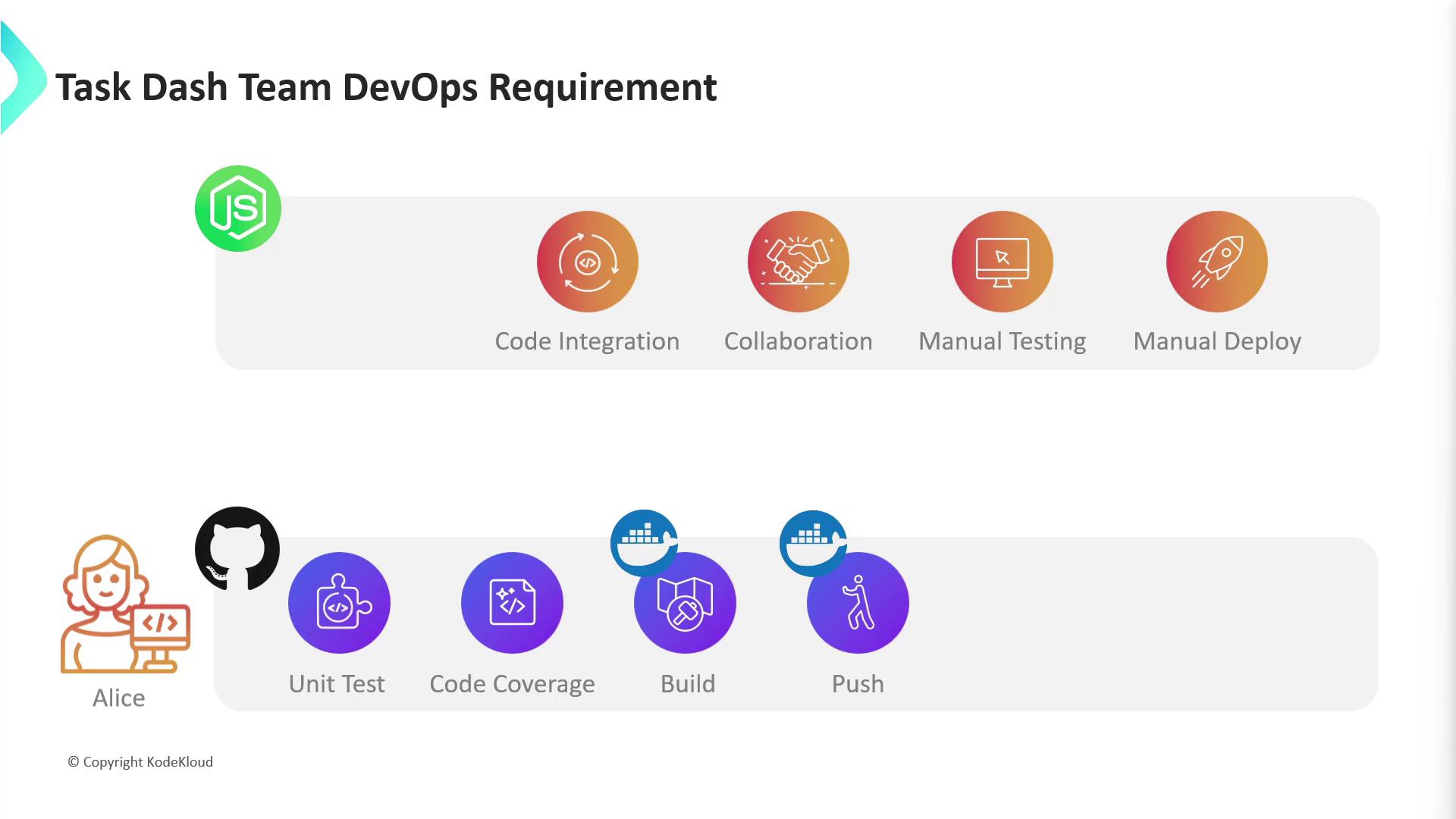
- No version control system
- Manual, slow testing
- Risky, manual deployments to development, staging, and production
- Adopt GitHub for version control and collaboration
- Automate unit testing and measure code coverage
- Build and push Docker images
- Deploy to Kubernetes clusters
- Integrate automated end-to-end testing
Workflow Challenges and Automation Roadmap
Alice also plans to add automated integration testing as a final step. Successful execution of these stages will eliminate current pain points—but first, the team must choose a CI/CD tool.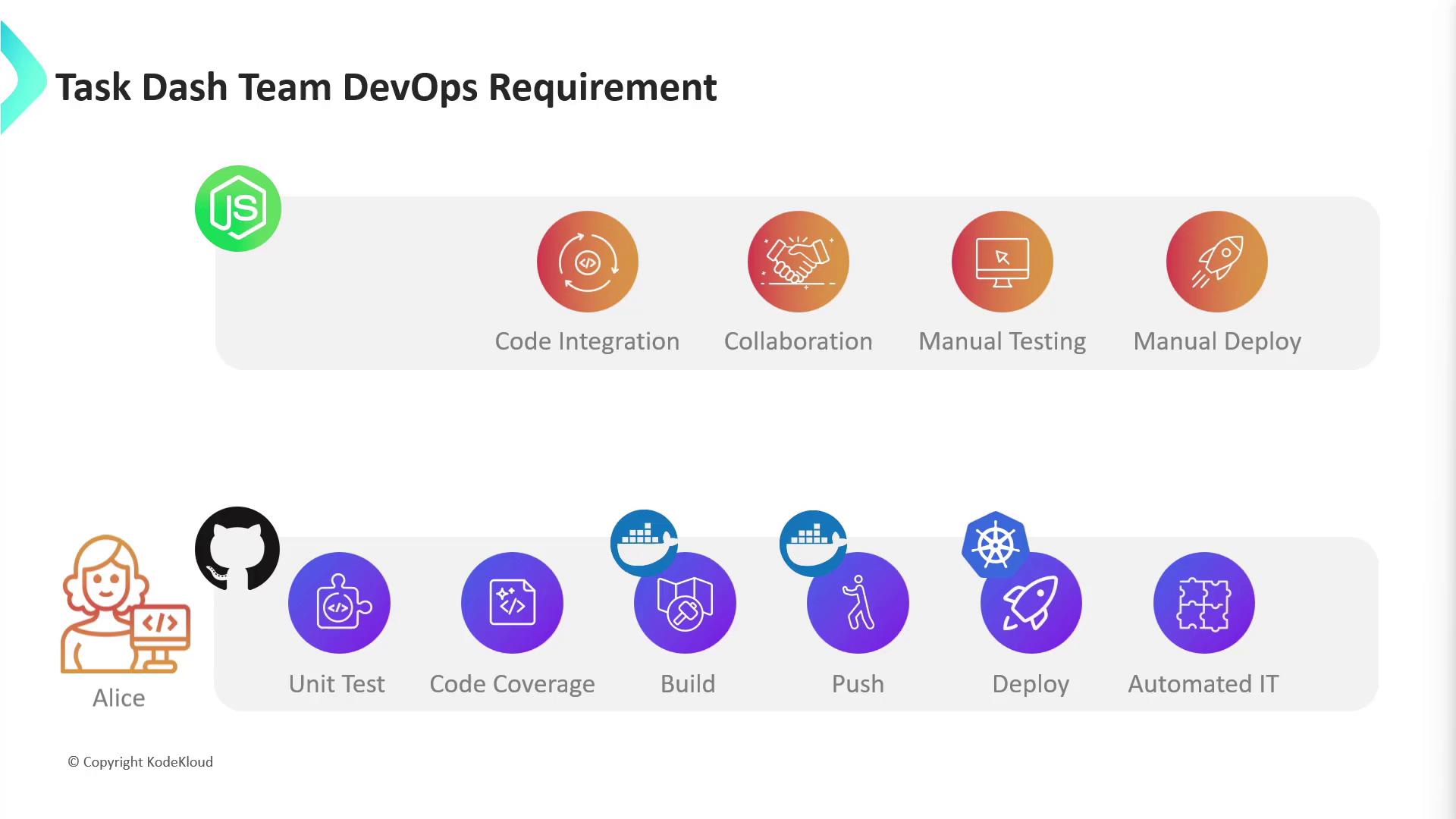
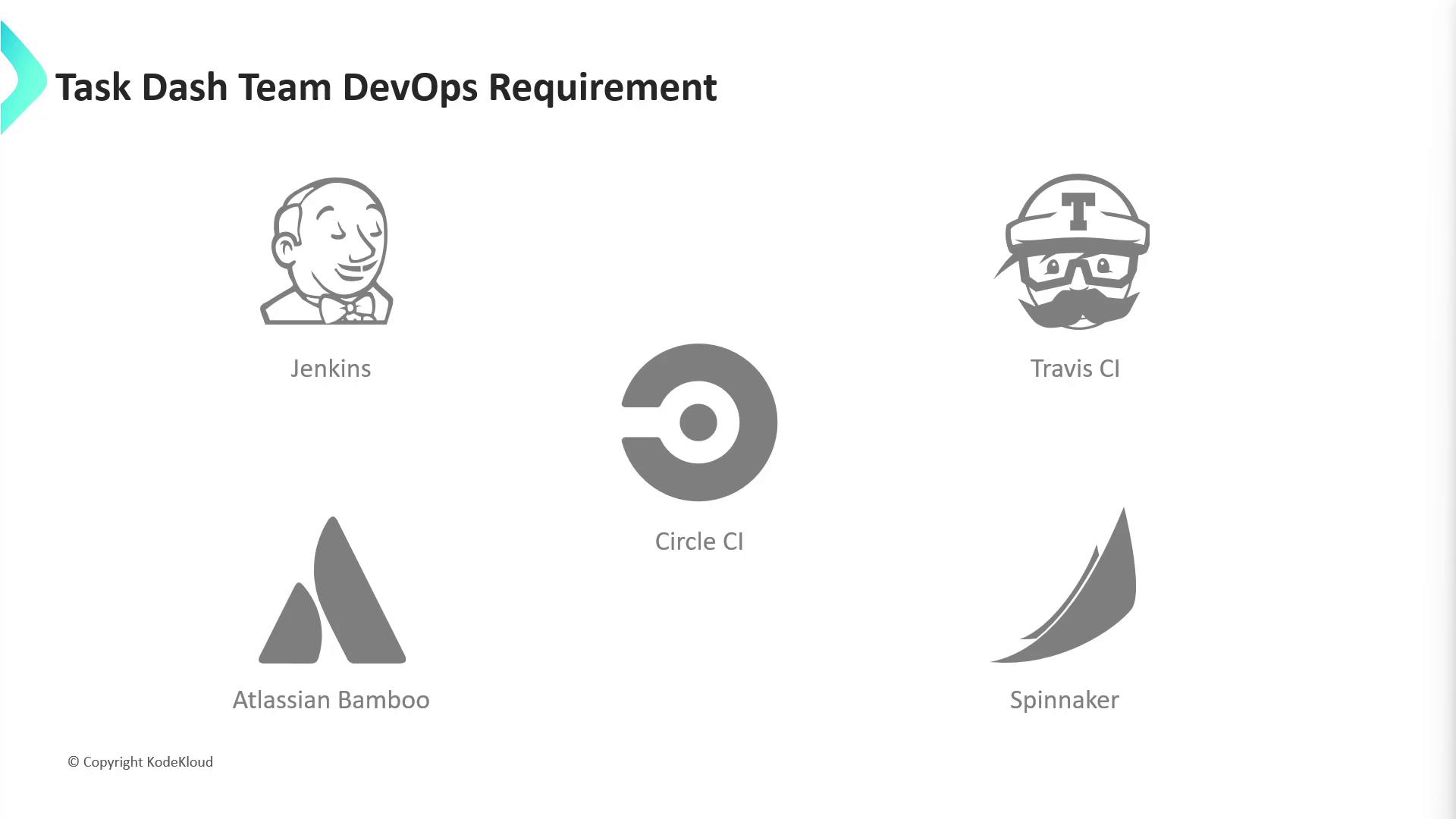
Comparing CI/CD Tools
The team evaluated several popular CI/CD platforms:| Tool | Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | Open source, self-hosted | Highly extensible with thousands of plugins |
| Travis CI | Cloud-hosted | Native GitHub integration |
| CircleCI | Cloud/CVM | Flexible resource classes |
| Bamboo | Commercial | Integrated with Atlassian suite |
| Spinnaker | Open source | Multi-cloud deployment pipelines |
Self-hosting Jenkins requires provisioning infrastructure, managing plugins, and ensuring compatibility across multiple language runtimes.
Jenkins Setup Complexity
To stand up a Jenkins server for the Node.js pipeline, Alice’s team must:- Provision a VM with sufficient CPU, memory, and disk
- Install and configure Java JDK, firewall rules, and Jenkins plugins
- Install Node.js and npm (multiple versions)
- Install Docker for container builds
- Add Kubernetes tools (
kubectl, Helm, etc.) - Set up external integration testing and reporting tools

GitHub Actions offers a native, cloud-scalable CI/CD solution directly within your GitHub repository—no separate servers required.
Next Steps: Building with GitHub Actions
In the upcoming sections, we’ll create GitHub Actions workflows for a real-world Node.js application. You’ll learn how to:- Automate code integration, linting, and unit testing
- Build and push Docker images to a registry
- Deploy to Kubernetes using Helm
- Run end-to-end integration tests