GitHub Copilot Certification
Using Copilot Efficiently
Creating API Documentation
Learn how to build and refine interactive API docs using FastAPI’s built-in OpenAPI support. You’ll set up a simple “Fake Data API,” write clear docstrings, and customize the generated Swagger UI and Redoc interfaces.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.7 or higher
- A virtual environment with
fastapi,uvicorn, andpydanticinstalled - SQLite for a local database
Table of Contents
- Project Layout & Dependencies
- Initializing the FastAPI App
- Database Context Manager
- Fetching Fake Data
- Defining the API Endpoint
- Running the Server
- Swagger UI & Redoc Interfaces
- Fine-Tuning Your OpenAPI Schema
- Links and References
1. Project Layout & Dependencies
Ensure your project uses this structure:
.
├── main.py
└── data
└── db
└── fakedata.db
| Dependency | Purpose |
|---|---|
| fastapi | Web framework with OpenAPI support |
| uvicorn | ASGI server |
| pydantic | Data validation and settings |
2. Initializing the FastAPI App
# main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
import sqlite3
from typing import List, Dict
from contextlib import contextmanager
from pathlib import Path
app = FastAPI(
title="Fake Data API",
description="Generate and retrieve random personal data entries via RESTful endpoints",
version="1.0.0",
)
class DataRequest(BaseModel):
count: int
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent
DATA_DIR = BASE_DIR / "data" / "db"
DB_PATH = DATA_DIR / "fakedata.db"
# Ensure database directory exists
DATA_DIR.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
3. Database Context Manager
# main.py (continued)
@contextmanager
def get_db_connection():
"""
Manage SQLite connections with row_factory for dict-like access.
Yields:
sqlite3.Connection: Active database connection.
Raises:
sqlite3.Error: On connection failures.
"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_PATH)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
try:
yield conn
finally:
conn.close()
4. Fetching Fake Data
# main.py (continued)
def fetch_fake_data(count: int) -> List[Dict]:
"""
Retrieve a random selection of fake data entries.
Args:
count (int): Number of records (1–1000).
Returns:
List[Dict]: Fake data entries.
Raises:
HTTPException(400): If count is out of range.
HTTPException(404): If no records are found.
"""
if not (1 <= count <= 1000):
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Count must be between 1 and 1000")
with get_db_connection() as conn:
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(
"""
SELECT first_name, last_name, email_address, age, city, occupation
FROM fake_data
ORDER BY RANDOM()
LIMIT ?
""",
(count,),
)
rows = cursor.fetchall()
if not rows:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="No data entries found")
return [dict(row) for row in rows]
Warning
Requests exceeding 1000 entries will return a 400 Bad Request. Always validate count before calling the endpoint.
5. Defining the API Endpoint
# main.py (continued)
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
@app.post(
"/api/v1/getfakedata",
response_model=List[Dict],
tags=["Fake Data Generation"],
summary="Generate random fake personal data entries",
)
async def get_fake_data(request: DataRequest):
"""
Generate and return fake personal data.
- **count**: Number of entries (min: 1, max: 1000)
**Responses**
- 200: Successfully retrieved data
- 400: Invalid parameters
- 404: No records found
- 500: Internal server error
"""
data = fetch_fake_data(request.count)
return JSONResponse(content=data)
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Successfully retrieved fake data |
| 400 | Invalid request parameters |
| 404 | No data entries found |
| 500 | Internal server error |
6. Running the Server
# main.py (continued)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
Start your server:
(venv) $ python main.py
INFO: Started server process [12345]
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Visit:
- Swagger UI: http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs
- Redoc: http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc
- OpenAPI JSON: http://127.0.0.1:8000/openapi.json
7. Swagger UI & Redoc Interfaces
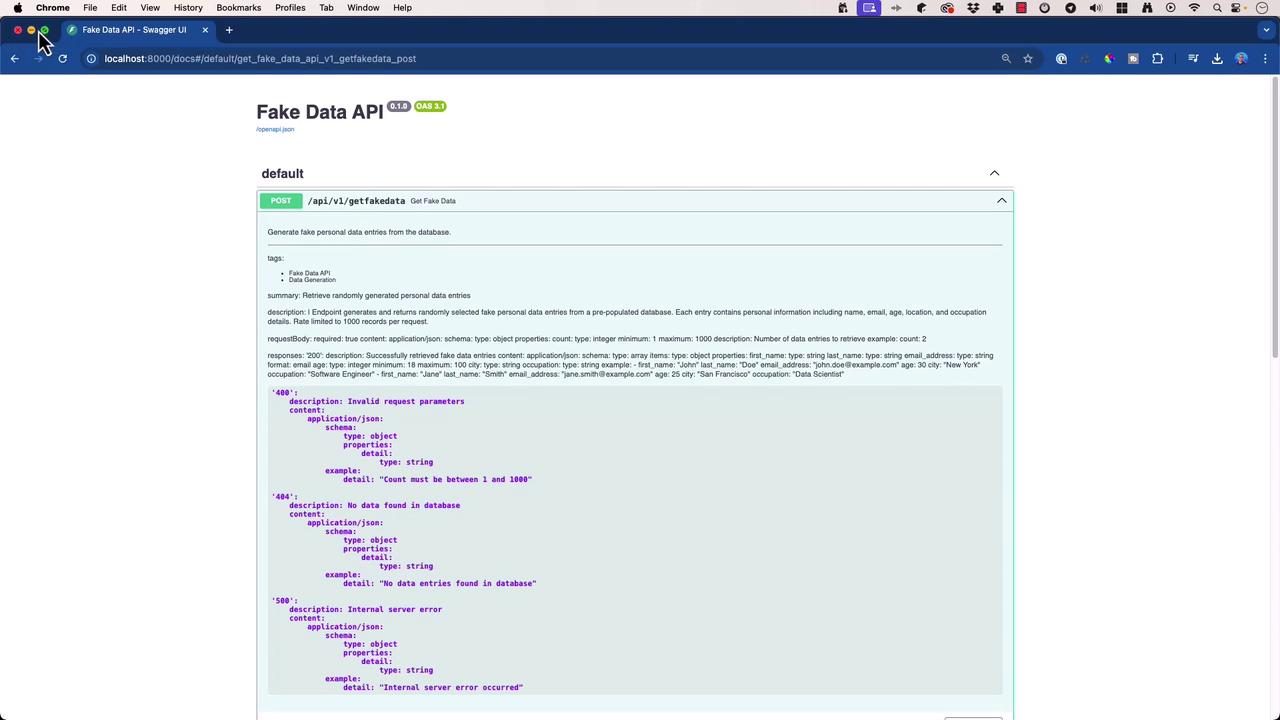
The interactive Swagger UI provides parameter descriptions, request/response examples, and error schemas.
8. Fine-Tuning Your OpenAPI Schema
- Docstring Conventions: Follow PEP 257 and embed OpenAPI YAML blocks for richer metadata.
- Examples & Schemas: Include
examplesections for request/response payloads. - Error Documentation: Clearly list possible HTTP error codes and messages.
- Security & Rate Limits: Add
securitySchemesand rate-limit info undercomponentsand endpoint descriptions.
FastAPI updates your docs in real time as you refine docstrings—no extra tooling required!
9. Links and References
- FastAPI Documentation
- Uvicorn — The Lightning-Fast ASGI Server
- Pydantic Documentation
- SQLite Official Docs
Watch Video
Watch video content