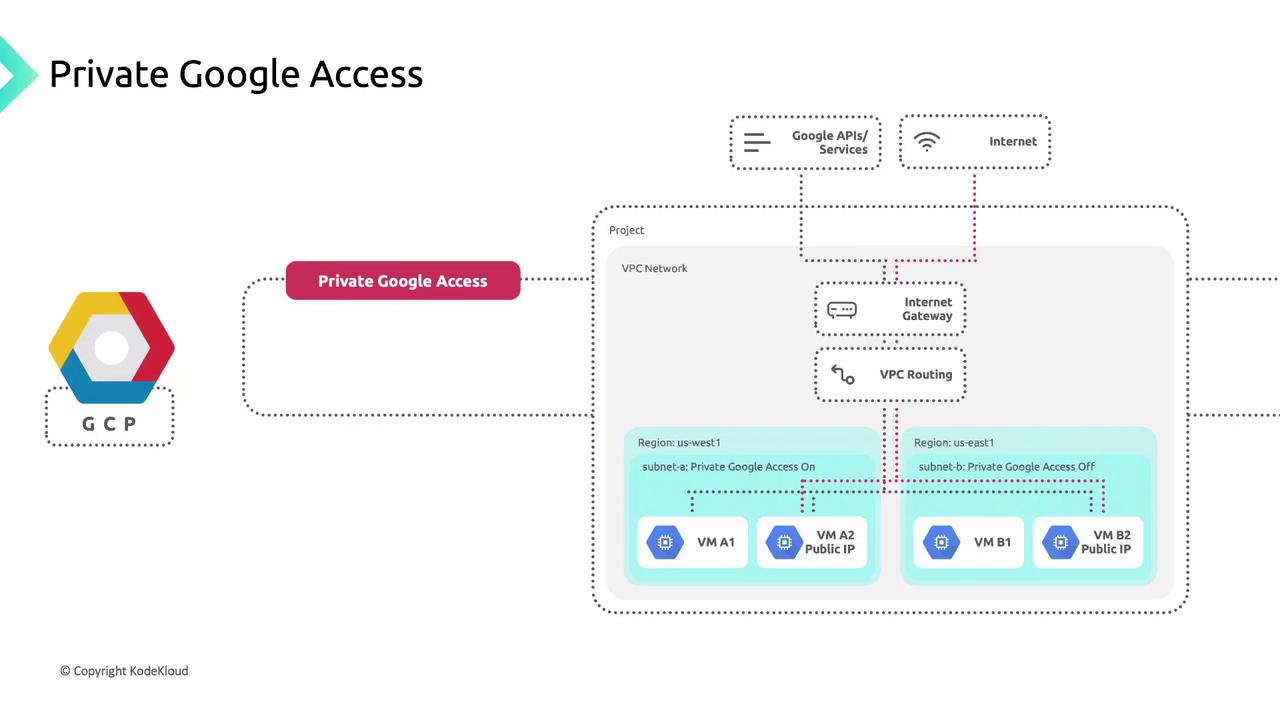
Private Google Access in Shared VPCs
For private clusters in a Shared VPC service project, Private Google Access is not enabled by default. A network administrator or project owner in the host project must manually enable it on each relevant subnet.