Git Workflow for Feature Development
All source code is versioned in a Git repository, often hosted on platforms like GitHub or GitLab. Teams typically follow this branching strategy:- main (or master): Production-ready code
- feature/*: Isolated branches for new work
- Create a feature branch off
main. - Commit code and open a Pull Request (PR).
- Run automated checks via CI.
- Peer-review and approve the PR.
- Merge back into
mainand trigger deployment.
Keeping
main always deployable reduces integration headaches and rollbacks.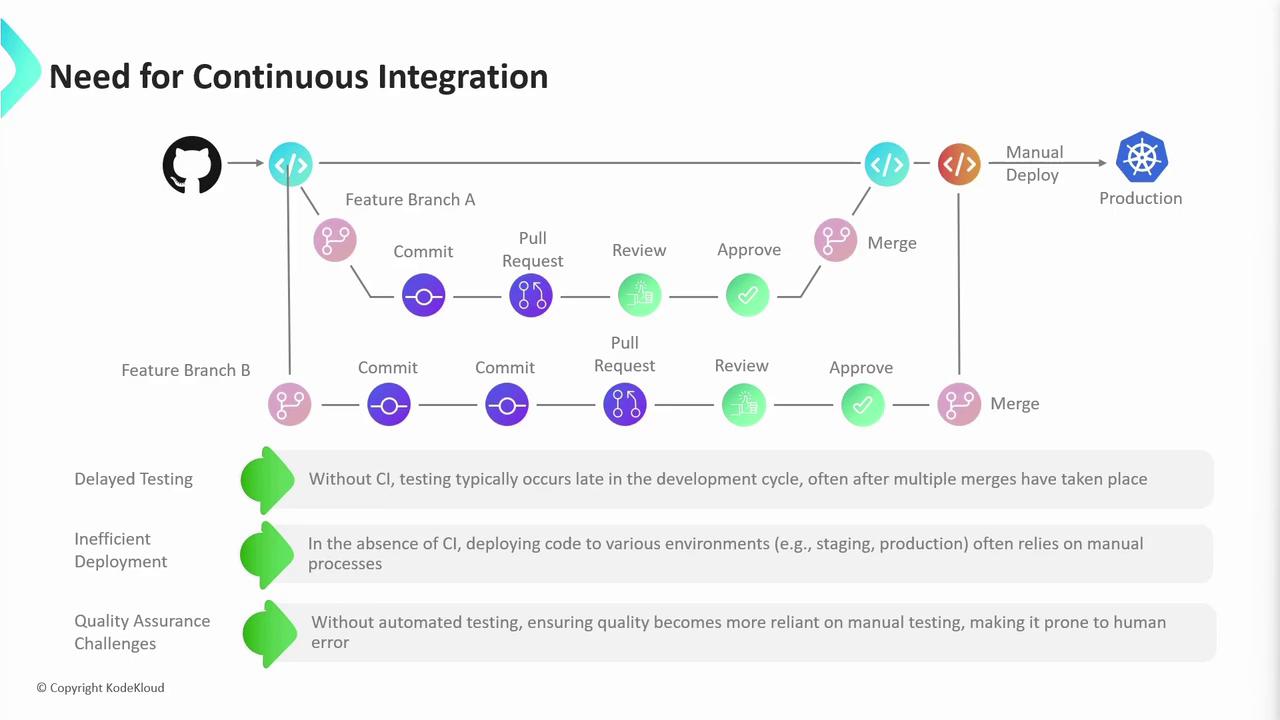
- Delayed feedback and bug discovery
- Configuration drift between environments
- Heavy reliance on manual QA
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) automates the moment code is pushed:-
Developer opens a PR against
main. -
A CI pipeline runs:
Stage Purpose Example Tool Unit Tests Verify individual components Jest, JUnit Dependency Scanning Identify outdated or vulnerable libs Dependabot, Snyk Build & Artifact Creation Compile code and produce deployables Docker, Maven Code Quality & Security Static analysis and vulnerability check SonarQube, CodeQL - Any failure halts the merge and notifies the author.
-
On success, the PR is merged and triggers a final CI run on the updated
mainbranch.
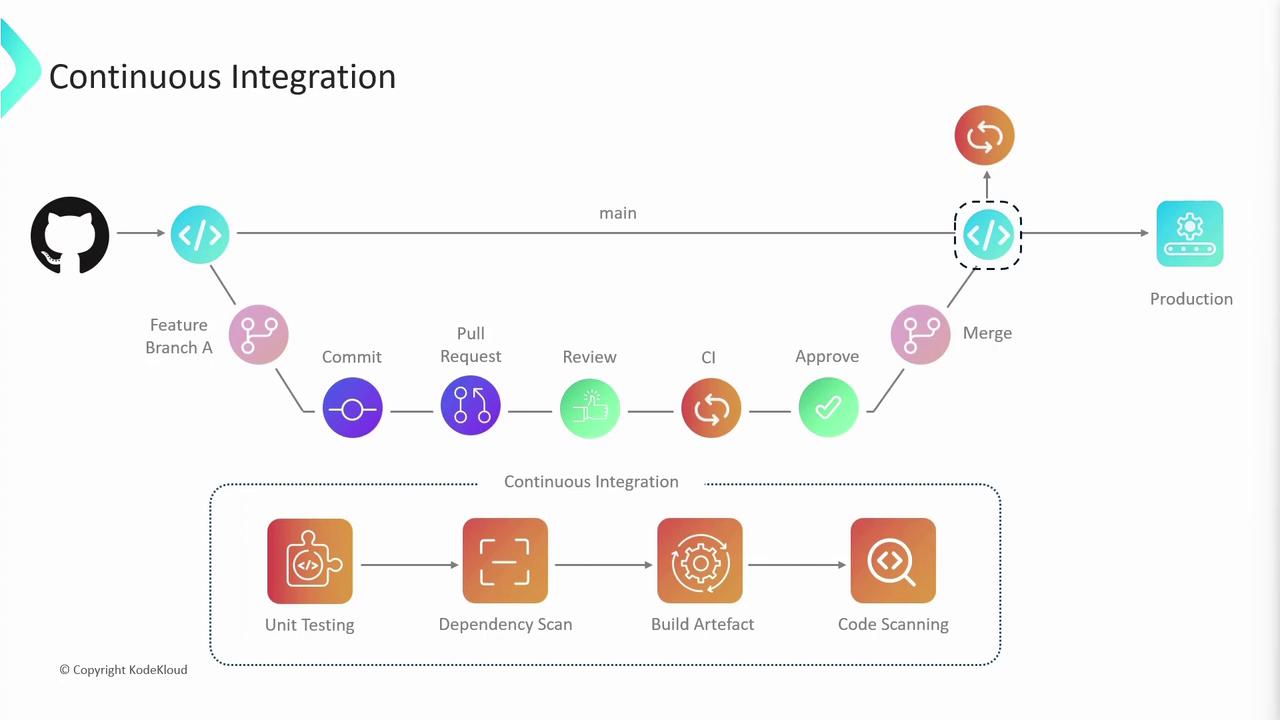
main ensures compatibility across all contributions.
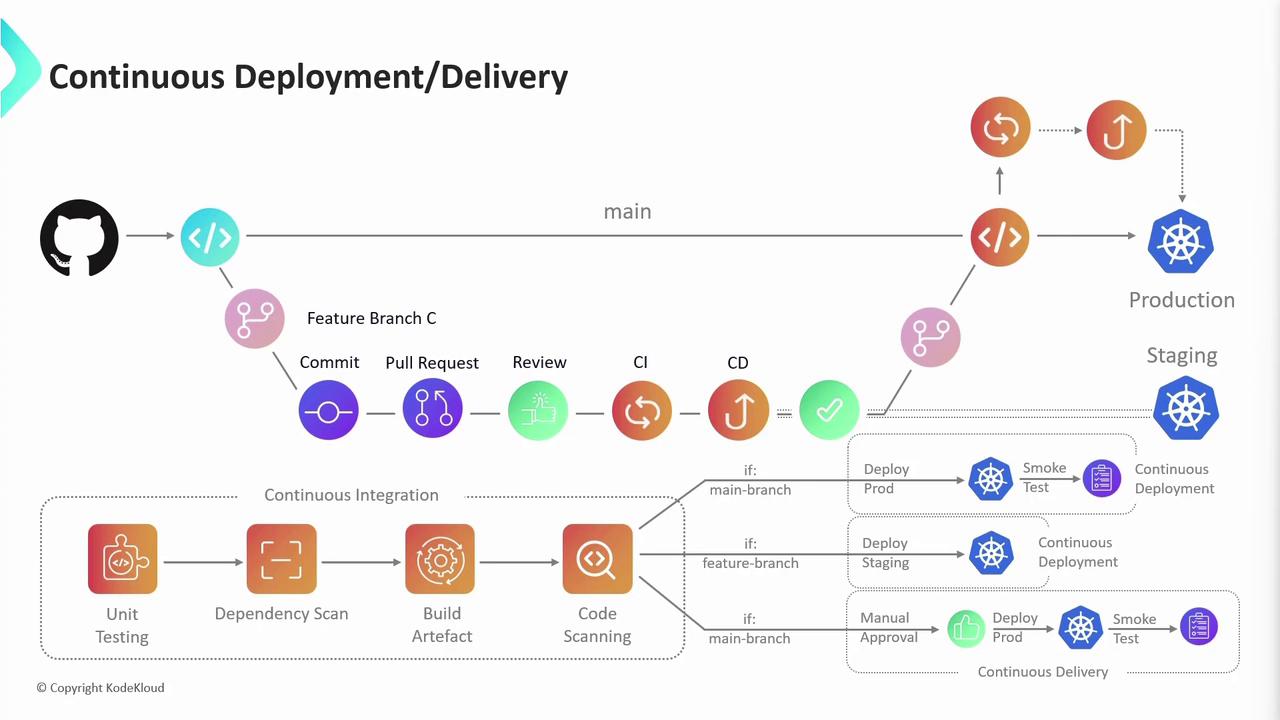
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment
After CI, the next stage is CD—either Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment:-
Continuous Delivery
- Deployments to staging happen automatically.
- Production releases require manual approval.
-
Continuous Deployment
- Every successful build on
mainis pushed straight to production without human intervention.
- Every successful build on
- Deploy to staging → run integration/regression tests
- (Optional) Manual approval for production
- Deploy to production
Automated production deployments can speed delivery but require robust rollback and monitoring strategies.