GitHub Actions Certification
GitHub Actions Core Concepts
Enable step debug logging in a workflow
Debug logging in GitHub Actions exposes low-level details about workflow execution, making it easier to diagnose issues in jobs and steps. This guide covers:
- What debug logging is and when to use it
- How to enable it via secrets or variables
- A demo workflow showing debug logging in action
- Managing debug settings by default at the repository level
What Is Debug Logging?
By default, GitHub Actions logs include only high-level execution output. When you need deeper insights—such as condition evaluations, environment variable settings, and runner internals—you can turn on debug logging.
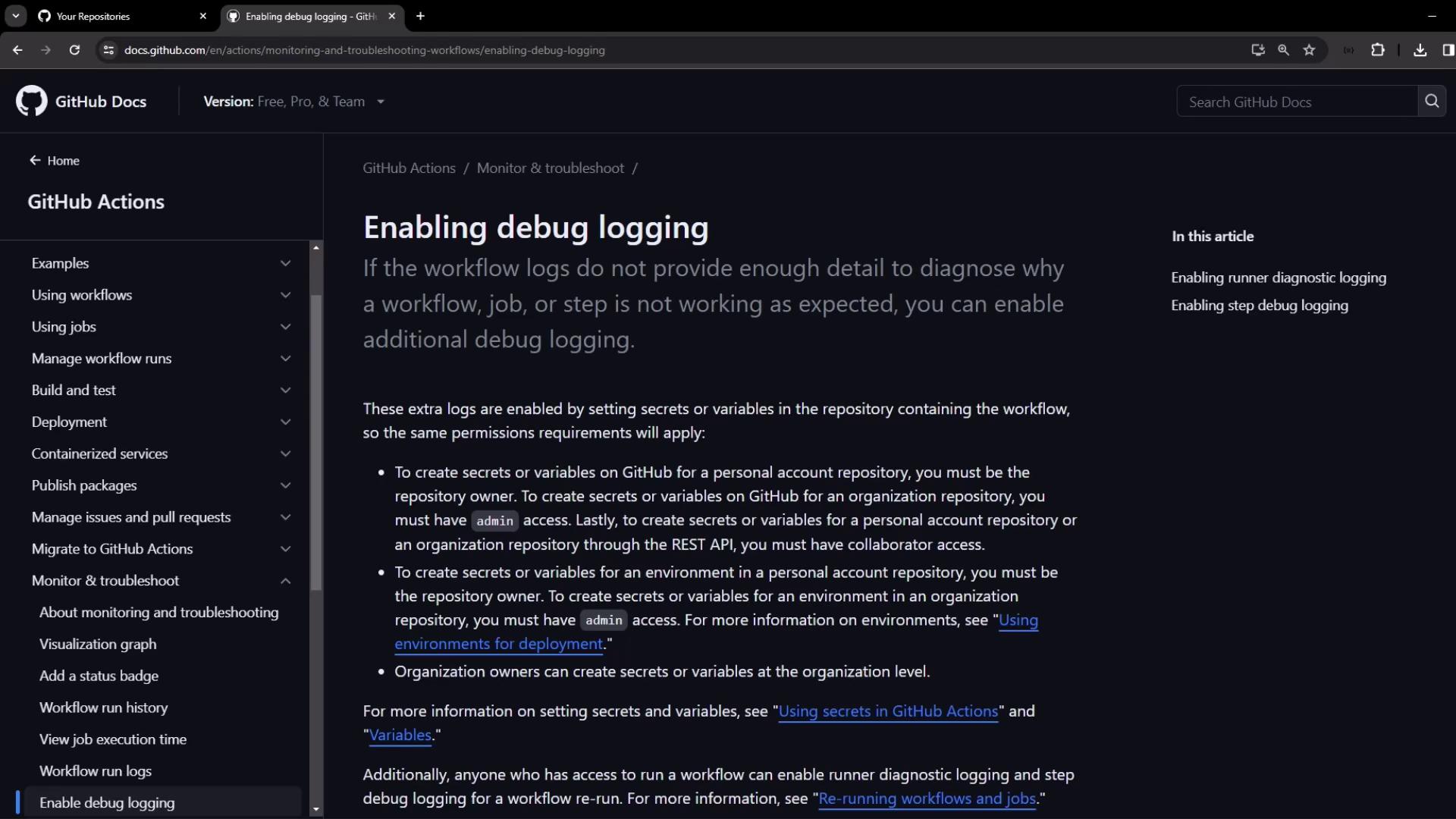
Types of Debug Logging
Use one or both of the following:
| Debug Type | Purpose | Secret/Variable Name |
|---|---|---|
| Runner Diagnostic Logging | Captures the runner’s internal execution details | ACTIONS_RUNNER_DEBUG |
| Step Debug Logging | Increases verbosity around each step’s execution | ACTIONS_STEP_DEBUG |
Note
If you set both a secret and a variable with the same name, the secret wins.
Ensure you configure the correct value in your repository settings.
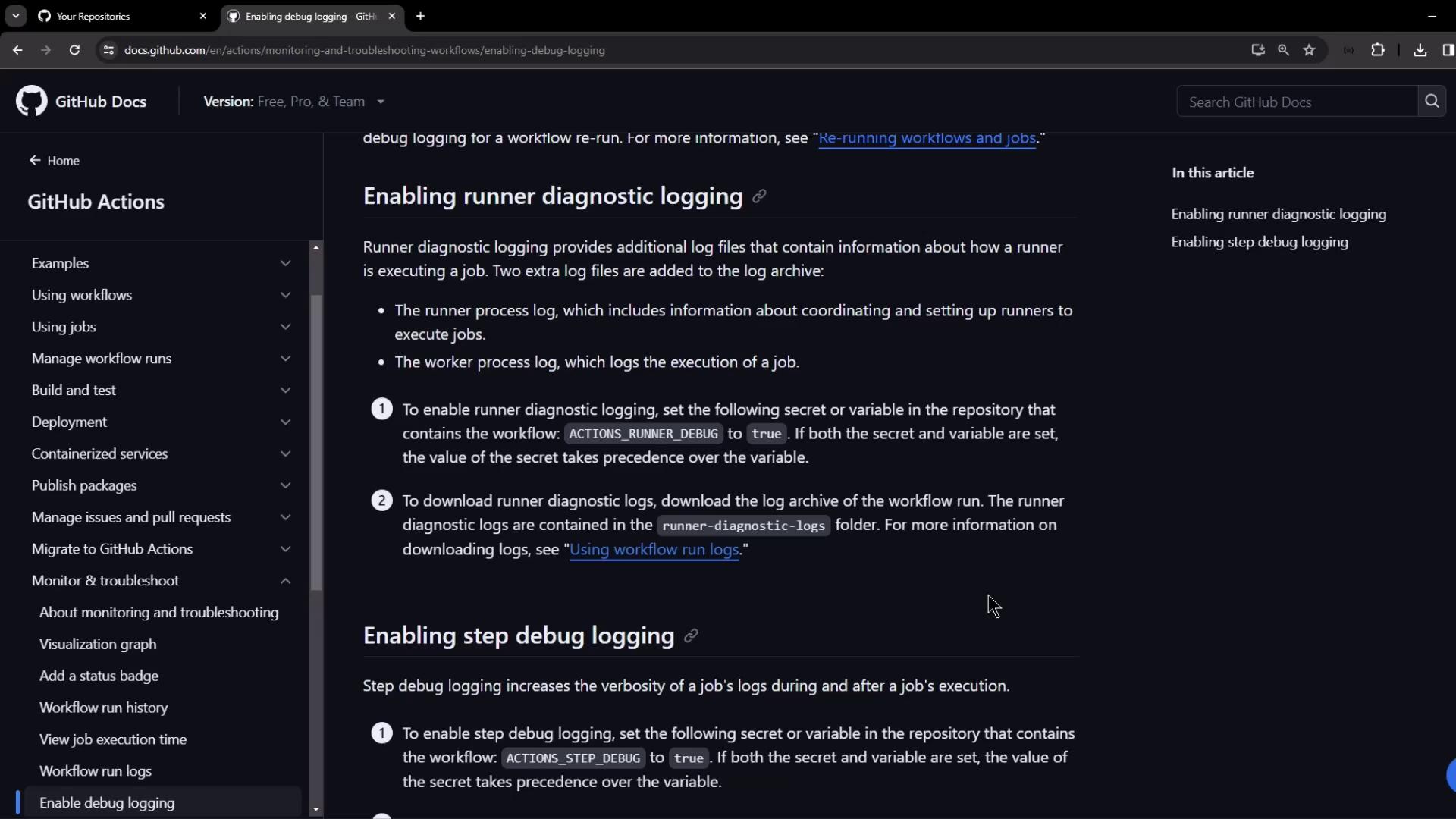
Enabling Debug Logging via Secrets or Variables
To activate debug logging for a run, add one or both keys as repository secrets or repository variables:
# Enable runner diagnostic logging
ACTIONS_RUNNER_DEBUG = true
# Enable step debug logging
ACTIONS_STEP_DEBUG = true
If both secret and variable exist for the same key, the secret value overrides the variable.
Demo: Creating and Observing a Debug Workflow
This demo shows a simple workflow that fails intentionally, illustrating how step debug logging provides extra detail.
1. Create a New Repository
- In GitHub, create a public repo named
debug-workflow-demowith aREADME.md. - Clone the repository locally or open it in VS Code.
2. Add the Workflow File
Create file .github/workflows/debug.yaml with the following content:
name: Debugging Demo
on:
workflow_dispatch:
env:
USER_1: "foo-user"
USER_2: "bar-user"
jobs:
debug_job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set USERNAME from USER_1
run: |
echo "USERNAME=$USER_1" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Print USERNAME and Fail
run: |
echo "Printing USERNAME from previous step"
echo "Username: $USERNAME"
exit 1
- name: Print USER_2
run: |
echo "Printing USER_2: $USER_2"
Commit and push:
git add .github/workflows/debug.yaml
git commit -m "Add debug workflow"
git push
3. Run Without Debug Logging
- In the repo, go to Actions → Debugging Demo.
- Click Run workflow.
The third step fails and the fourth step is skipped:
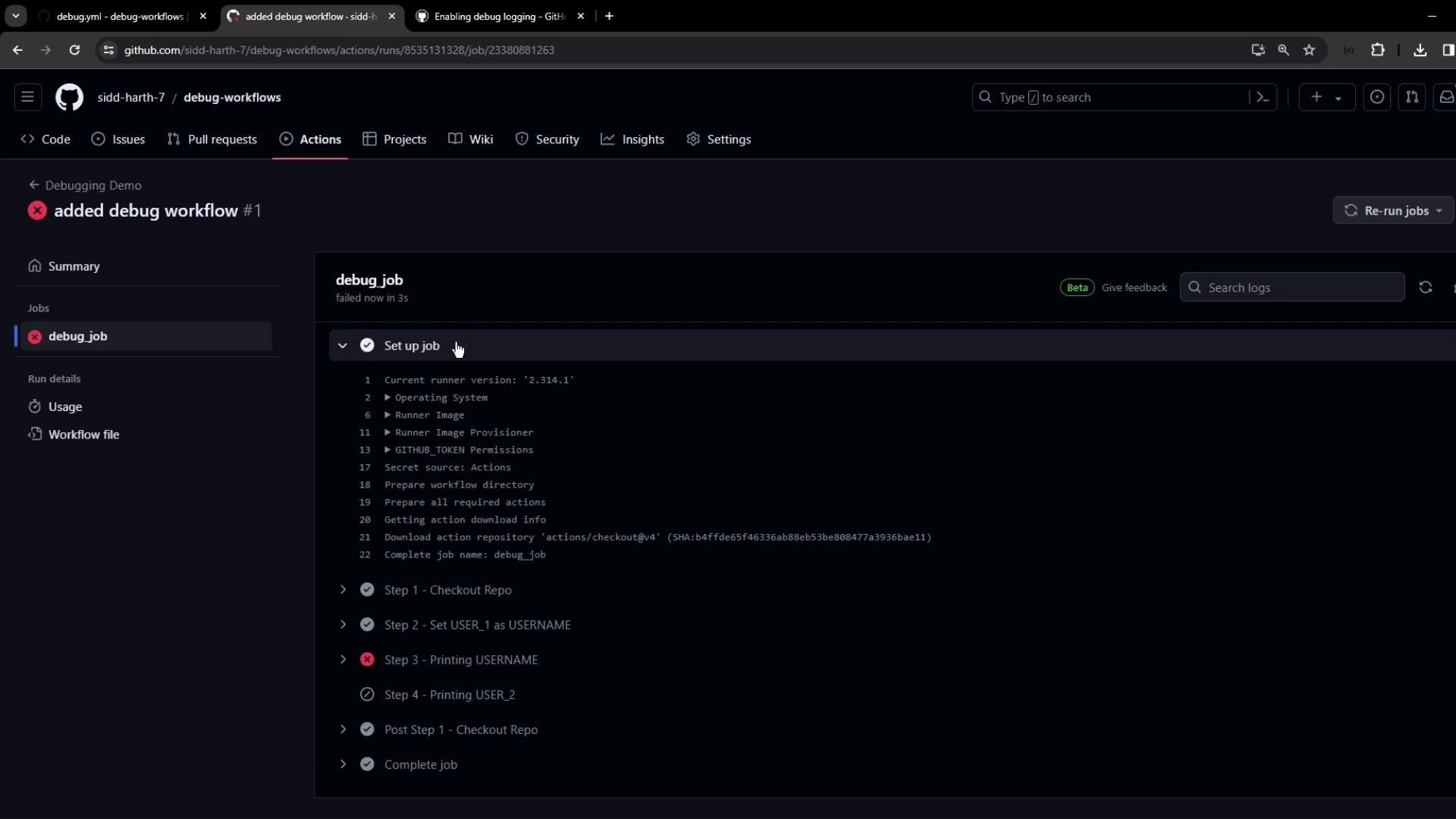
Default logs only display commands and outputs, without showing condition evaluations or skipped steps details.
Enabling Step Debug Logging in the UI
- On the failed run’s page, click Re-run jobs ▶︎ Re-run with debug logging.
- The job reruns and prepends each log line with
##[debug]:
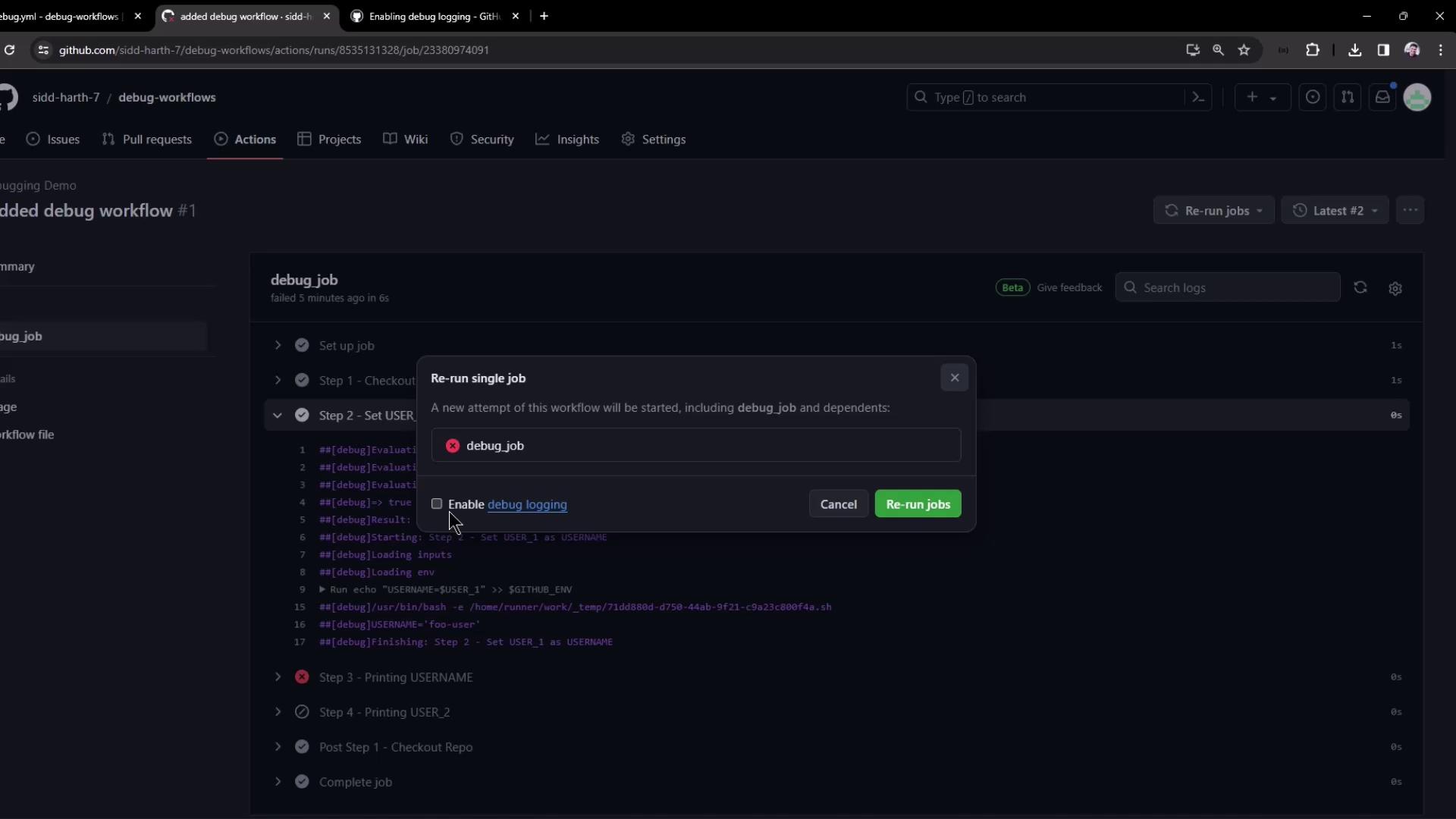
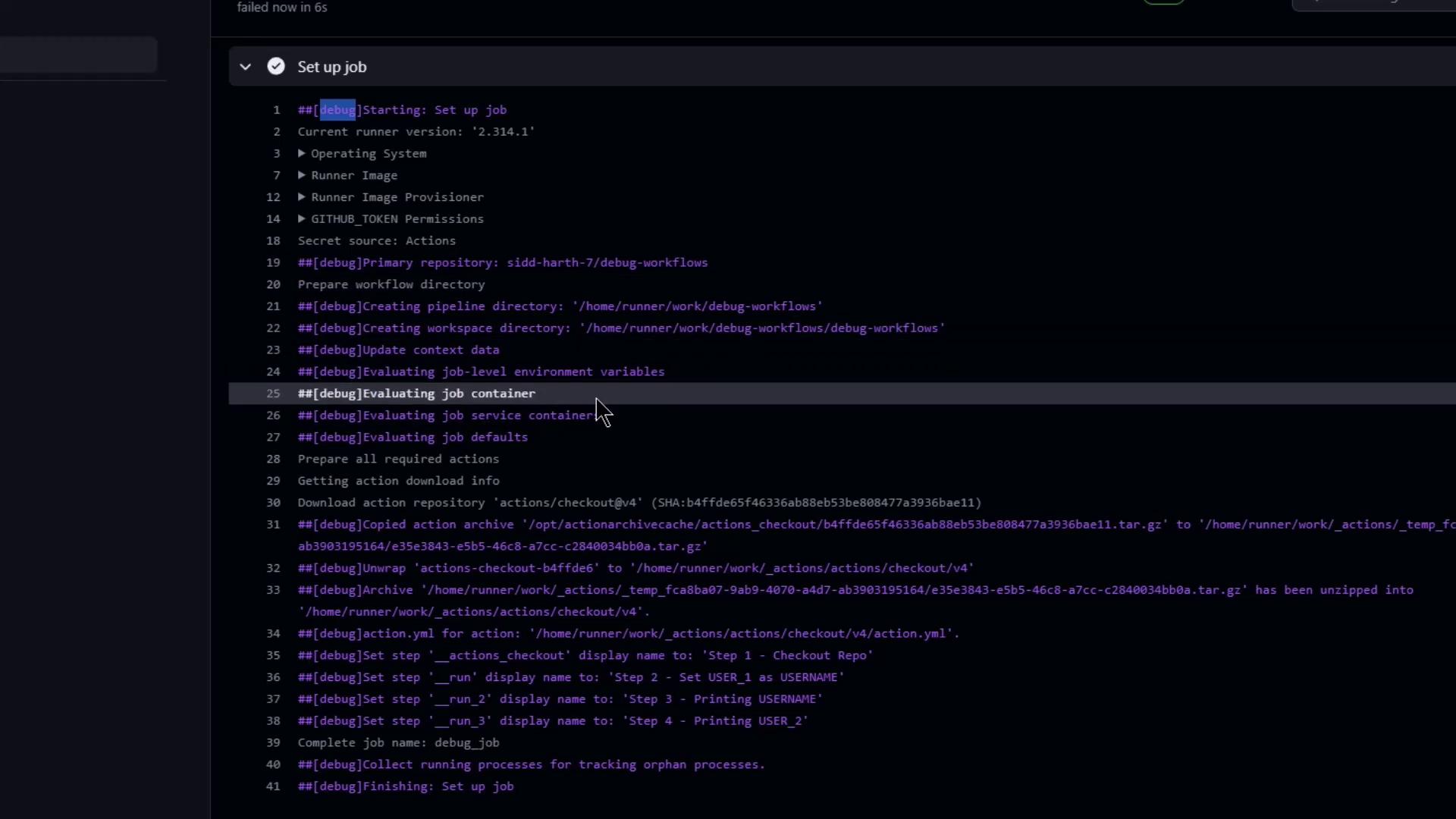
Sample condition evaluation output:
##[debug]Evaluating condition for step: 'Checkout Repository'
##[debug]Evaluating: success()
##[debug]=> true
##[debug]Result: true
##[debug]Starting: Checkout Repository
And insight into skipped steps:
##[debug]Evaluating condition for step: 'Print USER_2'
##[debug]=> false
##[debug]Skipping step 'Print USER_2'
Downloading Runner Diagnostic Logs
After rerunning with debug, you can Download log archive from the run’s summary. The ZIP includes:
- All job logs with
##[debug]entries - A
runner-diagnostic-logsfolder containing runner internals
Enabling Debug Logging by Default
To apply debug settings to every workflow run:
Navigate to Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions → Variables.
Click New repository variable and add:
ACTIONS_RUNNER_DEBUG = trueACTIONS_STEP_DEBUG = true
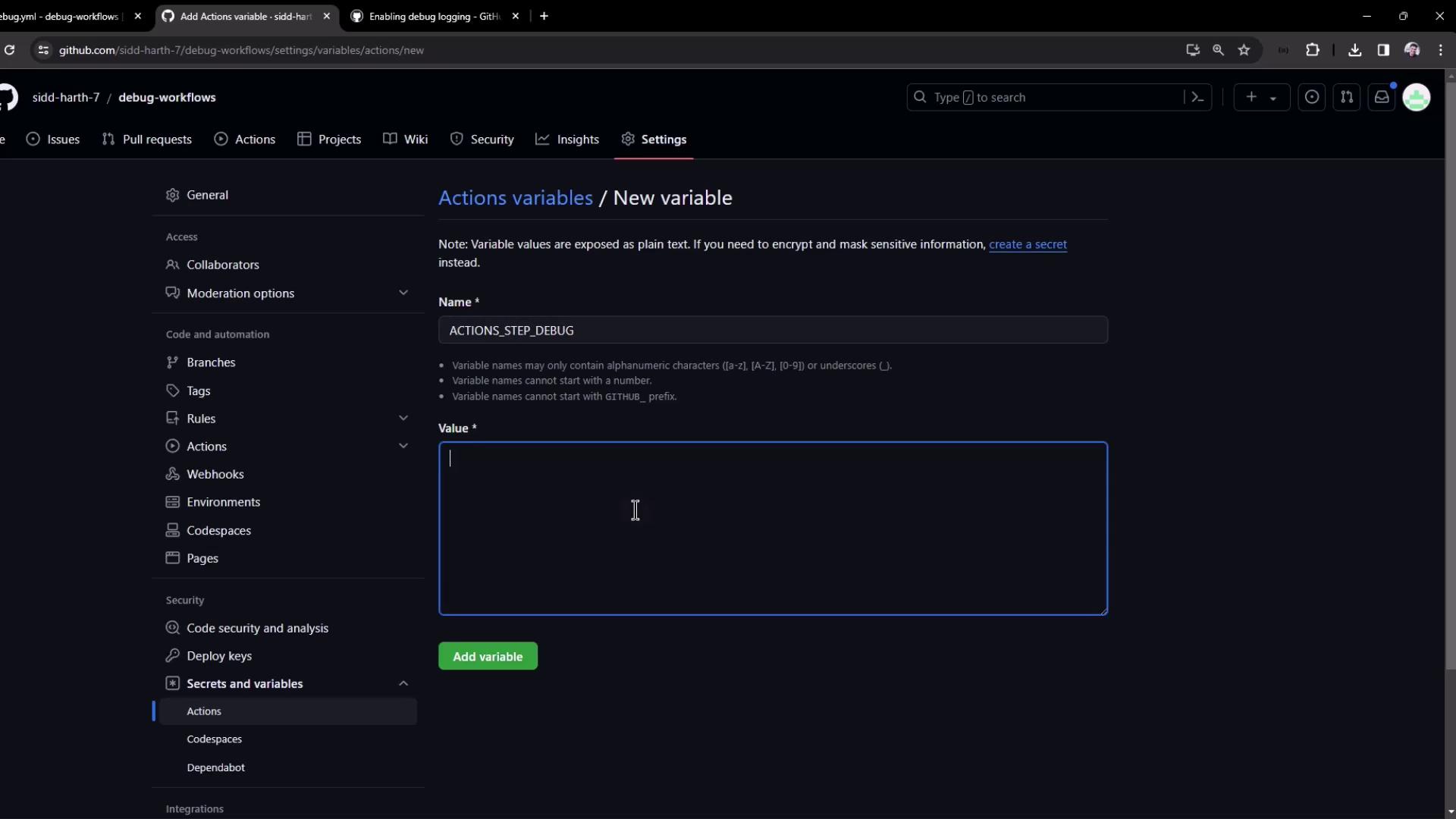
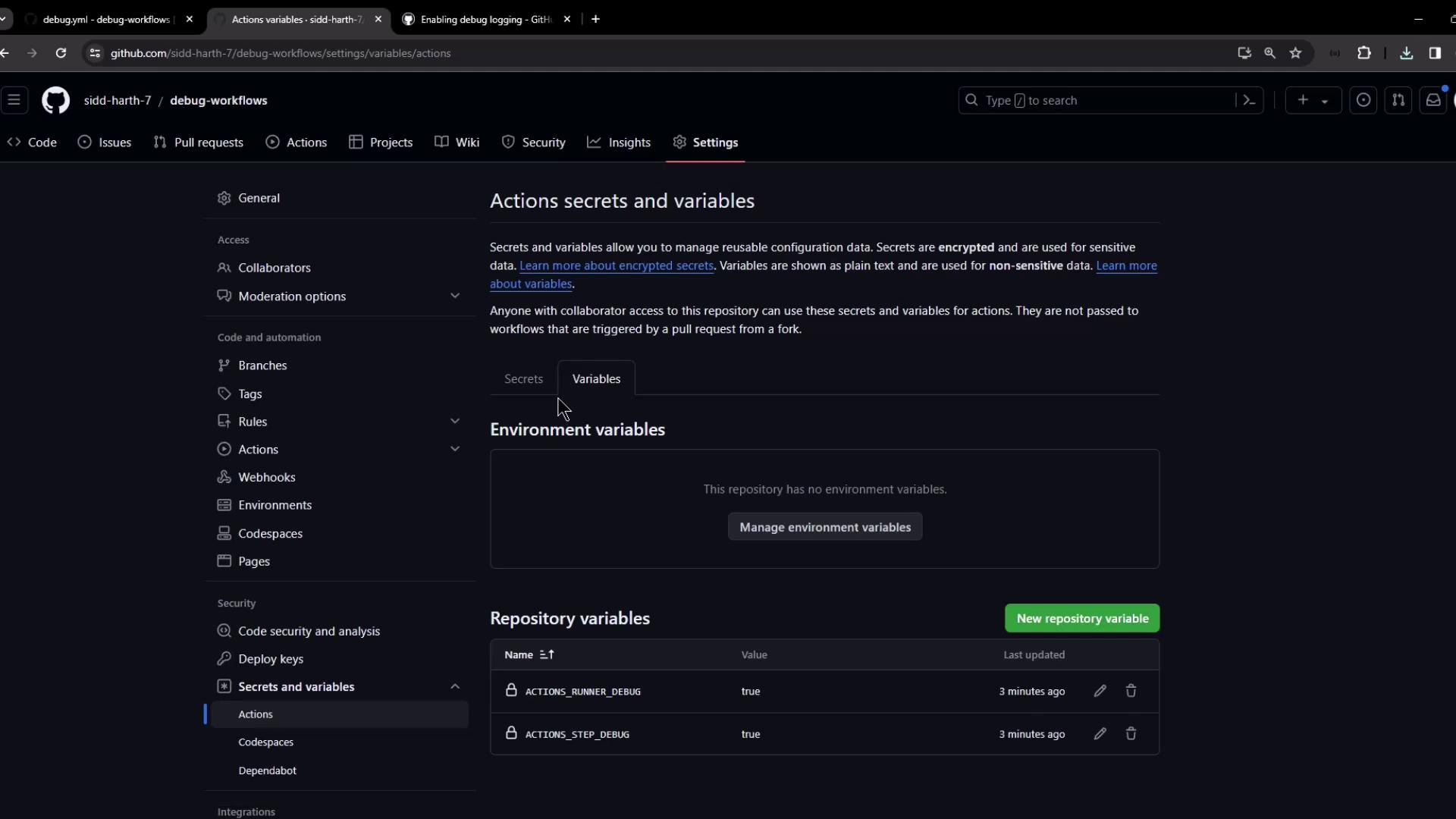
Precedence: Variables vs. Secrets
If a key exists as both a variable and a secret, the secret value takes precedence:
| Setting Type | ACTIONS_RUNNER_DEBUG | Resulting Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Repo Variable | true | Logging enabled by variable |
| Repo Secret | false | Logging disabled by secret |
Warning
Always verify the final debug log behavior when mixing variables and secrets. Secrets override variables, which may disable diagnostic logging if set to false.
By following these steps, you can enable and customize both step-level and runner-level debug logging in GitHub Actions, giving you full visibility into your workflow executions.
Watch Video
Watch video content