In this guide, we’ll automate the upload of Mocha test results and code coverage reports to an Amazon S3 bucket using GitHub Actions. Instead of scripting AWS CLI commands manually, we’ll use the popular jakejarvis/s3-sync-action from the GitHub Marketplace.
Prerequisites
An existing S3 bucket (e.g., solar-system-reports-bucket in us-east-1 ).
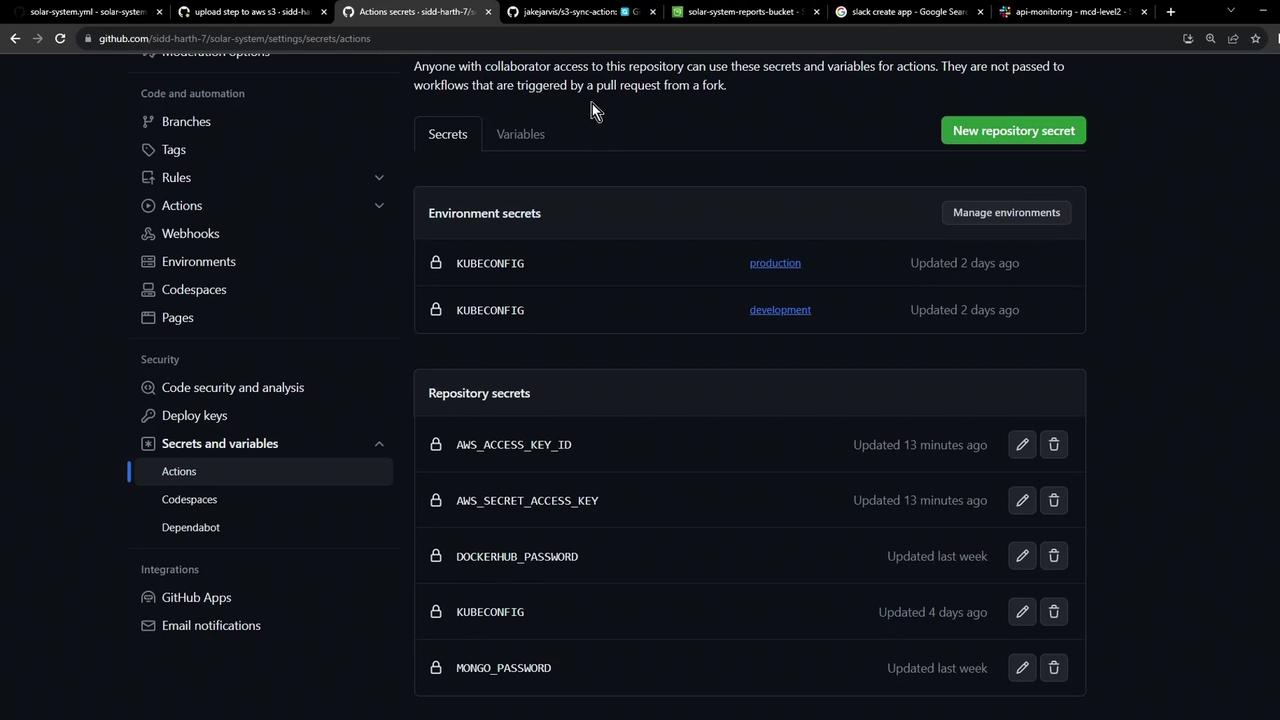
AWS credentials stored as GitHub repository secrets .
A workflow that uploads test artifacts via actions/upload-artifact.
1. Initial Workflow Stub Here’s our starting point. The reports-s3 job currently downloads artifacts, merges them into a folder, then echoes a placeholder message:
reports-s3 : needs : [ code-coverage , unit-testing ] name : AWS S3 - Upload Reports runs-on : ubuntu-latest continue-on-error : true steps : - name : Download Mocha Test Artifact uses : actions/download-artifact@v3 with : name : Mocha-Test-Result - name : Download Code Coverage Artifact uses : actions/download-artifact@v3 with : name : Code-Coverage-Result - name : Merge Test Files run : | ls -ltr mkdir reports-${{ github.sha }} mv cobertura-coverage.xml reports-${{ github.sha }}/ mv test-results.xml reports-${{ github.sha }}/ ls -ltr reports-${{ github.sha }}/ - name : Upload to AWS S3 run : echo "uploading......."
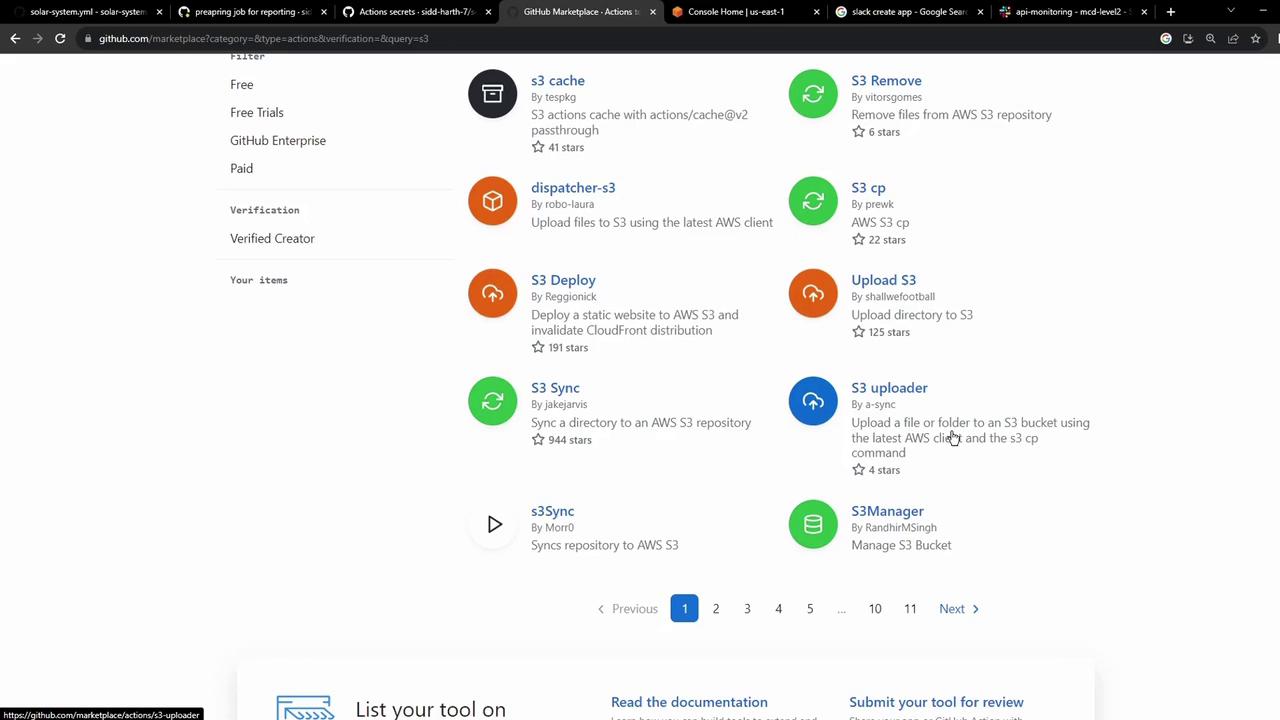
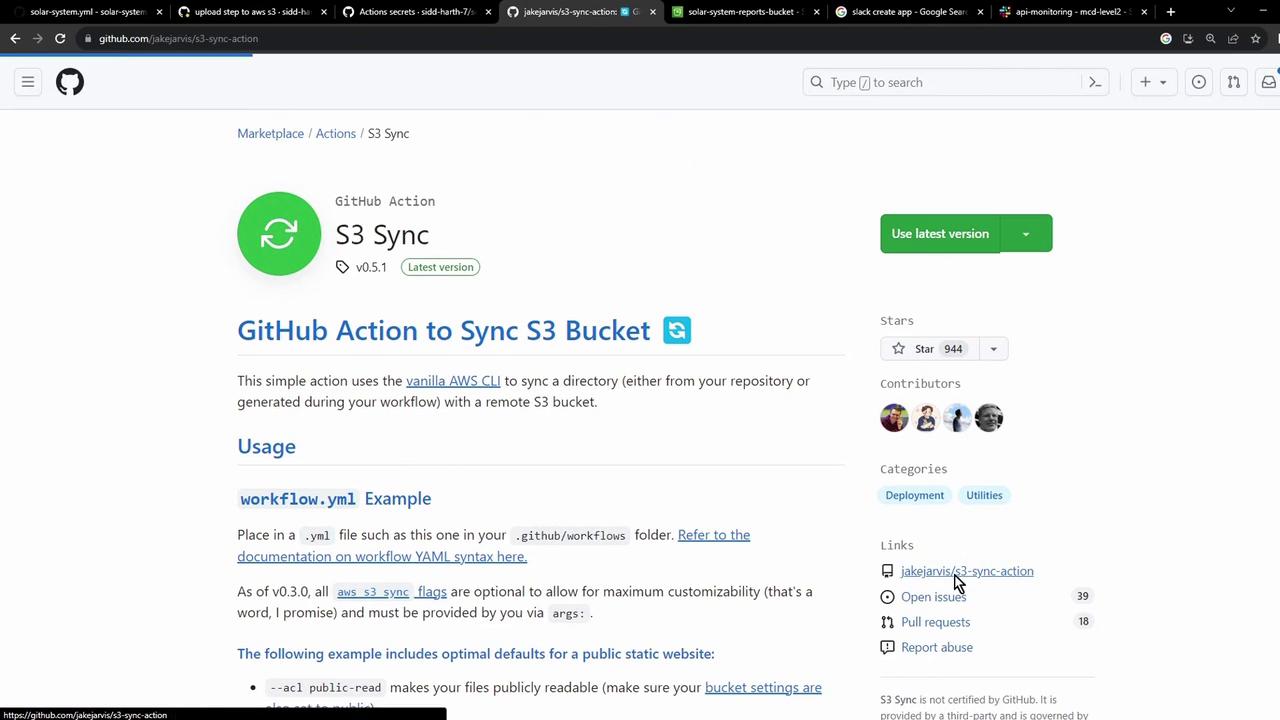
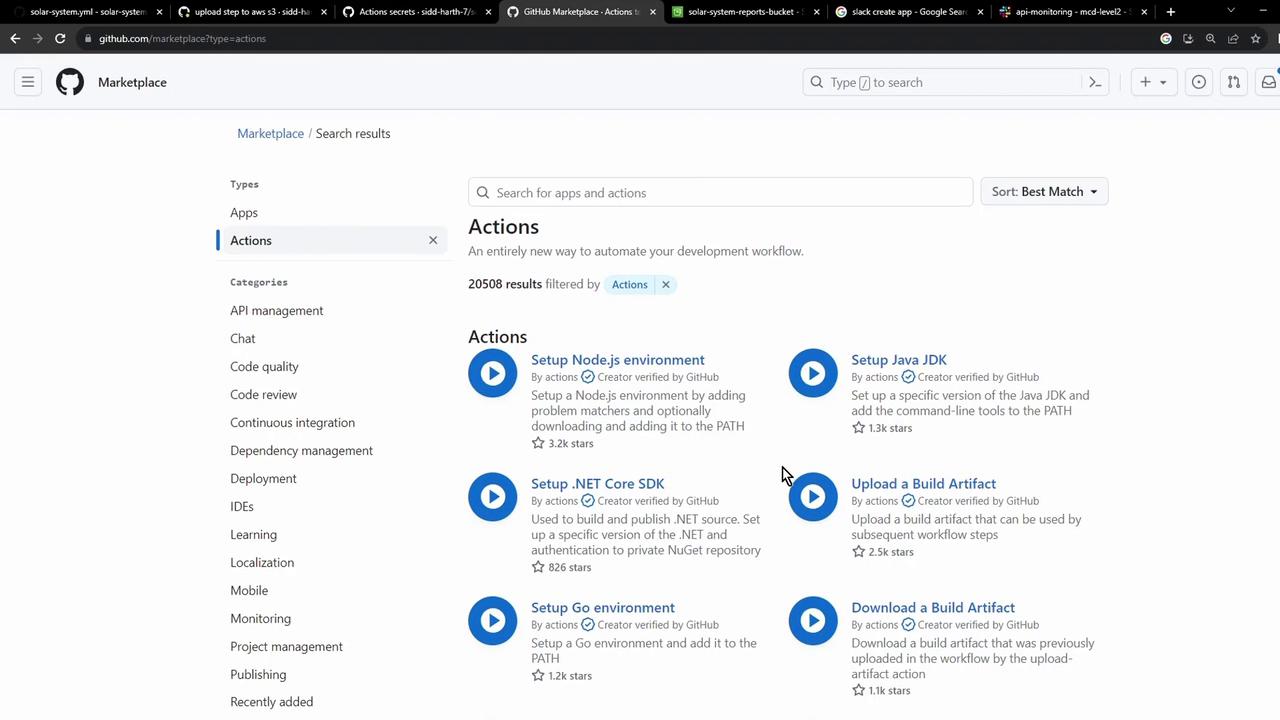
Choosing a Marketplace Action The GitHub Marketplace offers many AWS S3 actions for syncing, uploading, or deploying:
One of the most widely used is jakejarvis/s3-sync-action.
2. Sample Usage of jakejarvis/s3-sync-action - name : Sync to S3 uses : jakejarvis/s3-sync-action@master with : args : --acl public-read --follow-symlinks --delete env : AWS_S3_BUCKET : ${{ secrets.AWS_S3_BUCKET }} AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID : ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }} AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY : ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }} AWS_REGION : 'us-west-1' # Optional: defaults to us-east-1 SOURCE_DIR : 'public' # Optional: defaults to entire repo
Environment Variables Reference Variable Description Default AWS_S3_BUCKET Name of your S3 bucket none AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID AWS access key stored in GitHub secrets none AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY AWS secret key stored in GitHub secrets none AWS_REGION AWS region for your bucket us-east-1 SOURCE_DIR Directory to sync entire repo DEST_DIR Destination path within the bucket root of bucket
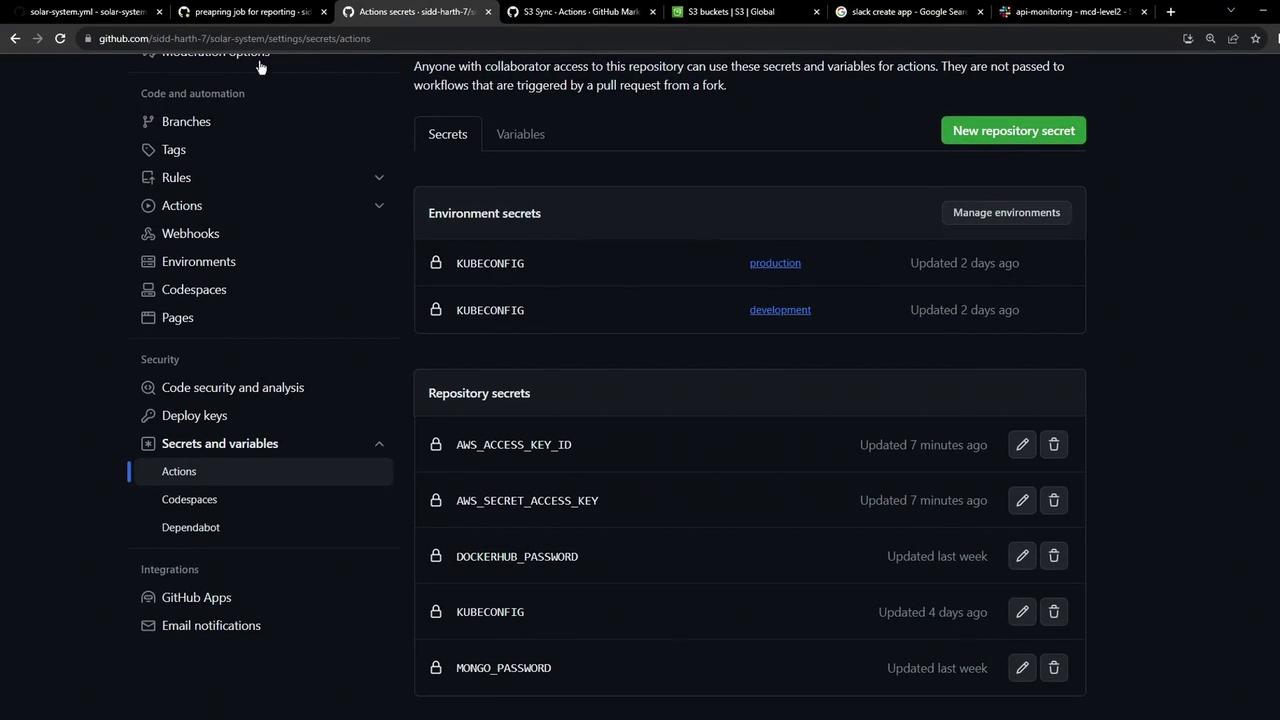
Store your AWS credentials securely under Settings → Secrets and variables in your GitHub repository.
3. Integrate the Sync Action into reports-s3 Replace the placeholder step with the s3-sync-action. The final job looks like this:
jobs : reports-s3 : needs : [ code-coverage , unit-testing ] name : AWS S3 - Upload Reports runs-on : ubuntu-latest continue-on-error : true steps : - name : Download Mocha Test Artifact uses : actions/download-artifact@v3 with : name : Mocha-Test-Result - name : Download Code Coverage Artifact uses : actions/download-artifact@v3 with : name : Code-Coverage-Result - name : Merge Test Files run : | ls -ltr mkdir reports-${{ github.sha }} mv cobertura-coverage.xml reports-${{ github.sha }}/ mv test-results.xml reports-${{ github.sha }}/ ls -ltr reports-${{ github.sha }}/ - name : Upload to AWS S3 uses : jakejarvis/s3-sync-action@master with : args : --follow-symlinks --delete env : AWS_S3_BUCKET : solar-system-reports-bucket AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID : ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }} AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY : ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }} AWS_REGION : us-east-1 SOURCE_DIR : reports-${{ github.sha }} DEST_DIR : reports-${{ github.sha }}
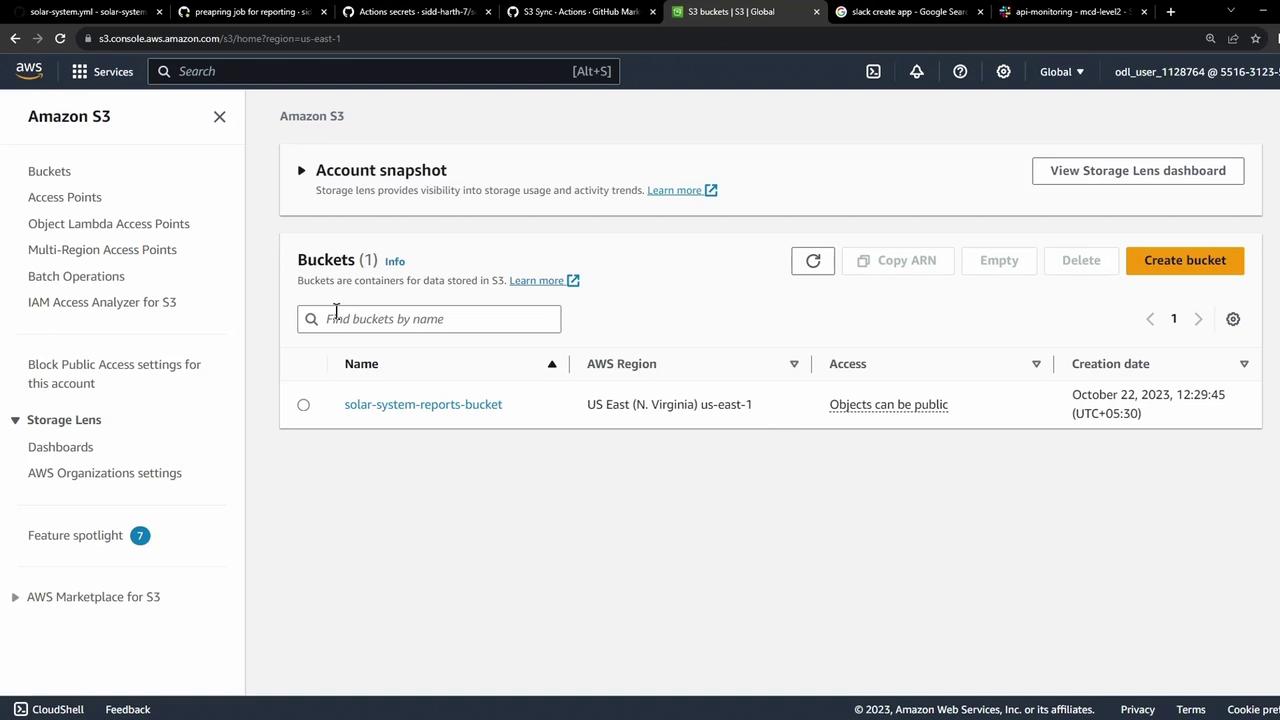
4. Verify Your S3 Bucket and Secrets Your bucket, solar-system-reports-bucket, is in US East (N. Virginia):
AWS credentials should appear in Secrets and variables :
At first, the bucket will be empty:
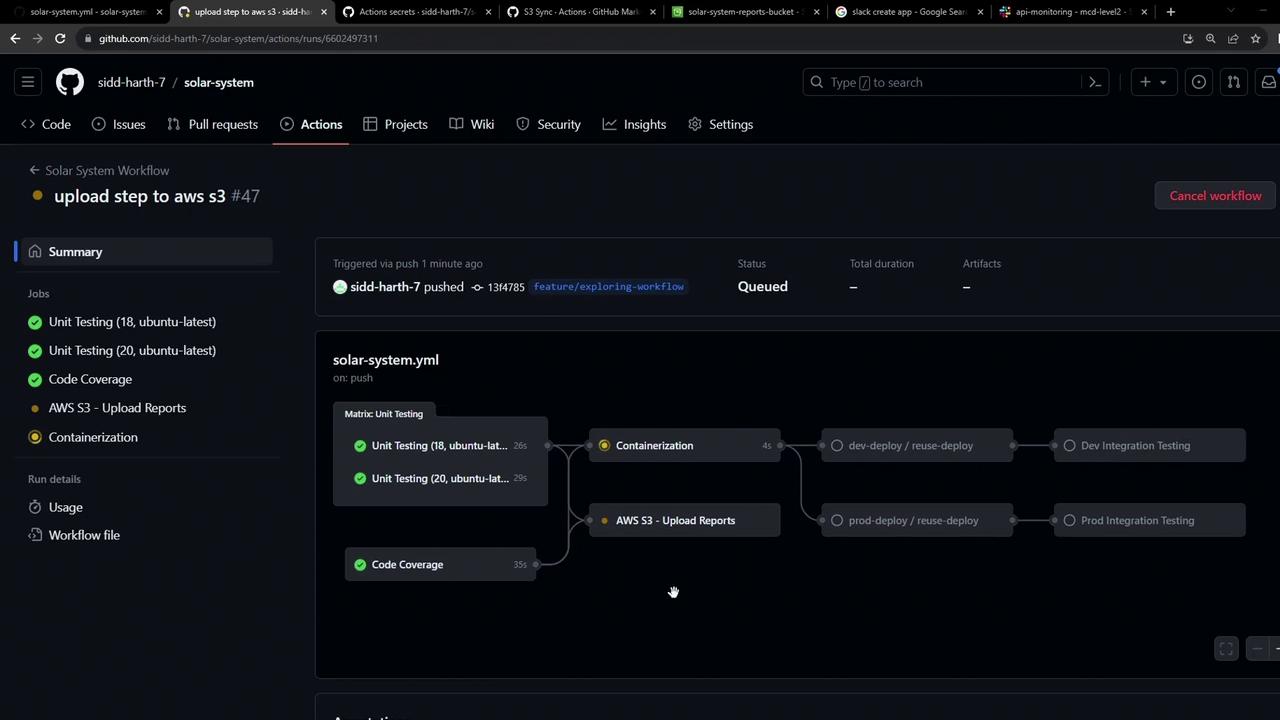
5. Trigger the Workflow Commit and push your changes. After unit-testing and code-coverage finish, you’ll see the reports-s3 job queued:
You may notice an extra build step as it prepares the sync container:
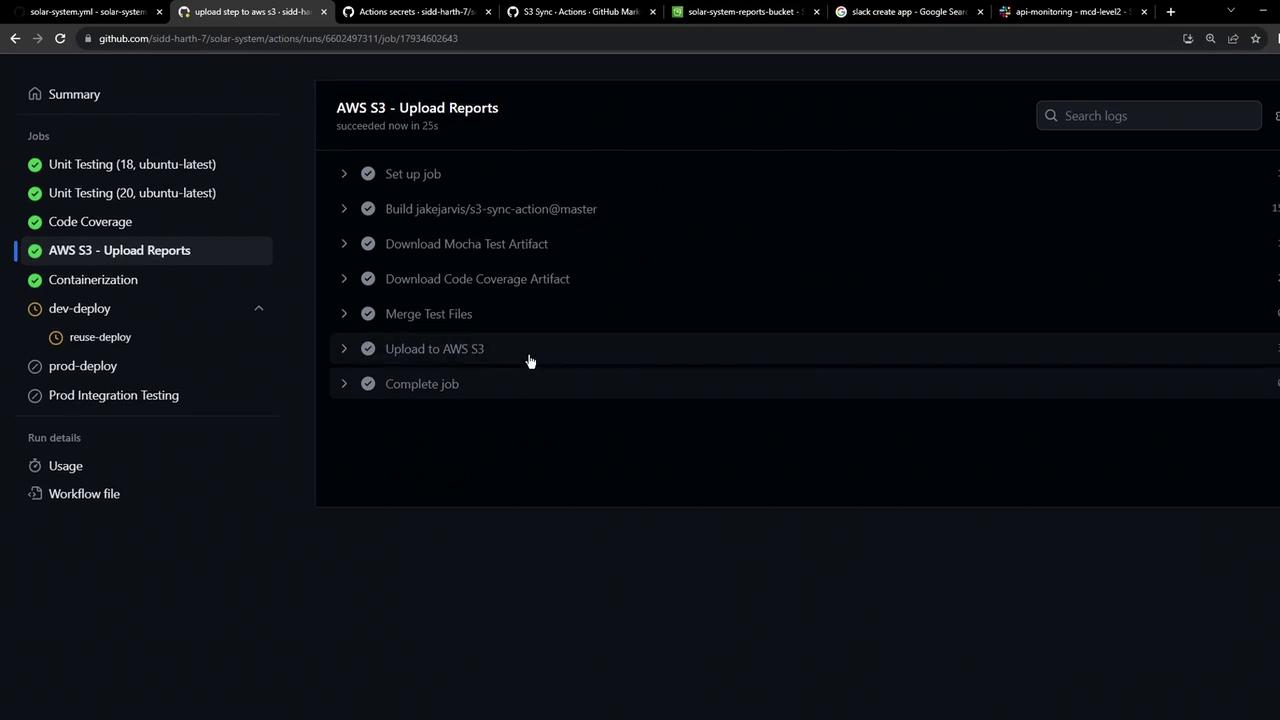
After the container is ready, the sync runs and uploads your reports:
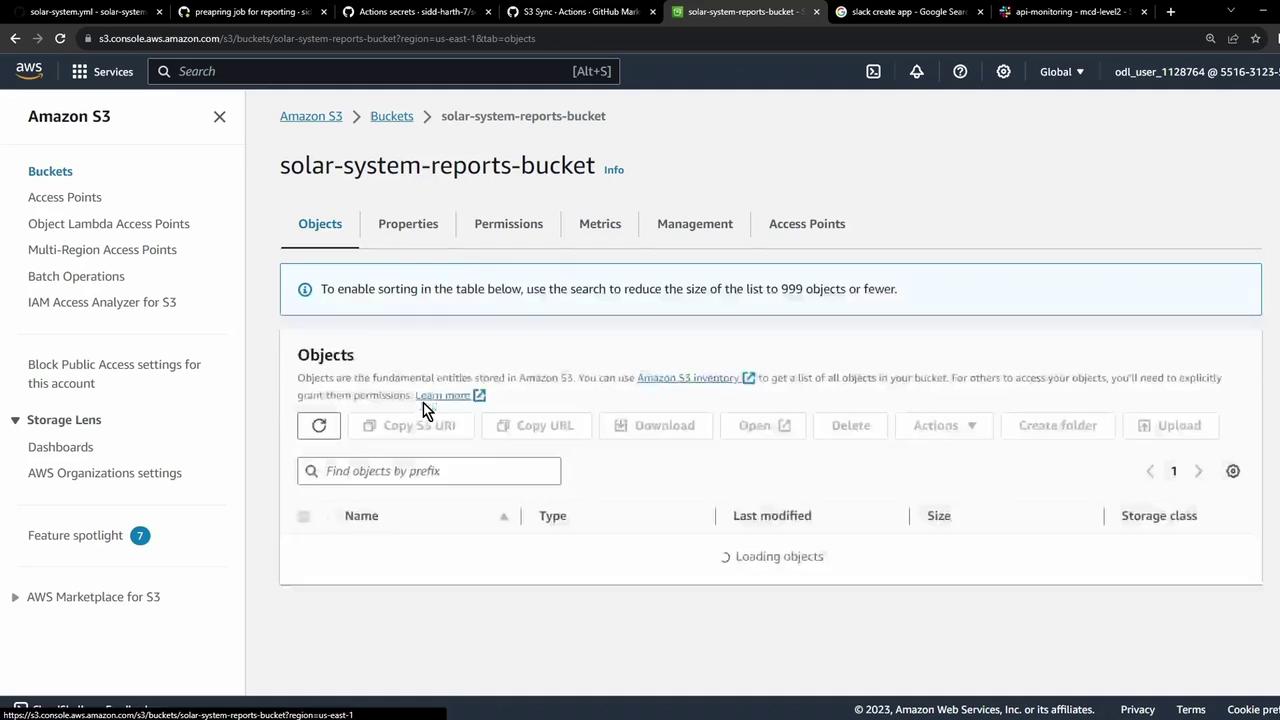
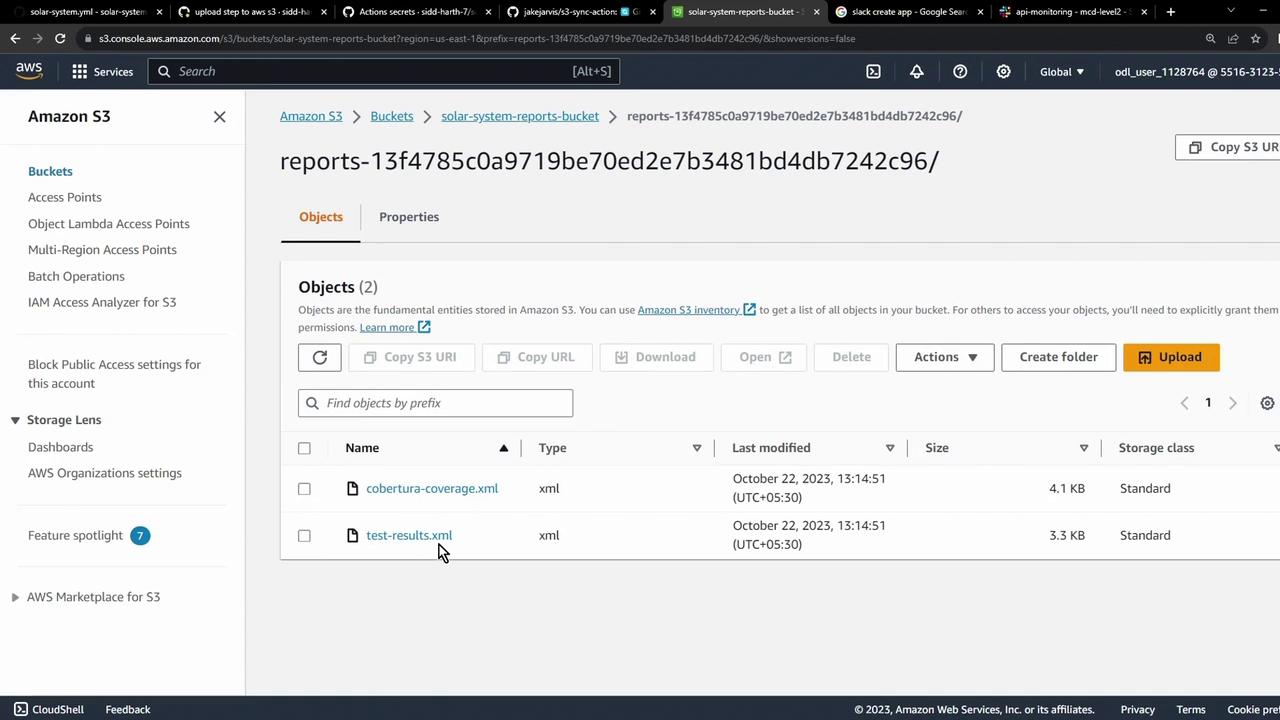
6. Confirm the Upload Refresh the S3 console to see your XML report files:
Next Steps
Browse the GitHub Marketplace for actions to integrate with other cloud providers and CI/CD tools. That’s it! You’ve automated the upload of your test and coverage artifacts to AWS S3.