GitHub Actions Certification
Security Guide
Securing Secrets using HashiCorp Vault
Managing sensitive credentials across multiple repositories can be challenging. GitHub Actions stores secrets at the repository or environment level, but lacks versioning and centralized policy controls. By integrating HashiCorp Vault, you can maintain a single source of truth and automate secret synchronization across all your workflows.
Why Centralize Secret Management?
GitHub Actions secrets are easy to configure but can become a maintenance burden as your organization scales:
| Storage Type | Versioning | Access Control | Maintenance Overhead |
|---|---|---|---|
| GitHub Repository | No | Per-repo / per-environment policies | Duplicate in each repo |
| HashiCorp Vault | Yes | Fine-grained, dynamic ACLs & tokens | Centralized, auditable |
By standardizing on Vault, you gain:
- Automatic versioning and rotation
- Detailed audit logs
- Consistent policies across environments
Defining a GitHub Actions Workflow
Create a workflow file under .github/workflows/vault-demo.yaml that manually triggers and checks for AWS_API_KEY:
name: Vault Demo
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
echo-vault-secret:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Verify AWS_API_KEY exists
run: |
if [[ -z "${{ secrets.AWS_API_KEY }}" ]]; then
echo "::error::Secret Not Found"
exit 1
else
echo "::notice::Secret Found"
exit 0
fi
Note
Ensure the workflow file is committed to the main branch (or your default branch) under .github/workflows.
When AWS_API_KEY is missing, the run fails:
# Simulated check when AWS_API_KEY is unset
if [[ -z "" ]]; then
echo "Secret Not Found"
exit 1
fi
# Output:
Secret Not Found
Provisioning HashiCorp Vault on HCP
HashiCorp Vault Secrets on the HashiCorp Cloud Platform provides a fully managed service for centralized secret storage.
Sign in at the HashiCorp Vault website.
From the HCP dashboard, select Vault Secrets:

Click Create application, name it (e.g., Secret App), then add the
AWS_API_KEYsecret:
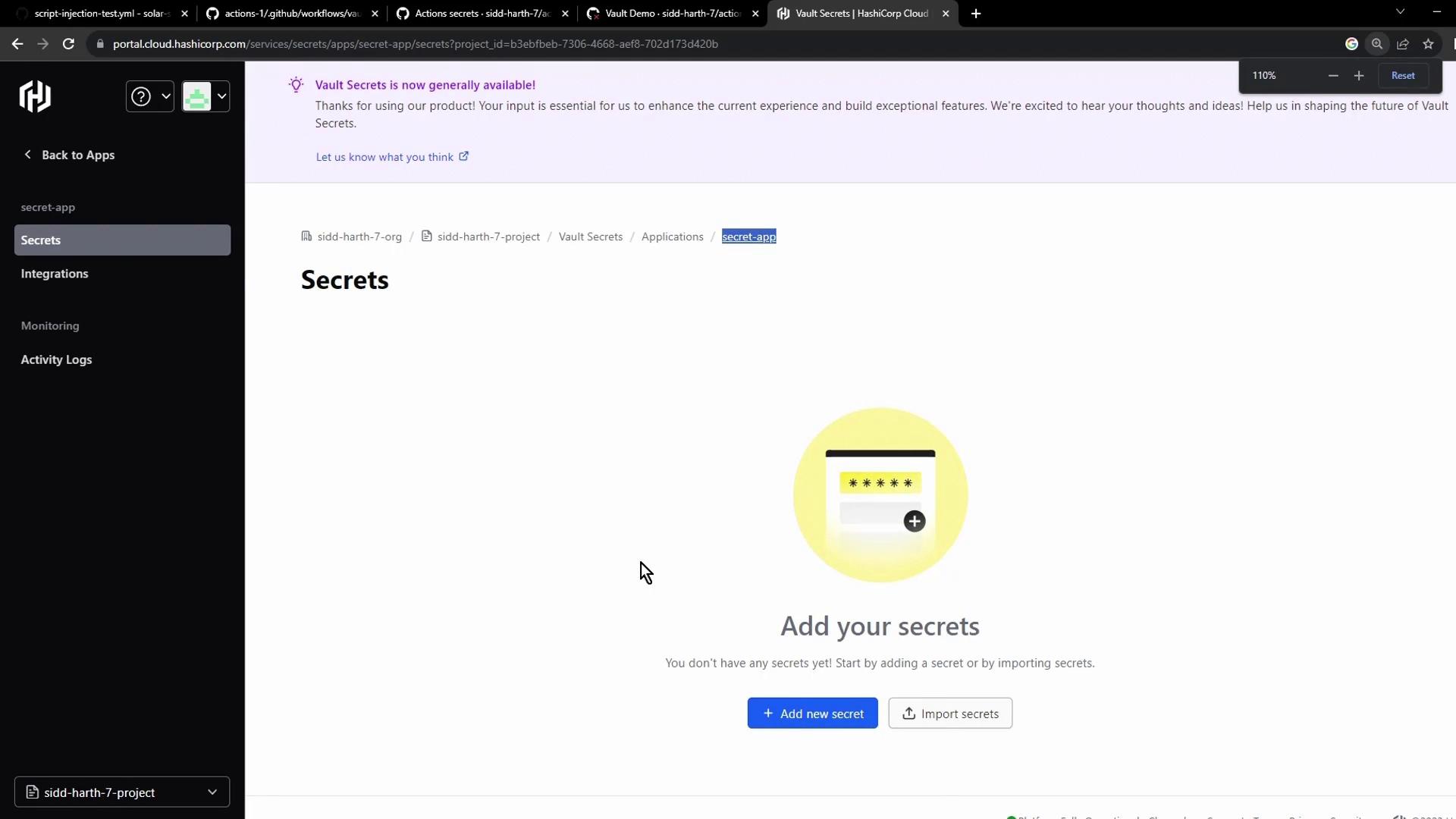
Use the Add secret button to insert your key/value pair:
Note
New users may be eligible for free credits on HCP. Check the pricing page for details.
Integrating Vault with GitHub Actions
Enable automatic synchronization so GitHub Actions can retrieve secrets directly from Vault:
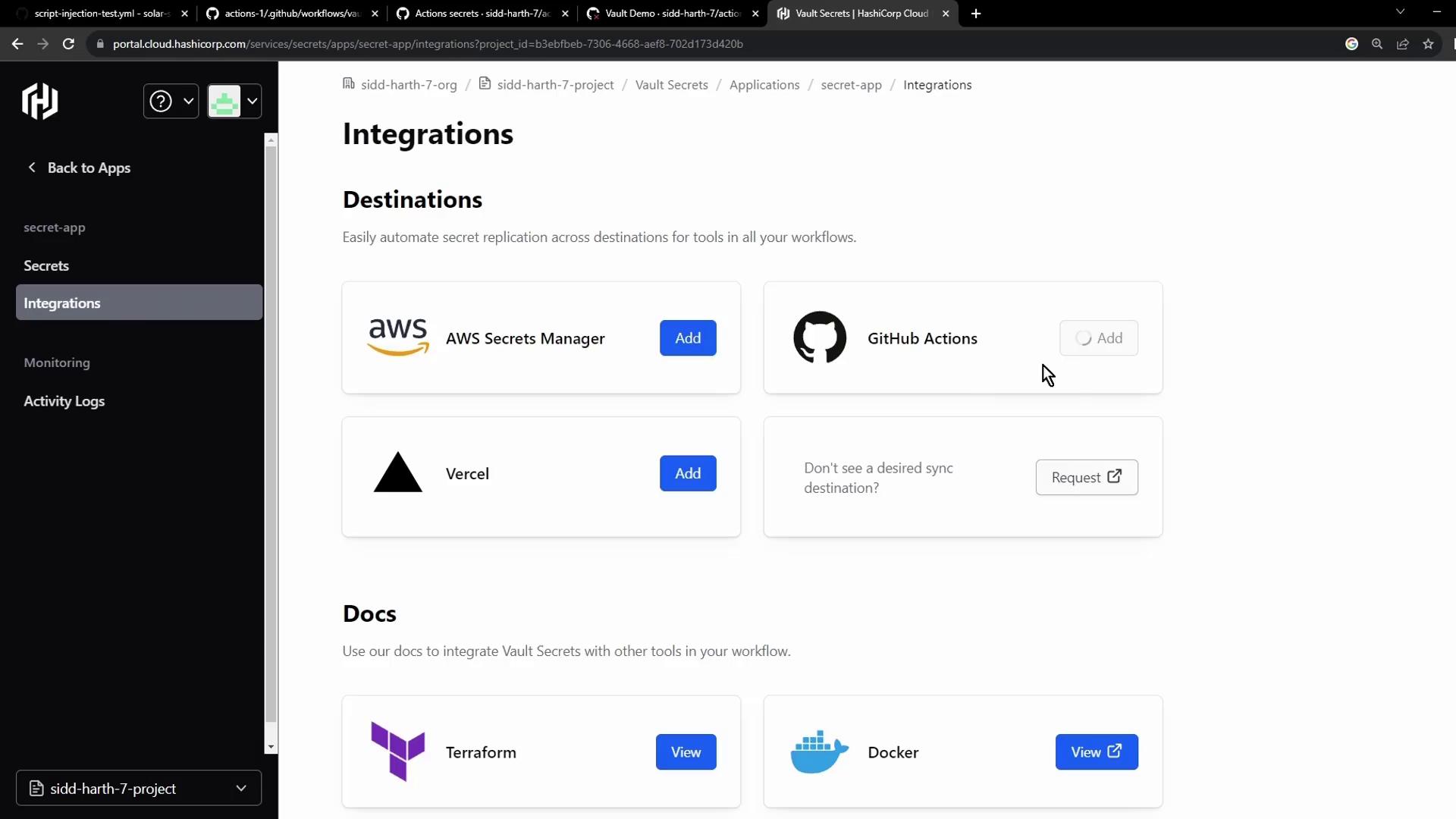
In the Vault console, select Integrations → GitHub Actions:
Authorize access to your GitHub account and grant Vault permission to the target repository:
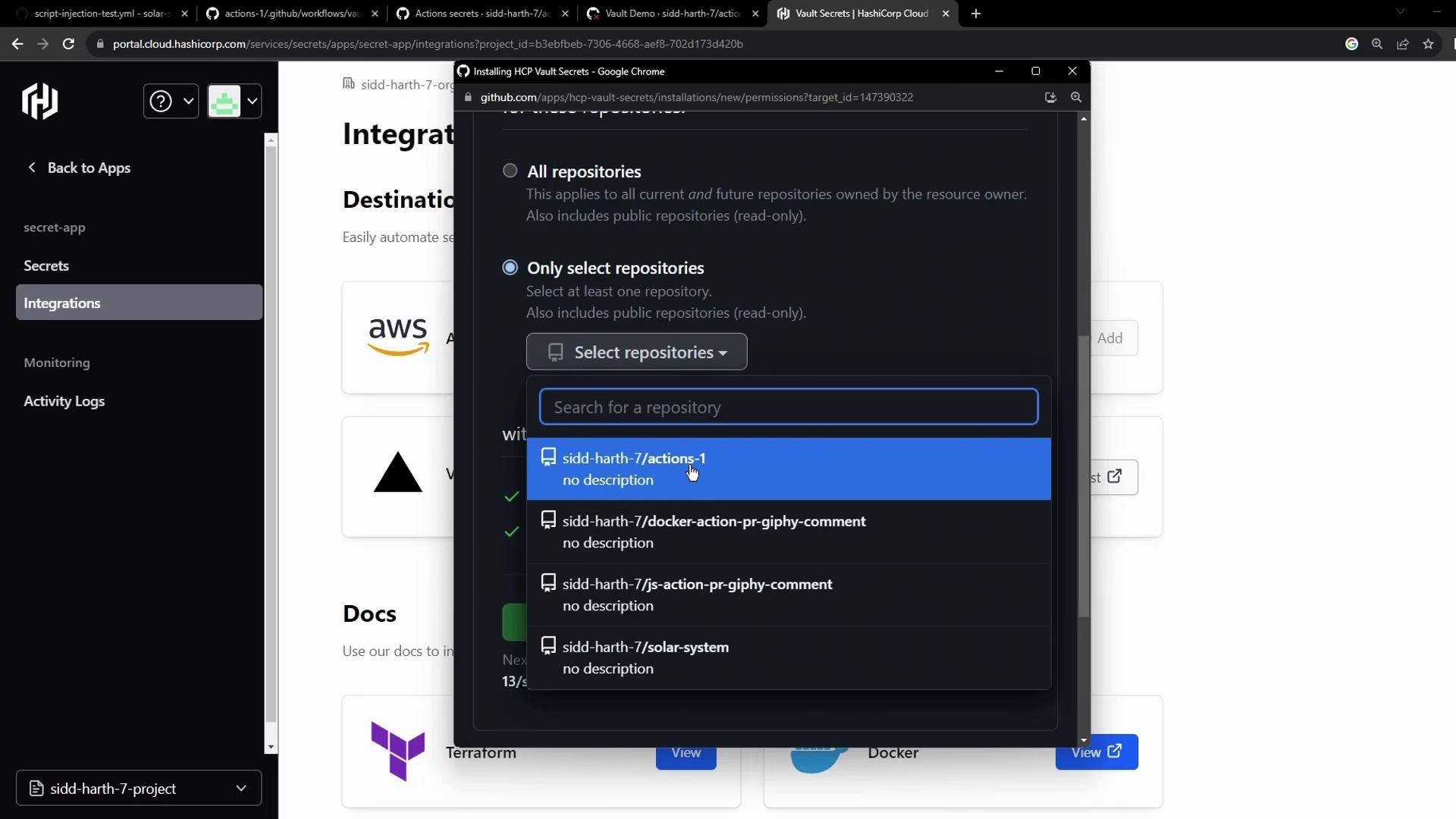
Configure the sync destination and save:
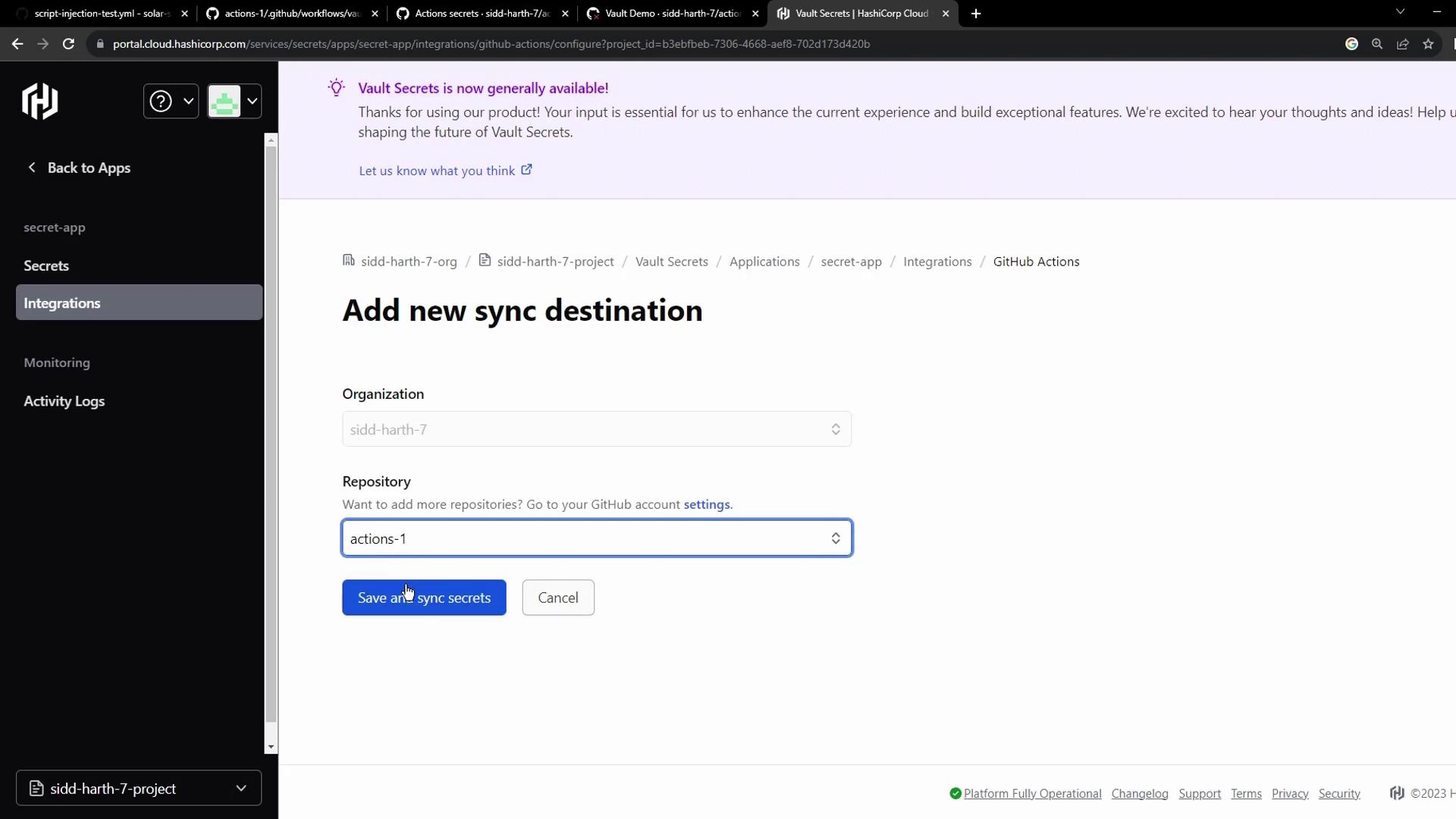
Integration at a glance:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorize GitHub | Grant Vault read access to selected repos |
| Select Repository | Choose the repo containing your workflow |
| Configure Sync | Map Vault path to GitHub secret name |
| Save & Sync | Trigger initial secret import |
Verifying the Workflow
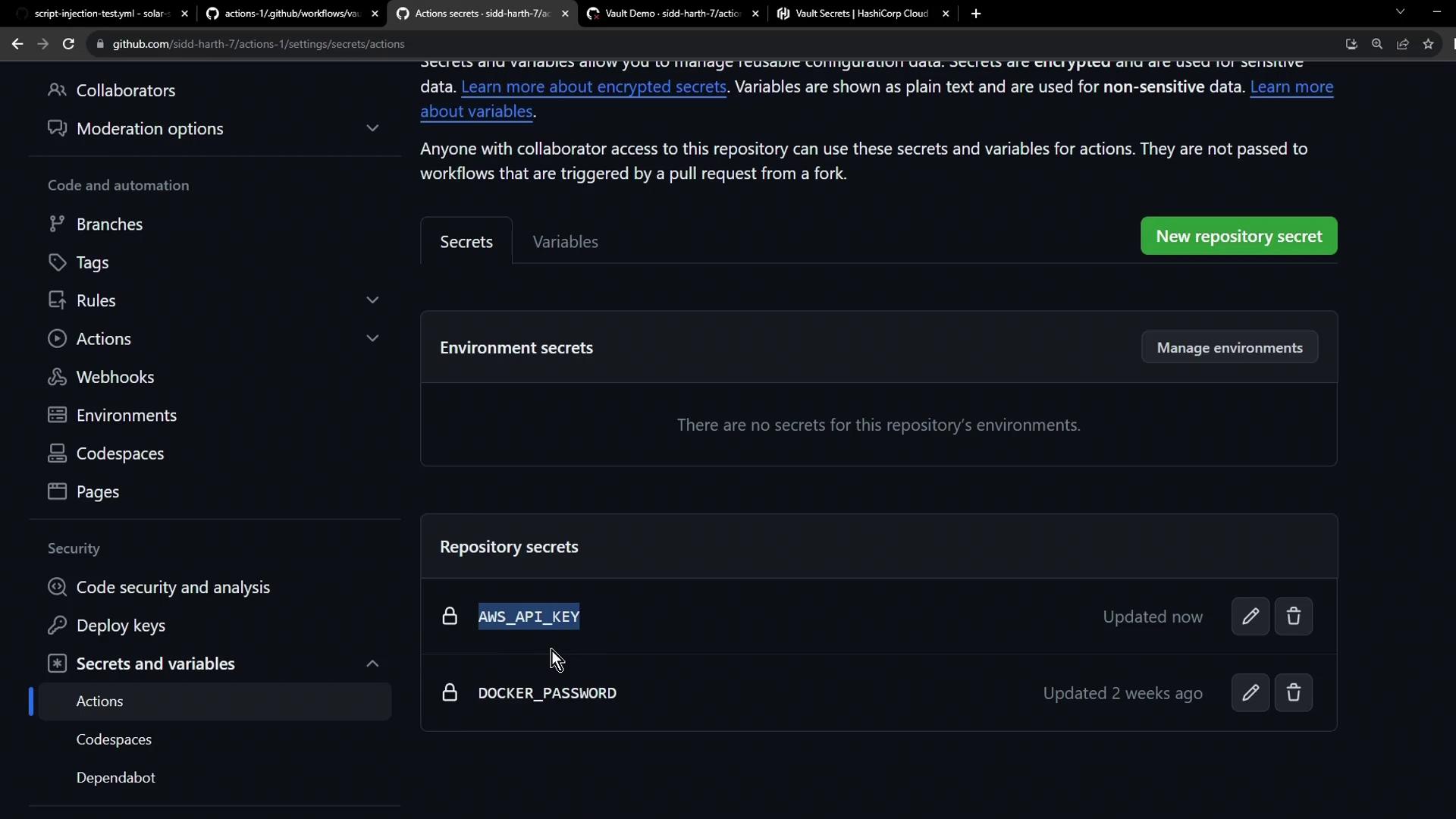
After syncing, revisit Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions to confirm AWS_API_KEY appears alongside other repository secrets:
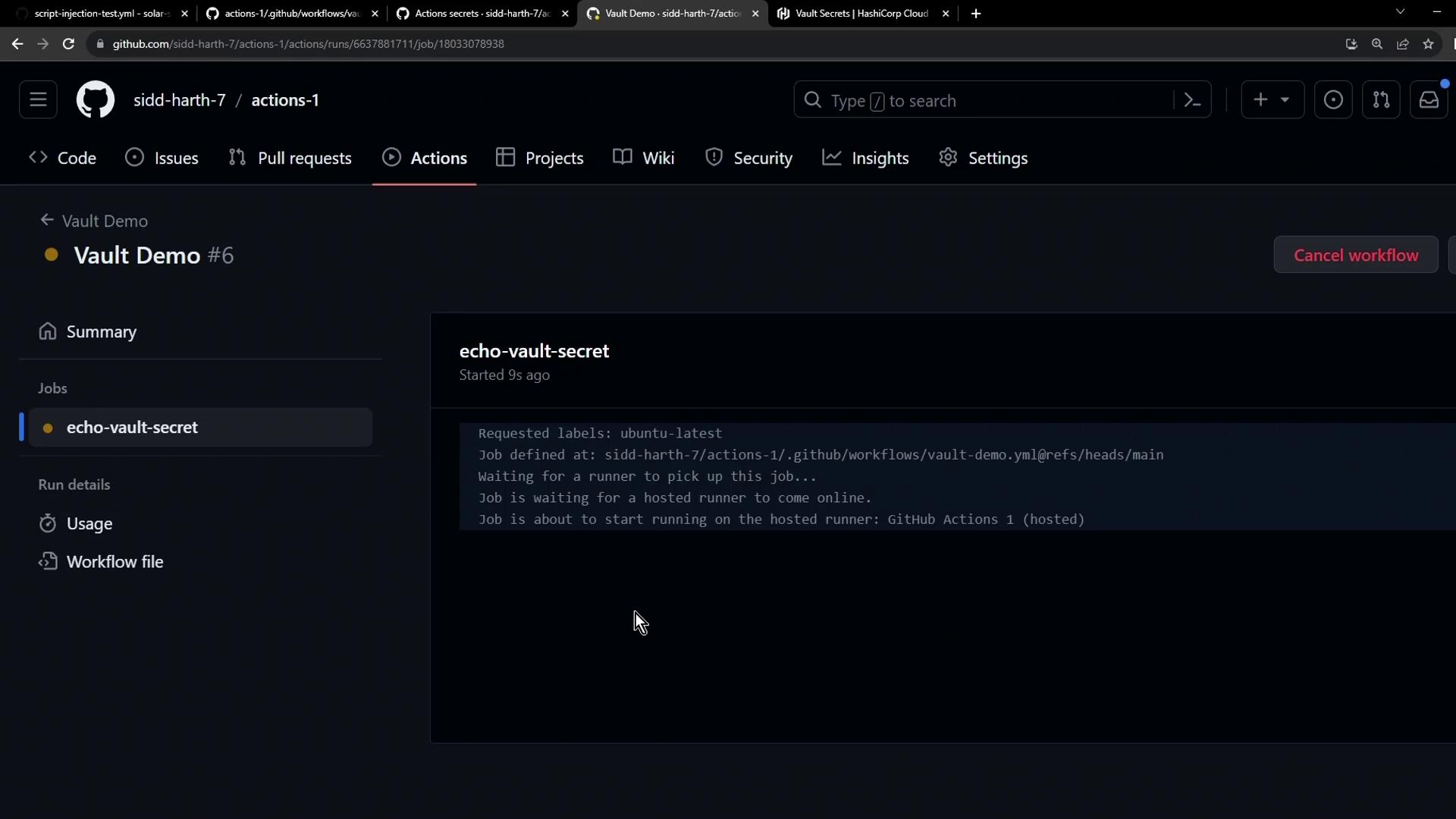
Re-run the Vault Demo workflow. The secret check now passes:
# Masked secret check
if [[ -z "***" ]]; then
echo "Secret Not Found"
exit 1
else
echo "Secret Found"
exit 0
fi
# Output:
Secret Found
Warning
Always verify that only the minimum required permissions are granted when authorizing integrations. Avoid exposing secrets in plaintext logs.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content