In this lesson, we’ll explore how to speed up GitHub Actions workflows by caching Node.js dependencies across jobs. Caching reduces redundant installs, lowers CI time, and saves costs.
Without caching, each job installs dependencies from scratch, adding significant overhead. For example, our previous workflow (~59 s total):
Job Duration Code coverage 21 s Unit tests (Ubuntu) 19 s Unit tests (macOS) 45 s Unit tests (Windows) 18 s Total 59 s
Inspecting the macOS unit test job:
Setup Node.js : ~20 snpm install : ~15 s
Especially in larger projects, fresh installs significantly inflate build times. Caching is the solution.
How Caching Works in GitHub Actions GitHub Actions provides the actions/cache action to store and restore files between workflow runs.
key : Unique cache identifier (often includes OS & file hash).path : Directories or files to cache.
The action checks for a cache hit; on miss, it runs normally and stores the cache for future runs.
Use a strong cache key (e.g., ${{ runner.os }}-deps-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }}) to invalidate the cache automatically when dependencies change.
Ensure you have:
A lockfile (package-lock.json or yarn.lock) at the repo root.
actions/cache@v3 available in your workflow.
A minimal cache example:
- name : Restore cache id : cache-restore uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : | path/to/dependencies some/other/dependencies key : ${{ runner.os }}-my-deps-${{ hashFiles('lockfile.json') }} - name : Save cache uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : | path/to/dependencies some/other/dependencies key : ${{ steps.cache-restore.outputs.cache-primary-key }}
Implementing Caching in Your Workflow Add cache steps before npm install in both unit-testing and code-coverage jobs. We use ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }} as the key.
Unit Testing Job with Cache jobs : unit-testing : name : Unit Testing strategy : matrix : nodejs_version : [ 18 , 20 ] operating_system : [ ubuntu-latest , macos-latest ] exclude : - nodejs_version : 18 operating_system : macos-latest runs-on : ${{ matrix.operating_system }} steps : - name : Checkout Repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Setup Node.js ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} uses : actions/setup-node@v3 with : node-version : ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} - name : Cache NPM dependencies uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : node_modules key : ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }} - name : Install Dependencies run : npm install - name : Run Unit Tests run : npm test - name : Archive Test Results if : always() uses : actions/upload-artifact@v3 with : name : mocha-test-results path : test-results.xml
path : node_modules directory.key : Includes OS and lockfile hash for automatic invalidation.
Code Coverage Job with Cache jobs : code-coverage : name : Code Coverage runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - name : Checkout Repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Setup Node.js 18 uses : actions/setup-node@v3 with : node-version : 18 - name : Cache NPM dependencies uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : node_modules key : ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }} - name : Install Dependencies run : npm install - name : Run Coverage continue-on-error : true run : npm run coverage - name : Archive Coverage Report uses : actions/upload-artifact@v3 with : name : coverage-report path : test-results.xml
Commit and push to trigger the workflow.
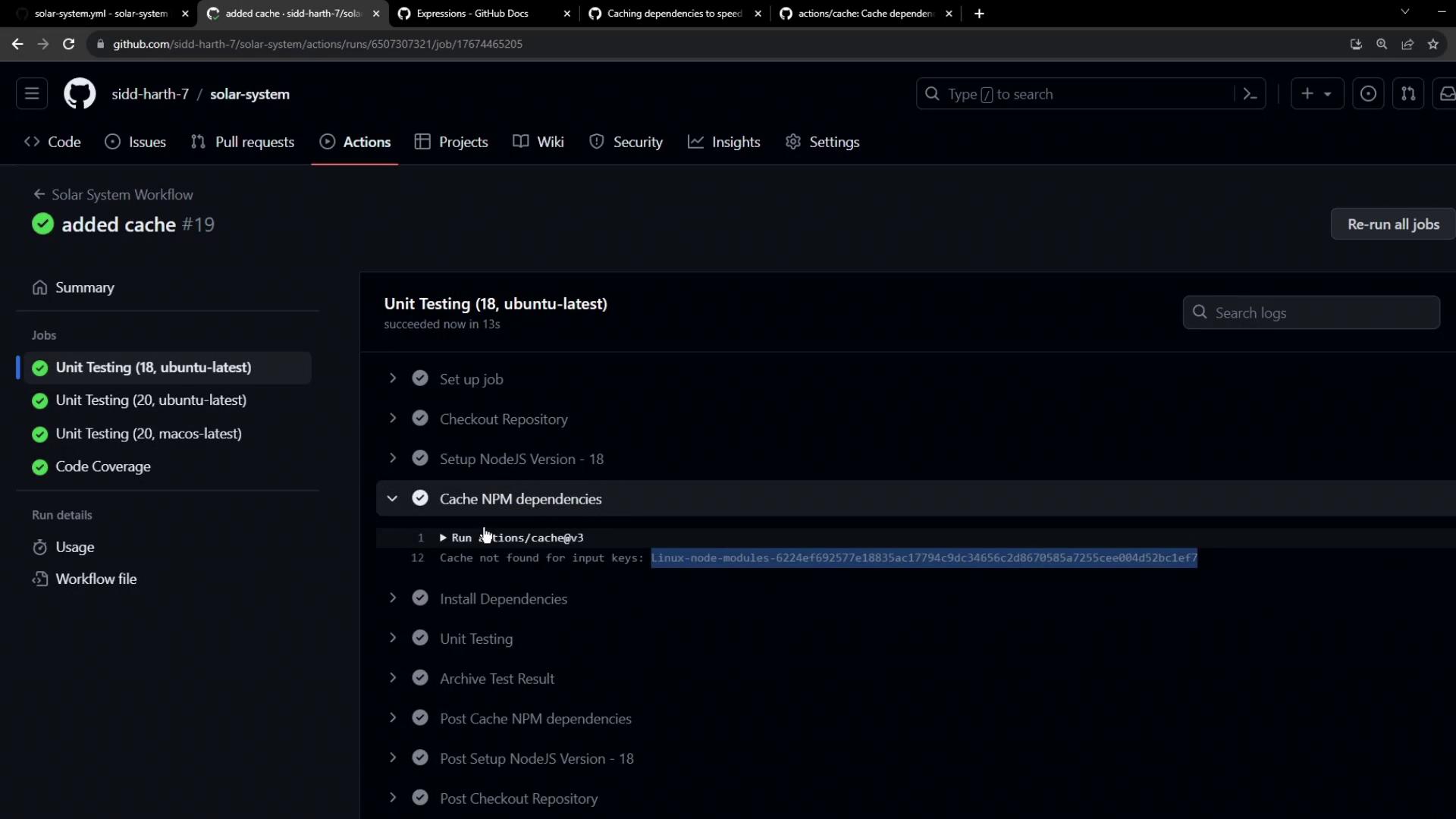
Verifying Cache Effectiveness On the first run , cache miss:
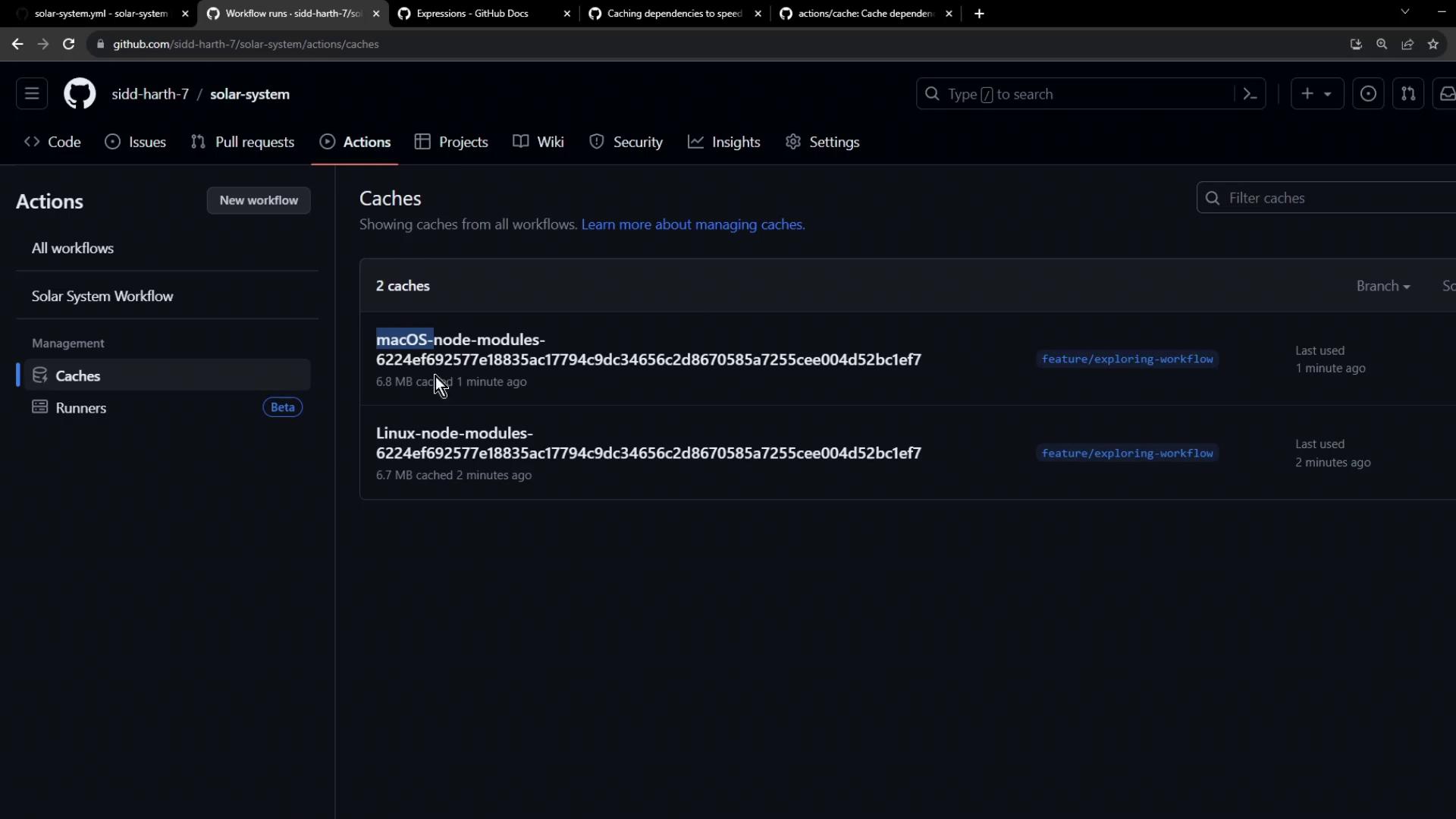
After completion, caches appear in the repository settings:
On the second run , cache hit reduces npm install to ~1 s:
Cache restored successfully Cache restored from key: Linux-node-modules-6224ef692577e18835ac17794c9dc34656c2d867685a7255cee004d52b1e7 $ npm install up to date, audited 366 packages in 1s
Cache restored successfully Cache restored from key: macOS-node-modules-6224ef69257718835ac17794g9dc34656785a7255cee00452bc1ef7 $ npm install up to date, audited 366 packages in 1s
Next Steps: Invalidate Cache on Dependency Changes To test cache invalidation, update your package.json dependencies and re-run the workflow. The hash changes, creating a fresh cache.
Avoid overly broad cache paths to prevent storing unwanted files. Restrict the path to necessary directories only.
Links and References