In this guide, we’ll show you how to speed up your GitHub Actions workflows by caching Node.js dependencies. By storing node_modules between runs, you can dramatically reduce install times and lower CI costs.
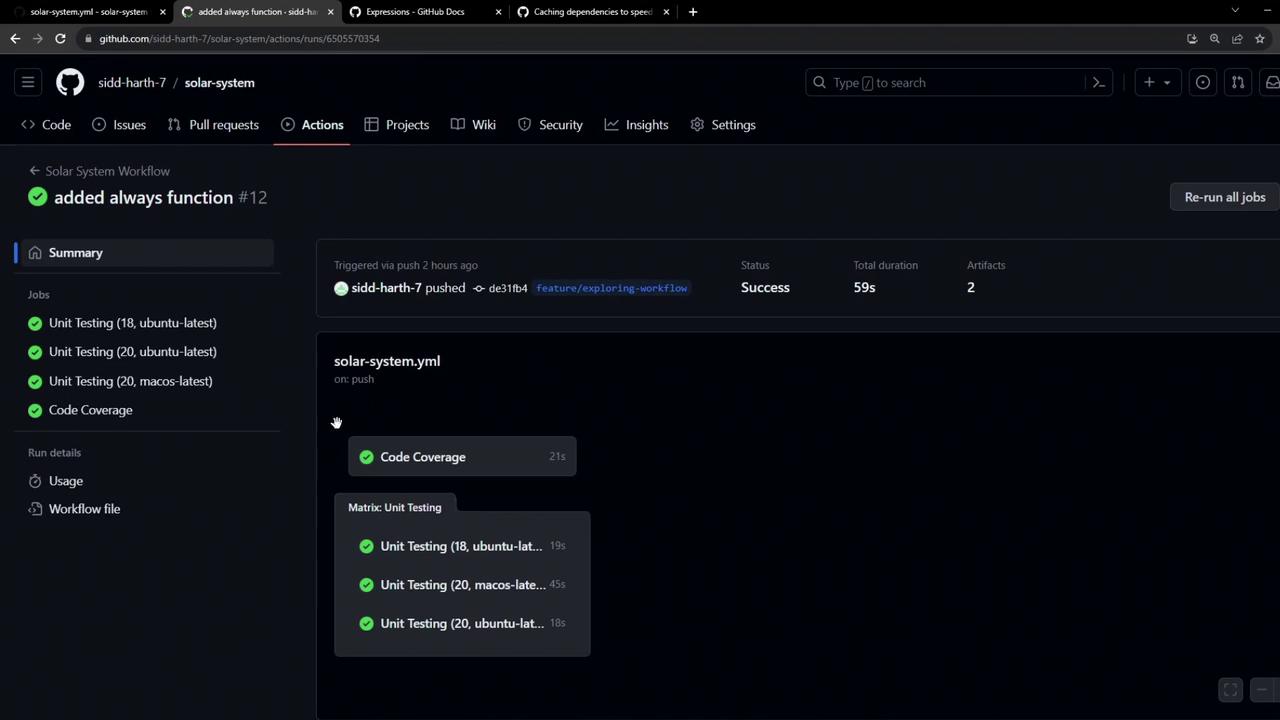
Our initial CI run for the solar-system project completed in 59 seconds :
Here’s the breakdown of job durations:
Job Duration Code Coverage 21s Unit Testing (Ubuntu) 19s Unit Testing (macOS) 45s Unit Testing (Windows) 18s
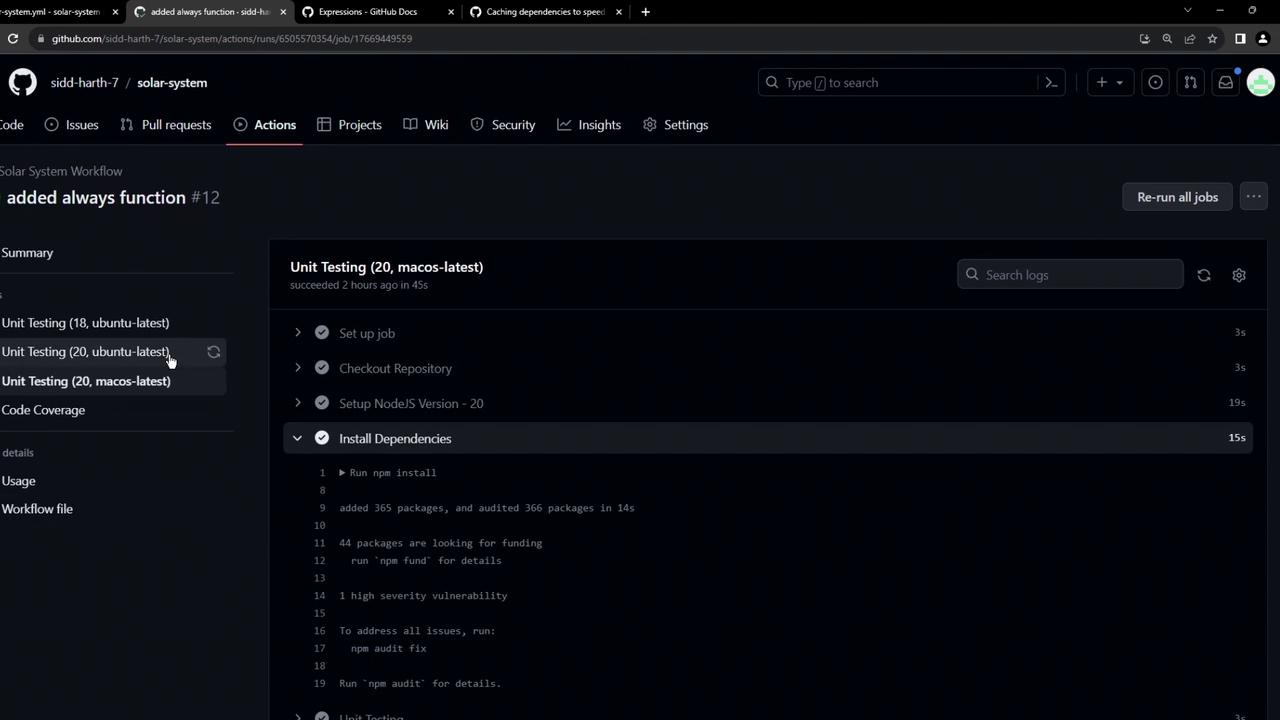
On macOS, the Setup Node.js and Install Dependencies steps took about 20s and 15s respectively:
By default each job runs:
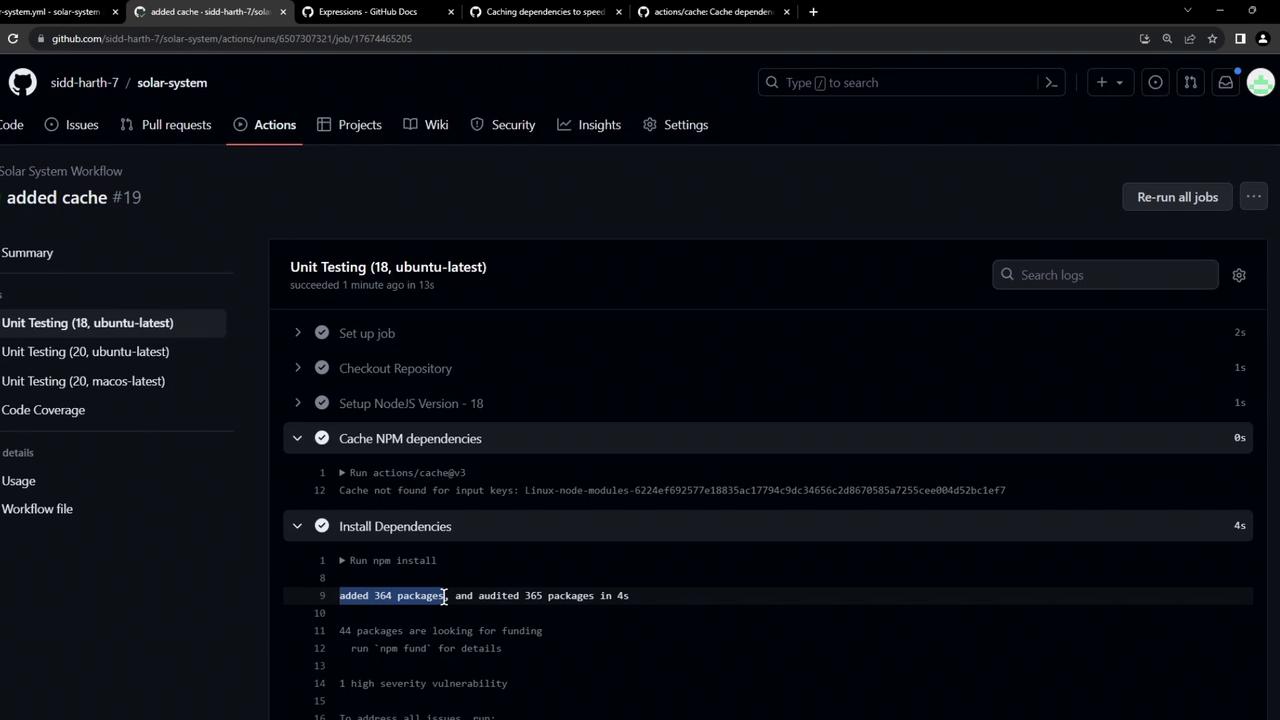
Run npm install added 364 packages, and audited 365 packages in 5s 44 packages are looking for funding run `npm fund` for details …
As your package.json grows, so do install times. Let’s fix that with caching.
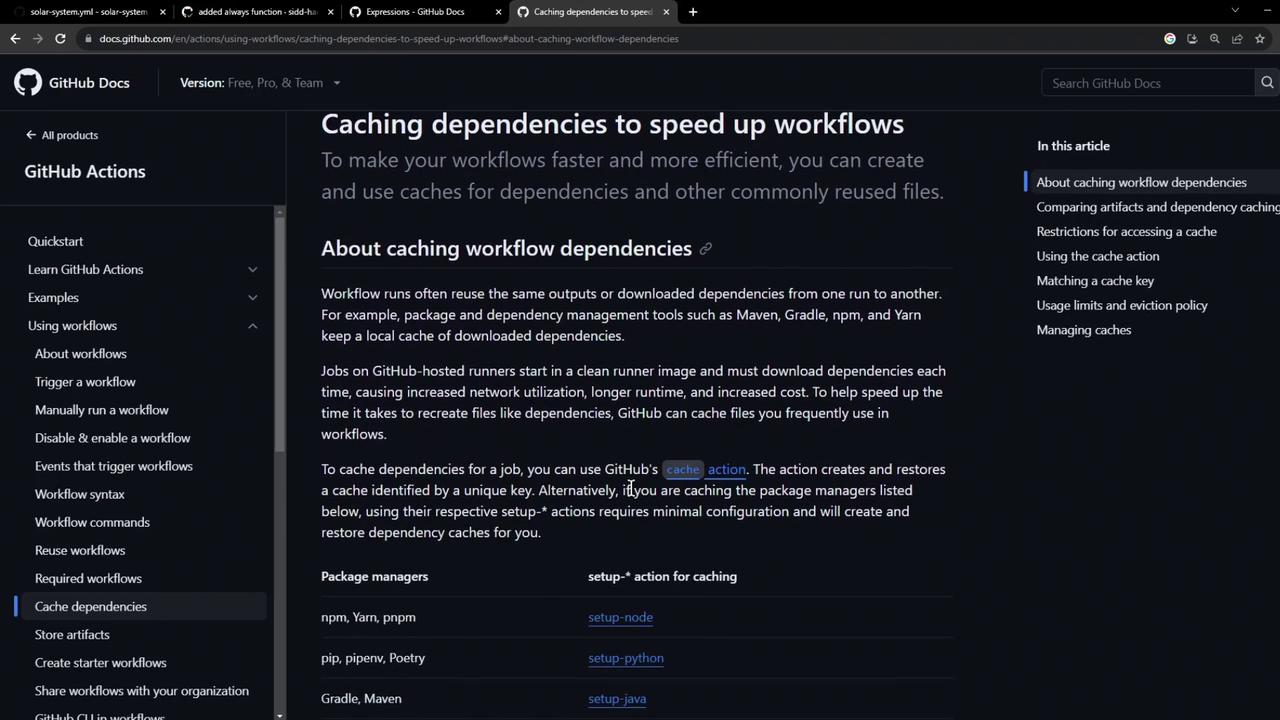
GitHub’s actions/cache action lets you save and restore directories or files across jobs and workflow runs. Unlike artifacts (which are job outputs), caches retain dependencies that rarely change—like node_modules.
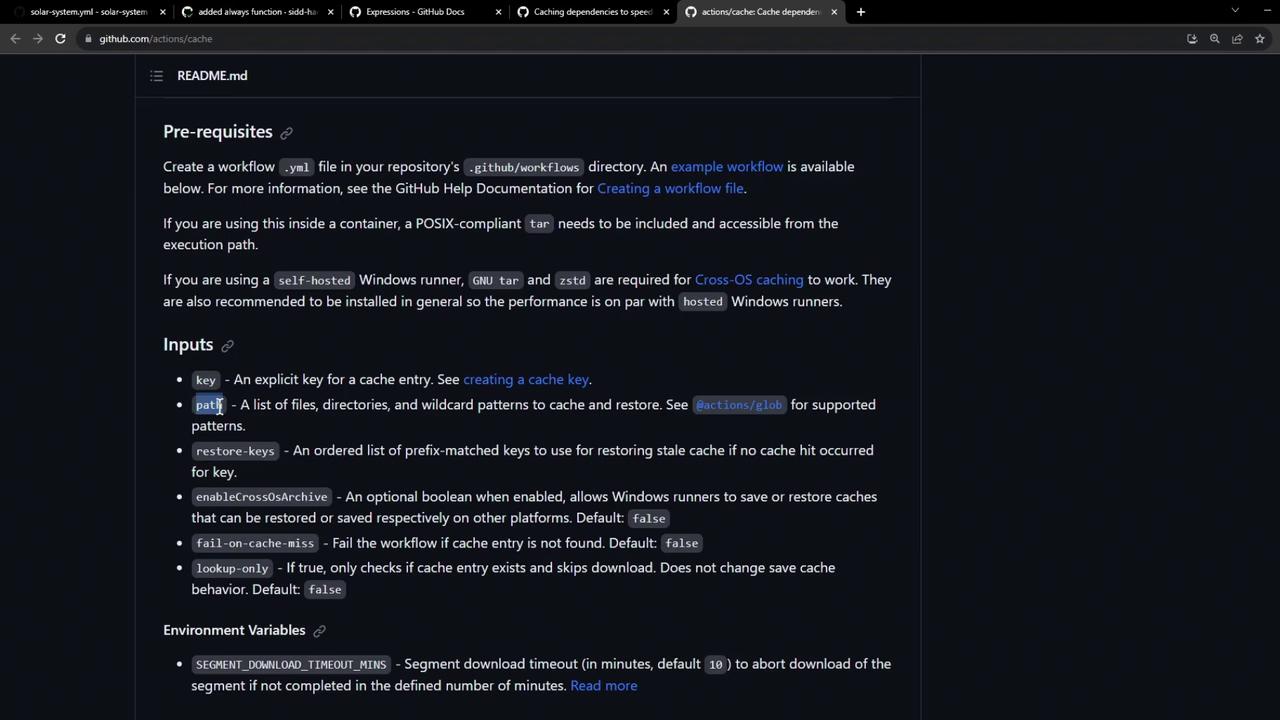
You need to specify two inputs:
path : The directory or file to cache (e.g., node_modules).key : A unique identifier for the cache, typically including OS and a hash of lockfiles.
Example from the docs:
- name : Save Primes id : cache-primes-save uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : | path/to/dependencies some/other/dependencies key : ${{ steps.cache-primes-restore.outputs.cache-primary-key }}
Including hashFiles('package-lock.json') in your key invalidates the cache whenever dependencies change.
Implementing Caching in Our Workflow We’ll integrate cache steps into both unit-testing and code-coverage jobs.
Unit Testing Job jobs : unit-testing : name : Unit Testing runs-on : ${{ matrix.operating_system }} strategy : matrix : nodejs_version : [ 18 , 20 ] operating_system : [ ubuntu-latest , macos-latest ] exclude : - nodejs_version : 18 operating_system : macos-latest steps : - name : Checkout Repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Setup Node.js ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} uses : actions/setup-node@v3 with : node-version : ${{ matrix.nodejs_version }} - name : Cache NPM dependencies uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : node_modules key : ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }} - name : Install Dependencies run : npm install - name : Run Unit Tests run : npm test - name : Archive Test Results if : always() uses : actions/upload-artifact@v3 with : name : mocha-test-results path : test-results.xml
Key configuration:
path: node_modules caches installed packages.key: ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }}
${{ runner.os }} separates caches per OS.hashFiles('package-lock.json') busts the cache when lockfile updates.
Code Coverage Job code-coverage : name : Code Coverage runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - name : Checkout Repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Setup Node.js 18 uses : actions/setup-node@v3 with : node-version : 18 - name : Cache NPM dependencies uses : actions/cache@v3 with : path : node_modules key : ${{ runner.os }}-node-modules-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }} - name : Install Dependencies run : npm install - name : Run Coverage continue-on-error : true run : npm run coverage - name : Archive Coverage Report uses : actions/upload-artifact@v3 with : name : coverage-report path : coverage
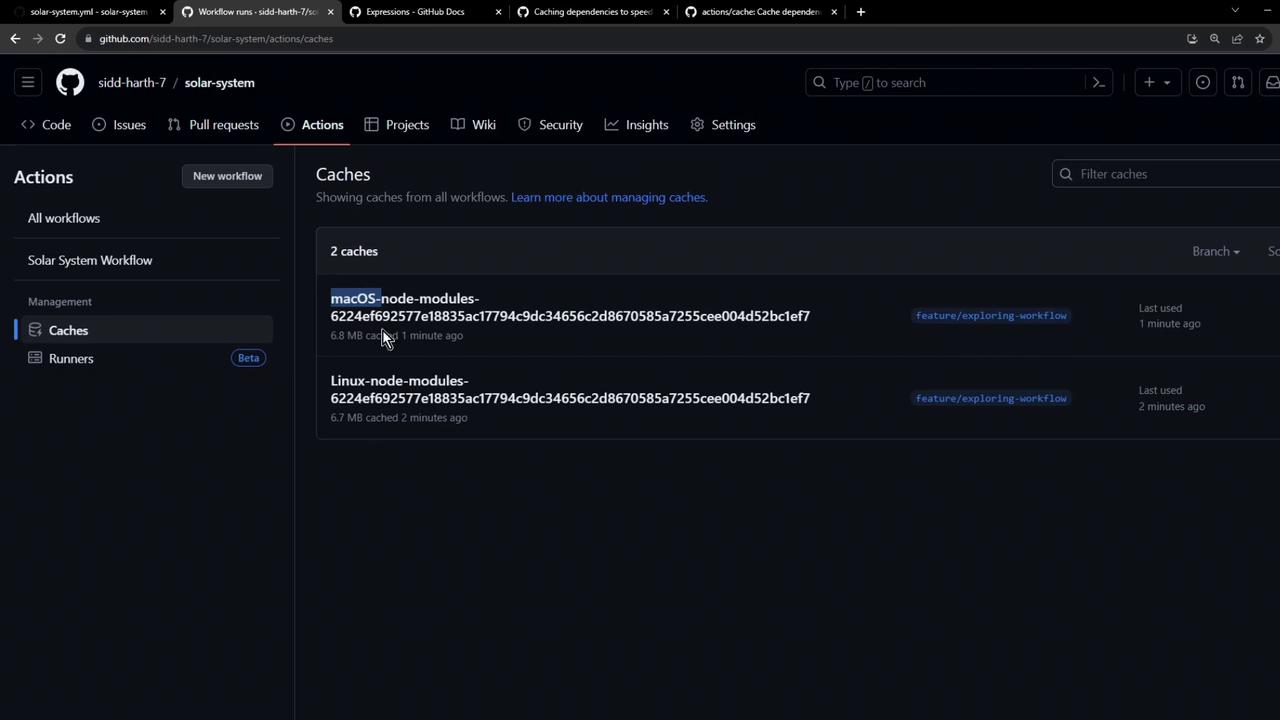
First Workflow Run: Cache Creation After pushing these changes, visit Settings → Caches in your repo to see cache entries:
On the first run, the Cache NPM dependencies step reports “Cache not found” and installs packages as usual:
Once installation completes, the cache is saved:
/usr/bin/tar --posix -cf cache.tzst ... Cache Size: ~7 MB (7025093 B ) Cache saved successfully Cache saved with key: Linux-node-modules-6224ef692577e18835ac17794c9dc34656c2d8679585a7255cee00452bc1ef7
You’ll now see separate cache entries for macOS and Linux:
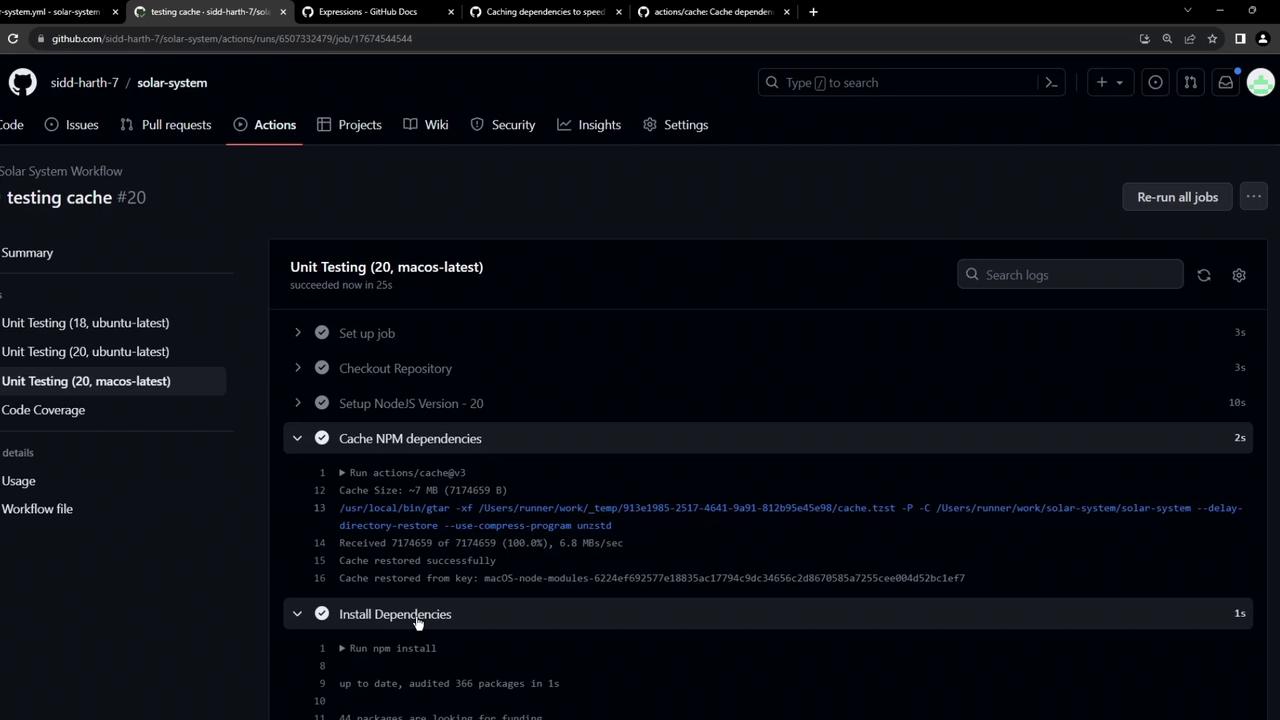
Subsequent Run: Cache Restoration On the next push, the workflow pulls down the saved cache in under a second:
# Run actions/cache@v3 Cache Size: ~7 MB (702593 B) /usr/bin/tar -xf .../cache.tzst ... Cache restored successfully Cache restored from key: Linux-node-modules-6224ef692577e18835ac17794c9dc34656c2d8679585a7255cee00452bc1ef7 # Run npm install up to date, audited 365 packages in 965ms ...
Install times drop from 10–20s to ~1s.
Conclusion By caching node_modules with actions/cache , you’ll see faster CI runs and reduced compute costs. In our next article, we’ll cover advanced cache invalidation strategies when dependencies change.
Links and References