package-lock.json to invalidate and refresh the NPM cache whenever dependencies change. By incorporating hashFiles('package-lock.json') into your cache key, you ensure that outdated artifacts aren’t reused and that a fresh cache is stored after updates.
Initial Cache Setup
Assume your repository includes a workflow that cachesnode_modules based on the lockfile’s hash. Here’s the original package.json:
package-lock.json changes.
Adding a New Dependency
When you introduce a new package, the lockfile hash changes, triggering a cache miss:package.json dependencies look like:
package-lock.json is updated, producing a new hash.
Using
npm install --save updates both package.json and package-lock.json, ensuring the cache key changes automatically.Workflow Configuration
Include these steps in your.github/workflows/ci.yml:
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Node.js | uses: actions/setup-node@v3 | Installs Node.js for the specified version. |
| Cache NPM dependencies | uses: actions/cache@v3 | Caches node_modules keyed by the lockfile’s hash. |
| Install Dependencies | run: npm install | Restores or installs NPM packages. |
hashFiles('package-lock.json'), any modification to your lockfile results in a cache miss.
Triggering the Workflow and Cache Invalidation
Once you push the updated lockfile:- Cache NPM dependencies: No existing cache matches the new key, so the step falls back to installing from npm.
- Install Dependencies:
npm installpopulatesnode_modules. - Upload Cache: One job uploads the newly generated cache.
- Parallel Jobs: Other jobs may see “Failed to save cache” if they attempt an upload after the first; this is expected.
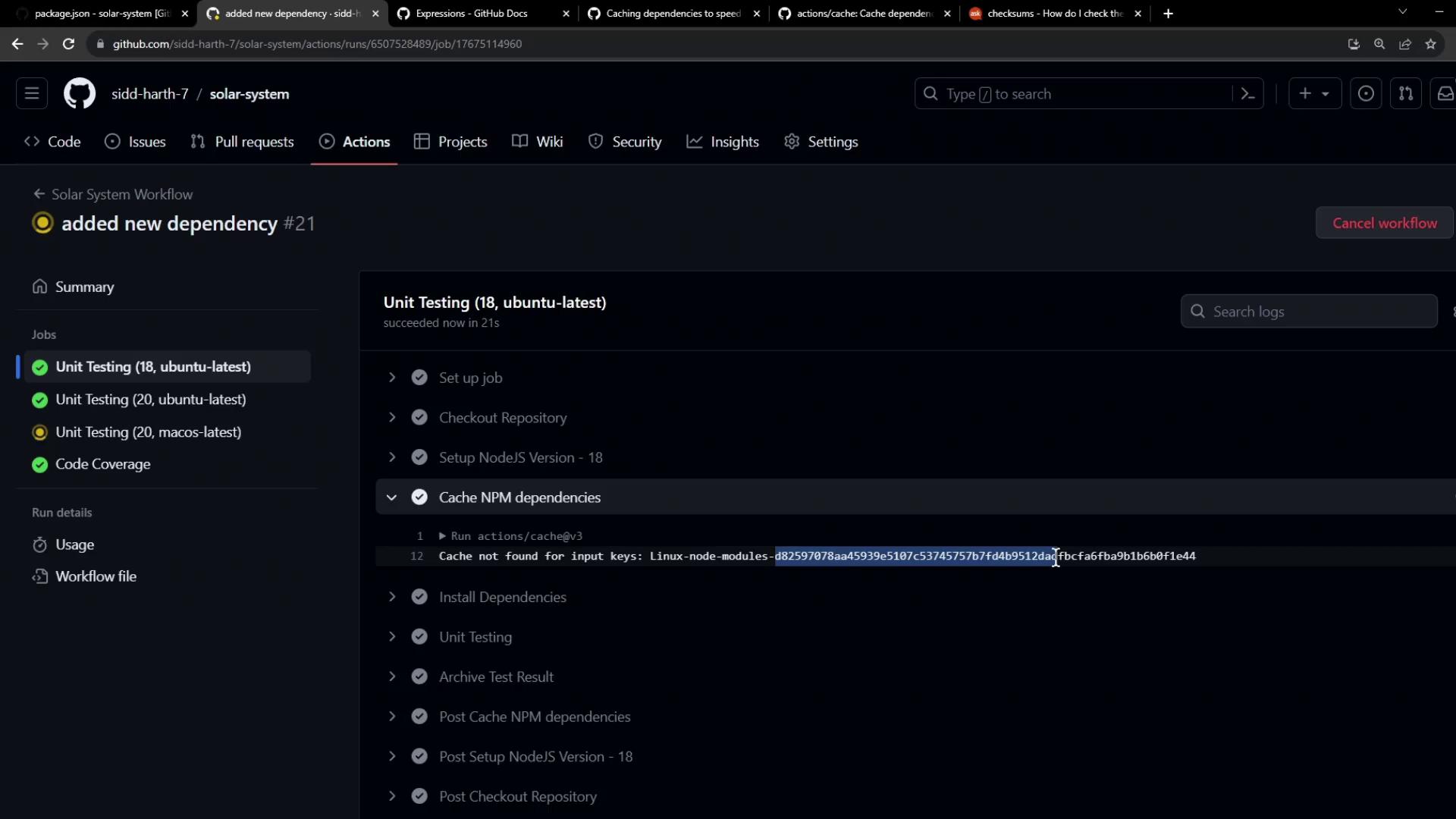
In parallel builds, only the first job to upload the cache succeeds. Subsequent jobs will skip uploading the same key.
Inspecting Cache Behavior Across Jobs
During a run, you might see logs like: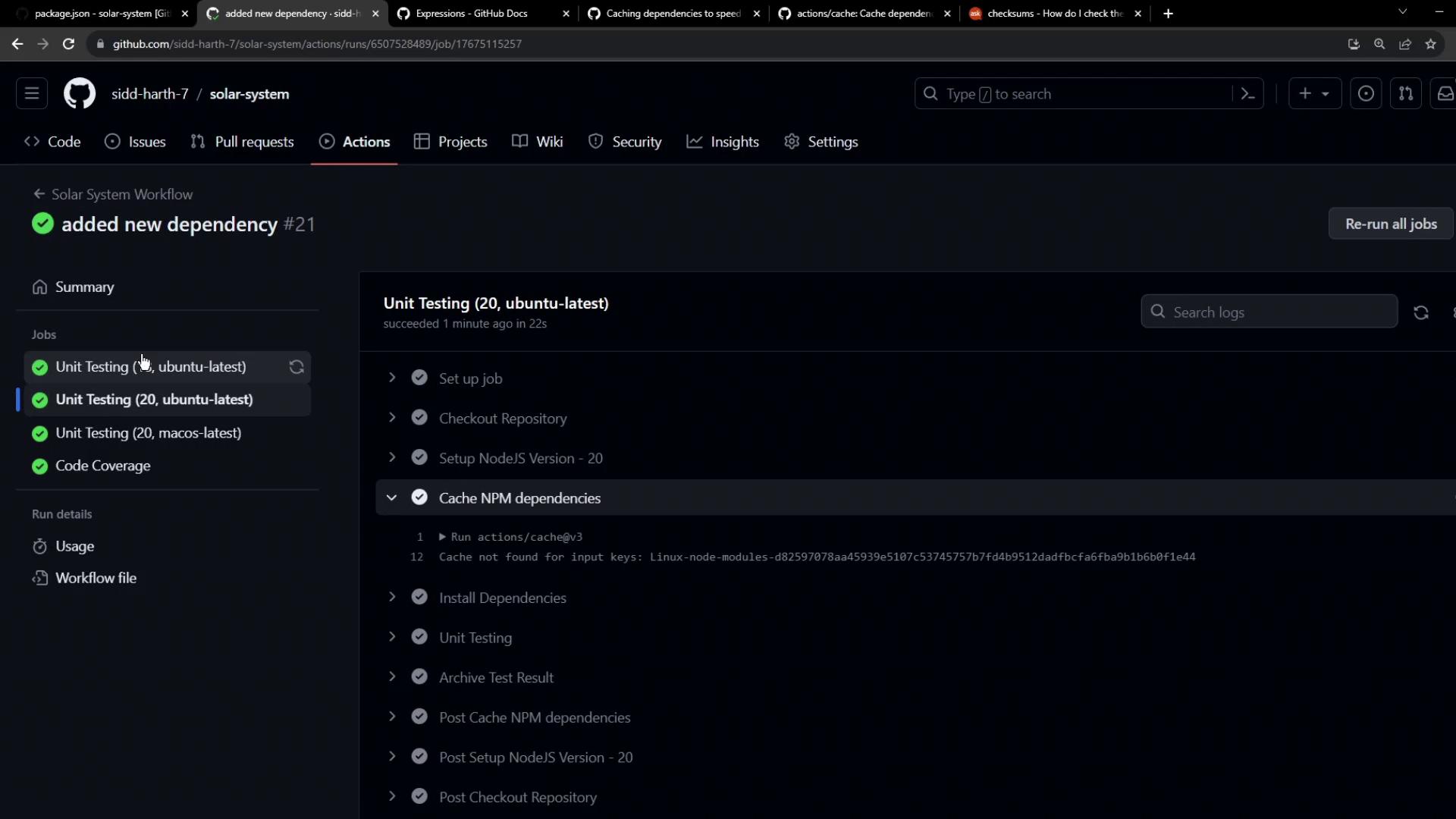
Viewing Saved Caches
You can review cache details in the GitHub Actions UI under the workflow run or by examining the tar logs. Example: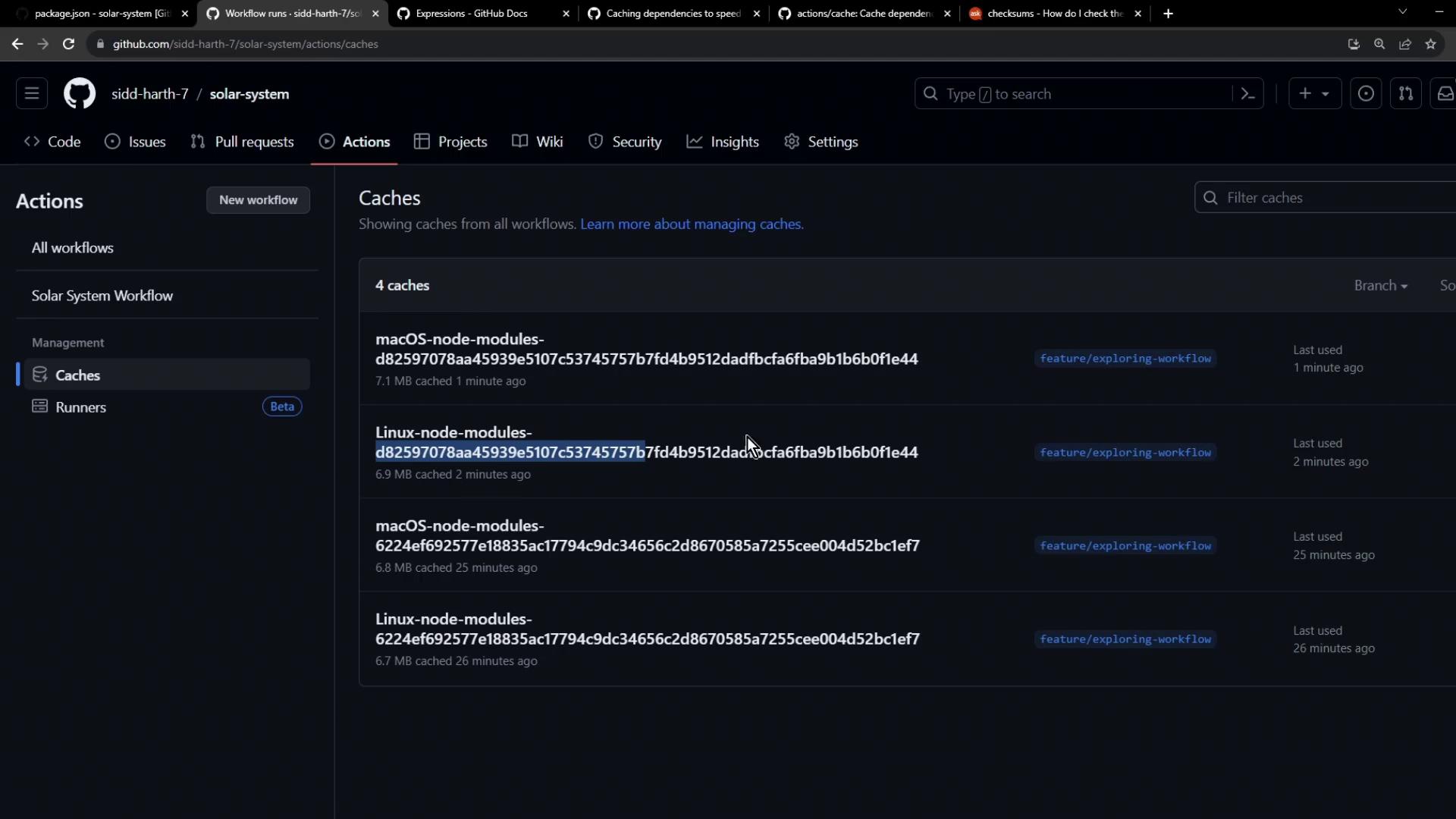
Conclusion
By hashingpackage-lock.json in your cache key:
- Each dependency update generates a new hash.
- The cache restore step misses on outdated keys.
- Dependencies are installed from scratch.
- A fresh cache is uploaded for subsequent runs.