GitHub Actions can respond to many events—from code pushes and pull requests to scheduled cron jobs and manual dispatch. In this guide, we’ll cover the most common triggers, show you how to configure them, and demonstrate how to combine multiple triggers in a single workflow.
For a complete list of events, see the official documentation .
Common Repository Events You can launch workflows in response to repository activity. Below is a quick reference:
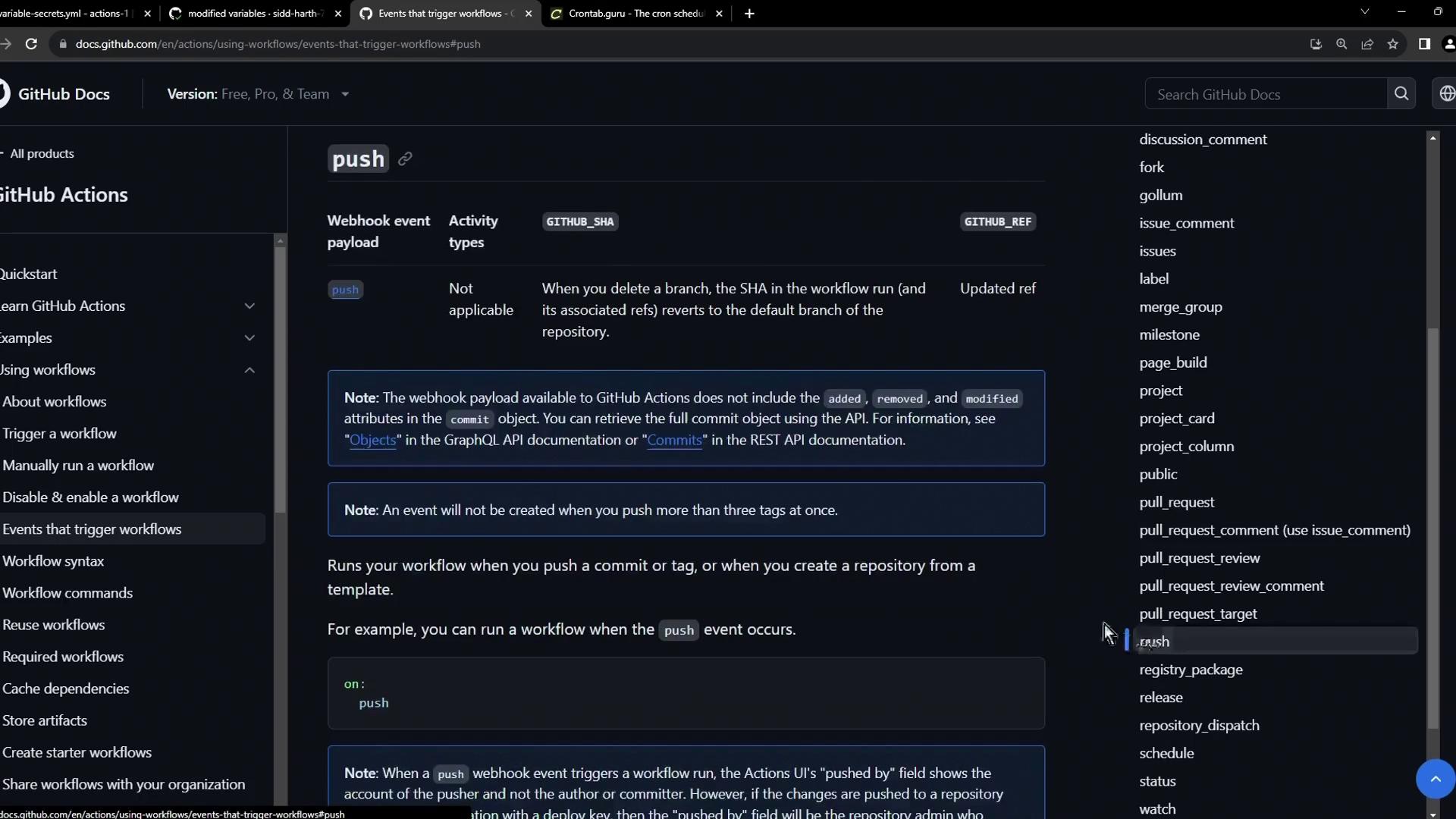
Event Description YAML snippet push Run on commits pushed to branches or tags on: pushpull_request Trigger on PR open, edit, close, etc. see example below issues Fire when issues are opened or modified on: issuesrelease Trigger on draft, published, or edited on: releasefork Run when someone forks the repository on: fork
1. Push The simplest trigger is push. It fires whenever you push commits:
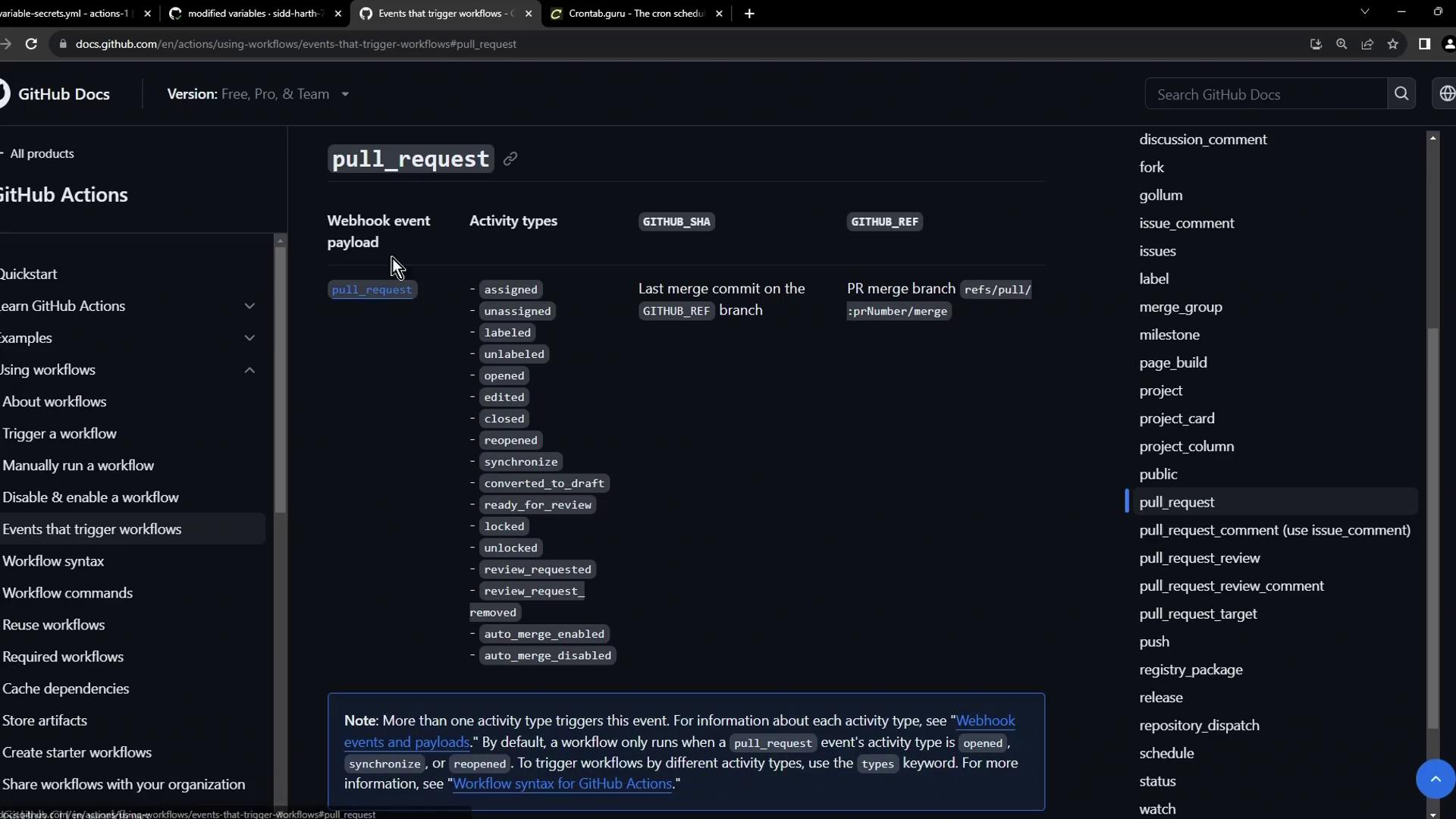
2. Pull Request Trigger workflows when pull requests change state—opened, edited, assigned, or closed:
on : pull_request : types : [ opened , edited , closed , assigned ]
You can filter by branches or tags under each event to narrow down when the workflow runs. See GitHub Actions filters for details. Scheduled Workflows Use schedule with cron syntax to run jobs at regular intervals.
on : schedule : # Quote strings because '*' has special meaning in YAML - cron : '30 5 * * 1-5' - cron : '0 0 * * 0'
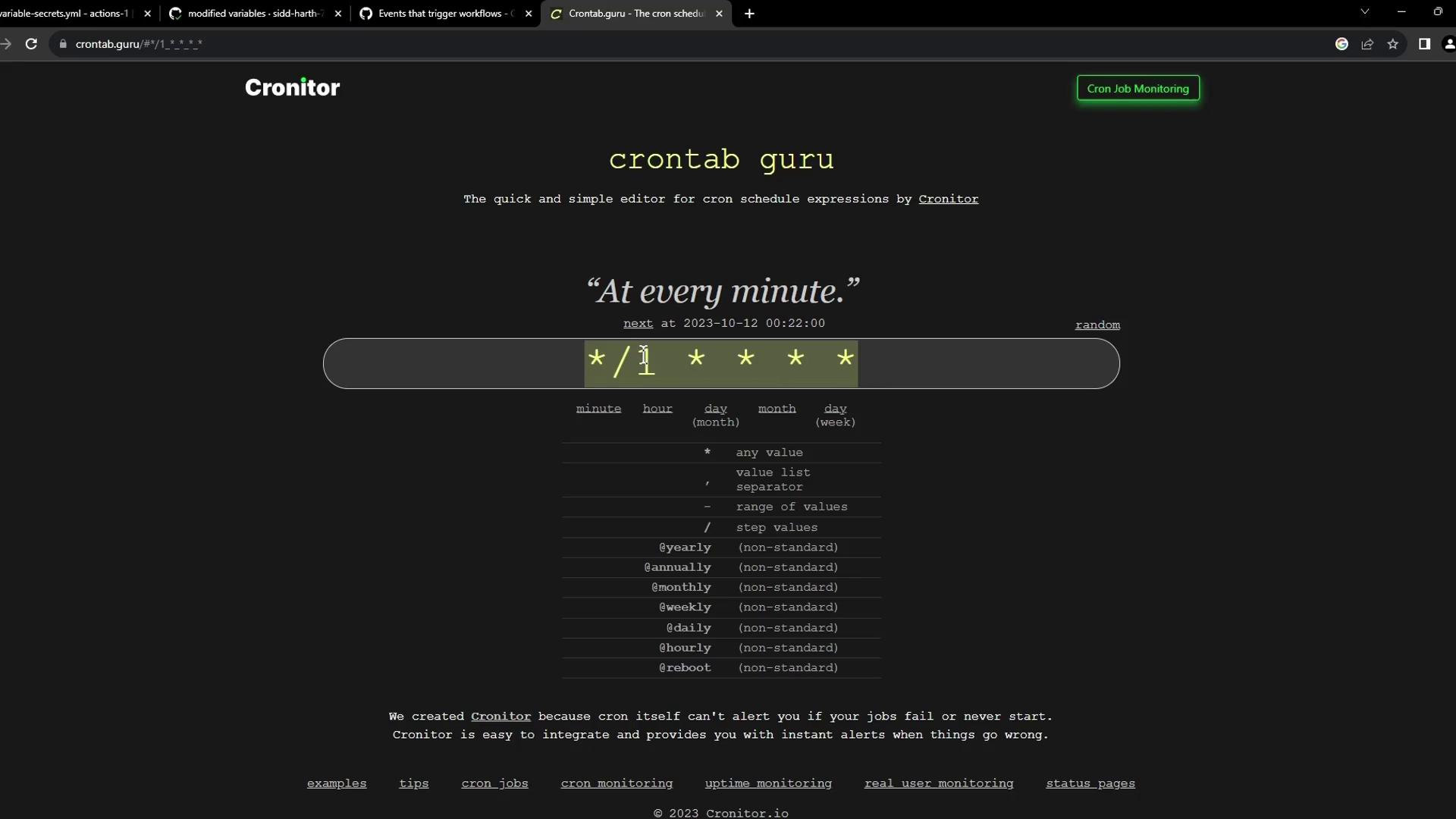
Running jobs too frequently can exhaust your GitHub Actions minutes. Always double-check your cron schedules.
If you need to test or build complex expressions, Crontab Guru is a fantastic visual tool:
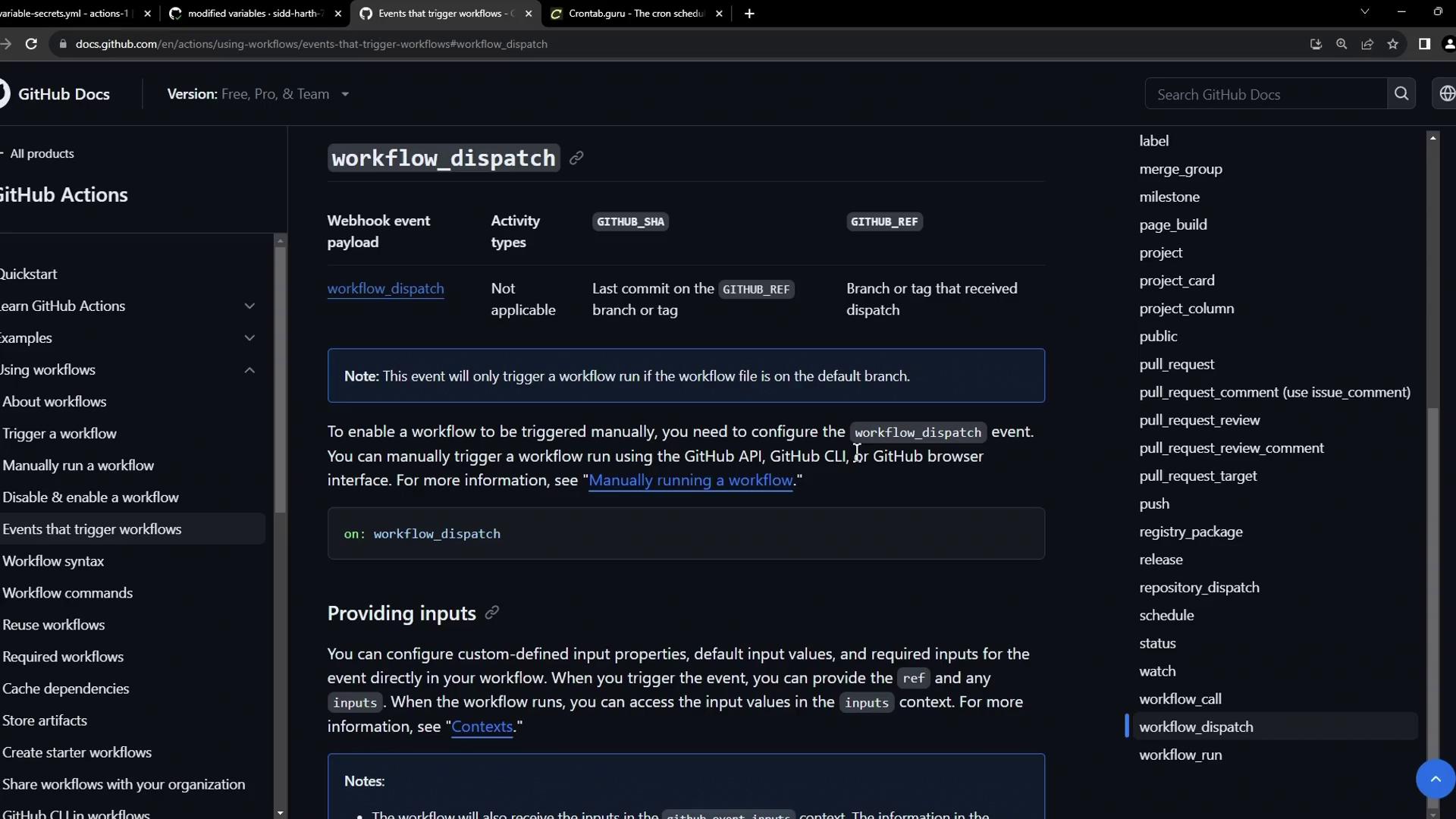
Manual Triggers with workflow_dispatch Add workflow_dispatch to let users kick off a workflow by pushing a button. You can even define input parameters:
on : workflow_dispatch : inputs : logLevel : description : 'Log level' required : true default : 'warning' type : choice options : - info - warning - debug tags : description : 'Include test scenario tags' required : false type : boolean environment : description : 'Target environment' required : true
Use these inputs in your job steps:
jobs : display-inputs : runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - name : Show inputs run : | echo "Log level: ${{ inputs.logLevel }}" echo "Tags: ${{ inputs.tags }}" echo "Environment: ${{ inputs.environment }}"
Combining Schedule and Manual Dispatch You can merge multiple triggers into one workflow. Here’s an example that builds, logs in, and pushes a Docker image on both a schedule and via manual dispatch.
name : CI/CD Docker Pipeline on : schedule : - cron : '*/1 * * * *' workflow_dispatch : env : CONTAINER_REGISTRY : docker.io IMAGE_NAME : github-actions-nginx jobs : build-and-publish : runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - name : Build image run : | docker build -t ${{ env.CONTAINER_REGISTRY }}/${{ vars.DOCKER_USERNAME }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:latest . - name : Authenticate run : | echo "${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}" | docker login \ --username ${{ vars.DOCKER_USERNAME }} --password-stdin - name : Push image run : | docker push ${{ env.CONTAINER_REGISTRY }}/${{ vars.DOCKER_USERNAME }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:latest
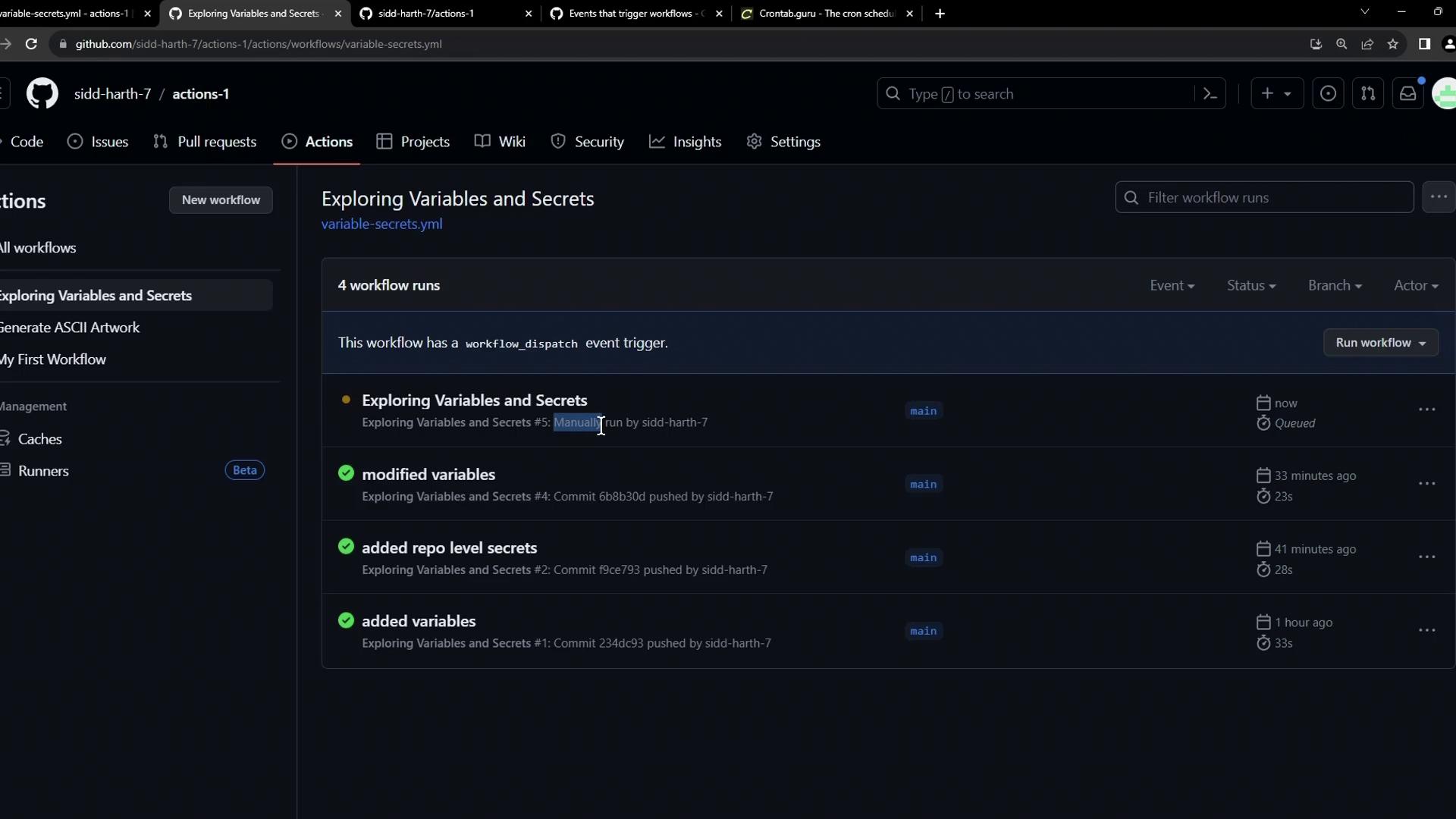
Once you push this file, the Actions tab will display scheduled runs alongside a Run workflow button for manual execution:
Each entry shows its trigger type—push, schedule, or manual—so you can tailor your CI/CD process to any scenario.
Links and References