GitHub Actions Certification
Continuous Integration with GitHub Actions
Using if expressions with Step contexts
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use if-expressions together with the steps context to ensure your test artifacts are always archived—even when a job fails. By assigning IDs to steps and leveraging status functions, you can control exactly when uploads occur, making debugging and reporting much easier.
1. Initial Workflow Configuration
Here’s our starting Unit Testing job. It runs tests via npm test and then uploads the results:
name: Unit Testing
strategy:
matrix:
nodejs_version: [18, 20]
operating_system: [ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
exclude:
- nodejs_version: 18
operating_system: macos-latest
runs-on: ${{ matrix.operating_system }}
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node.js ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }}
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }}
- name: Install Dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Unit Testing
run: npm test
- name: Archive Test Results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: Mocha-Test-Result
path: test-results.xml
Note
By default, when a step fails, all later steps (including uploads) are skipped.
2. Simulating a Test Failure
To demonstrate, we’ll break one of our tests in app-test.js so that it fails:
// app-test.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const server = require("../app");
const chai = require("chai");
const chaiHttp = require("chai-http");
chai.should();
chai.use(chaiHttp);
describe("Planets API Suite", () => {
describe("Fetching Planet Details", () => {
it("should fetch a planet named Mercury", (done) => {
const payload = { id: 1 };
chai.request(server)
.post("/planet")
.send(payload)
.end((err, res) => {
res.should.have.status(200);
// Intentionally wrong expected value
res.body.should.have.property("name").eql("Mercury_ERROR");
done();
});
});
// ... other tests ...
});
});
After committing, the Unit Testing job fails and the upload step is skipped:
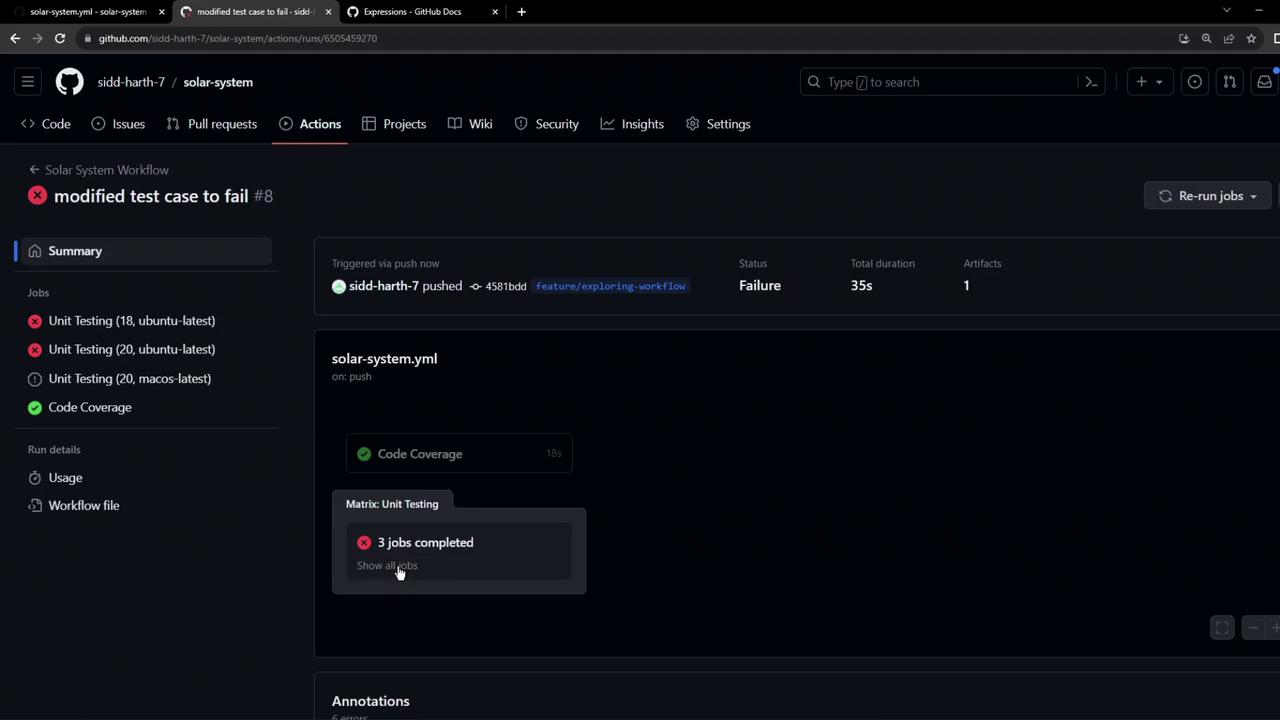
3. Guarding with steps.<id>.outcome
Give your test step an id, then use if to check its outcome:
- name: Unit Testing
id: nodejs-unit-testing
run: npm test
- name: Archive Test Results
if: steps.nodejs-unit-testing.outcome == 'failure' || steps.nodejs-unit-testing.outcome == 'success'
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: Mocha-Test-Result
path: test-results.xml
The steps context provides each step’s outcome property:
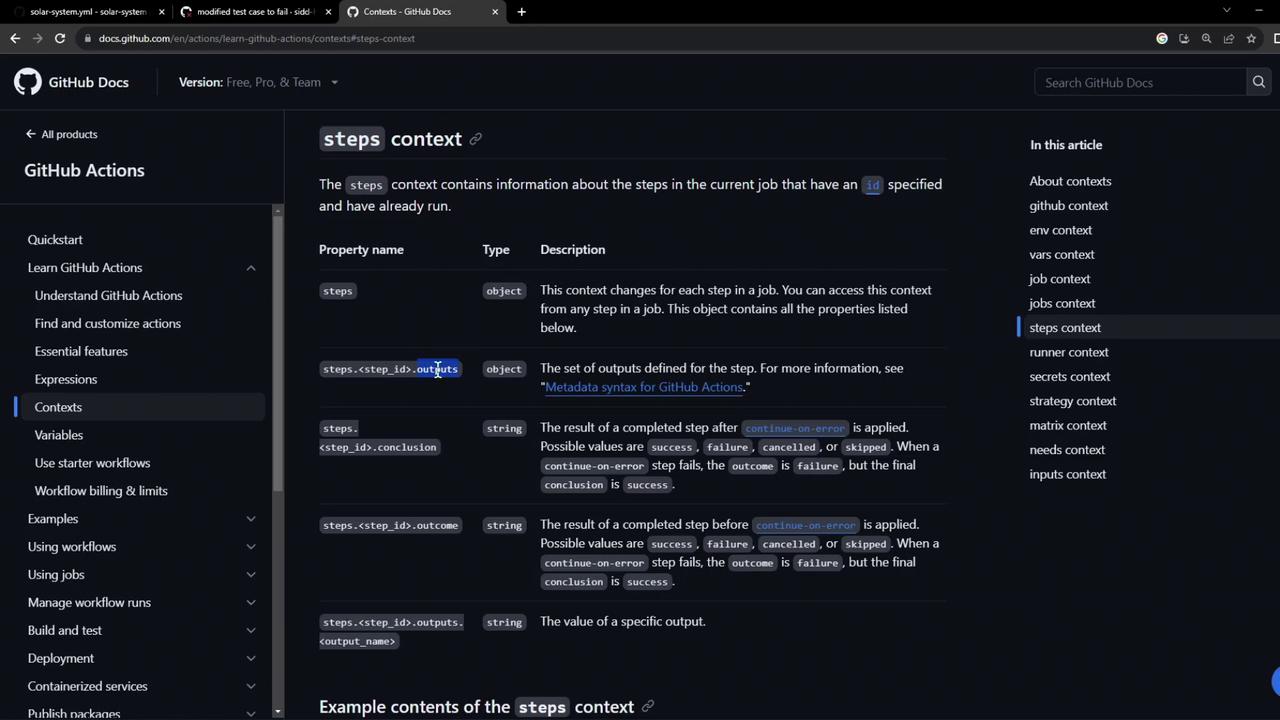
Expressions 101
You can use comparison operators (==, !=, >, <) and functions in expressions to control step execution.
Here’s the official expressions reference:
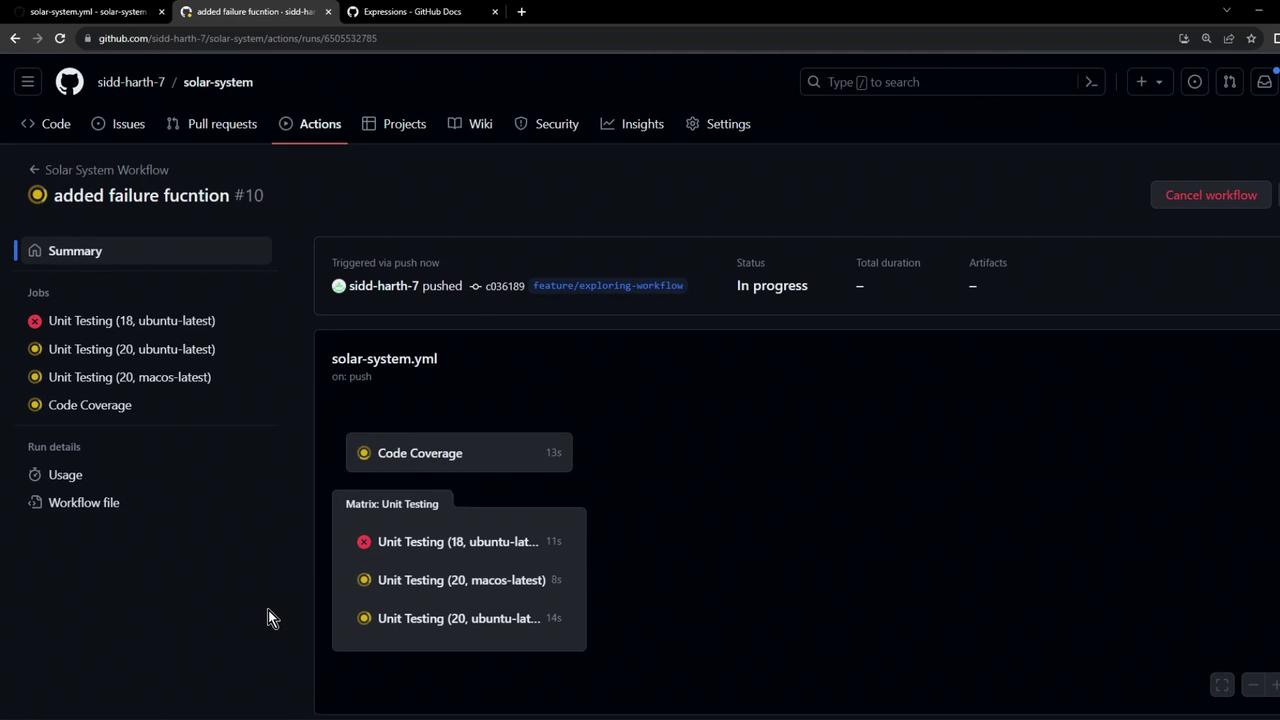
Rerun the workflow, and you’ll see the Archive step execute in all scenarios:
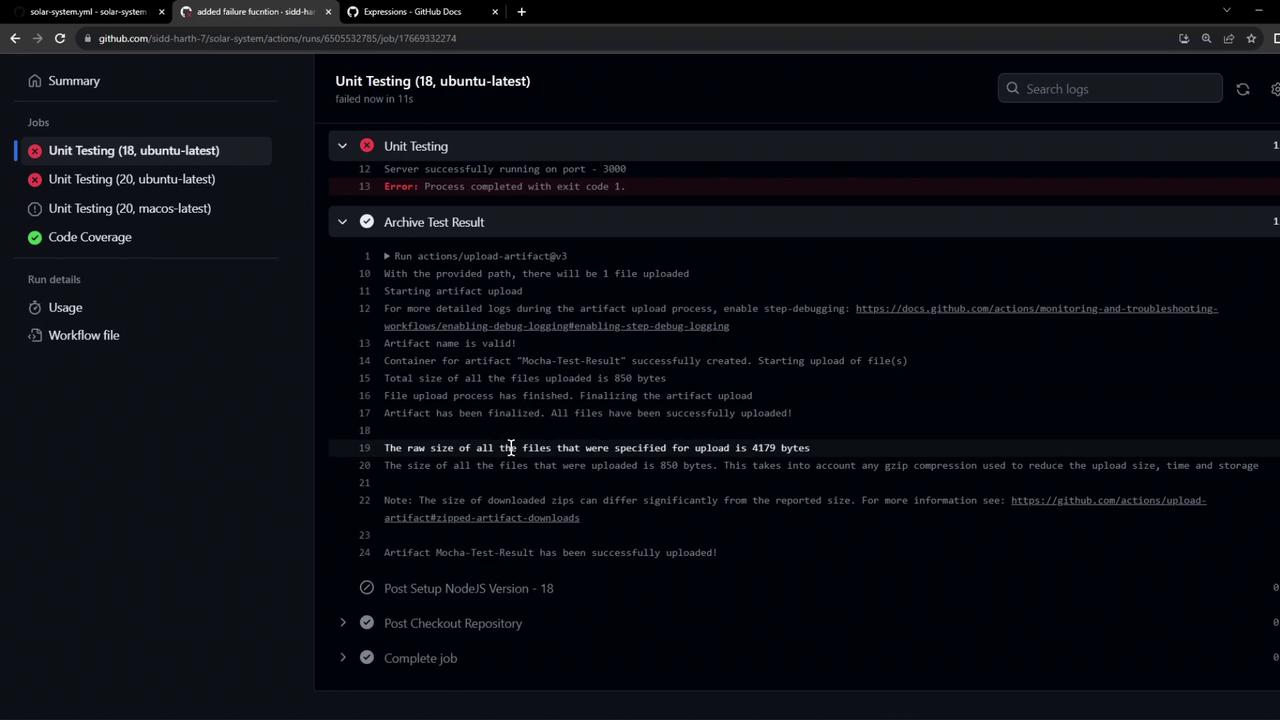
Inspecting the logs confirms the upload ran:
> Solar [email protected] test
> mocha app-test.js --timeout 10000 --reporter mocha-junit-reporter --exit
Server successfully running on port - 3000
Error: Process completed with exit code 1.
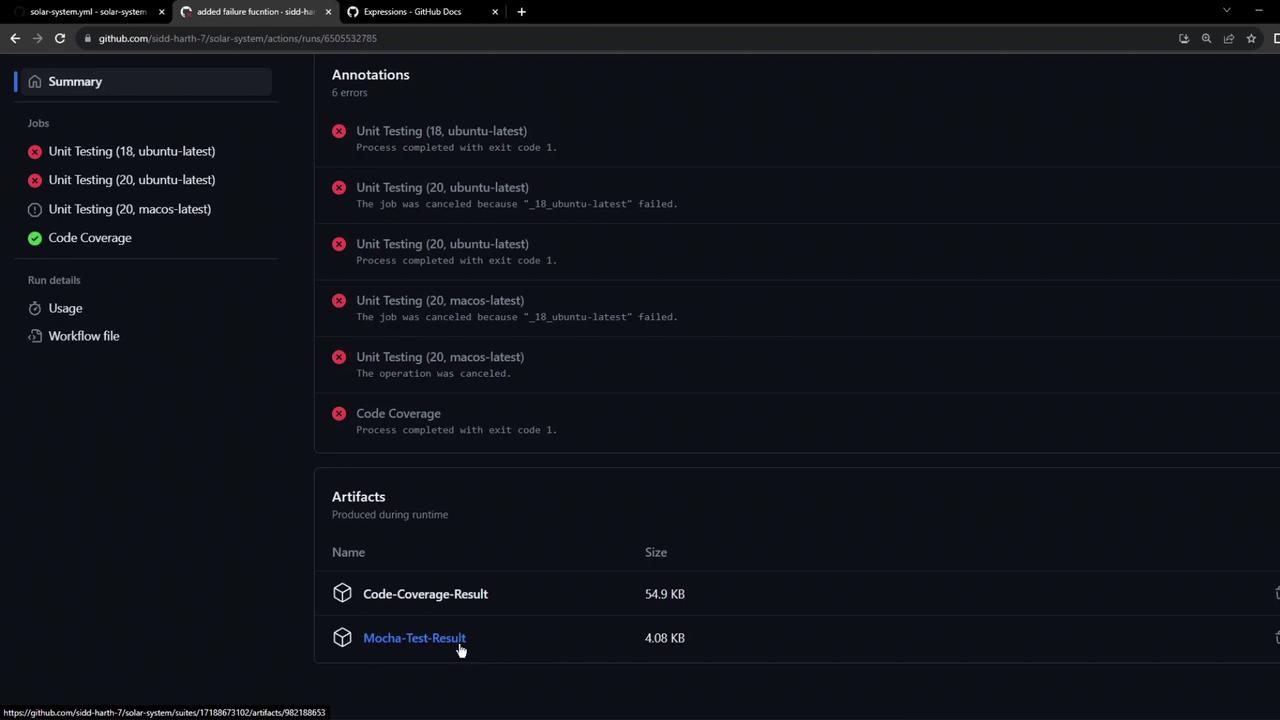
The workflow summary now lists the test-result artifact:
4. Simplifying with always()
Testing both failure and success is redundant. Use always() to run the step unconditionally:
- name: Archive Test Results
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: Mocha-Test-Result
path: test-results.xml
With always(), the upload executes on success, failure, or cancelation:
5. Quick Reference: Status Functions
| Function | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| always() | Runs step regardless of outcome | if: always() |
| success() | Runs step only when all prior steps succeed | if: success() |
| failure() | Runs step only when a prior step fails | if: failure() |
| cancelled() | Runs step when the job is canceled | if: cancelled() |
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab