GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Architecture Core Concepts
Executing Shell Scripts in a Job
Streamline your GitLab CI/CD pipelines by extracting complex commands into standalone shell scripts. This approach improves readability, maintainability, and version control for your build logic.
1. Example Inline Job
Below is a simple .gitlab-ci.yml that installs the cowsay gem and runs commands directly:
workflow:
name: Generate ASCII Artwork
ascii_job:
before_script:
- gem install cowsay
script:
- echo "Generating ASCII Artwork using COWSAY Program"
- cowsay -f dragon "Run for cover, I am a DRAGON....RAWR" >> dragon.txt
- grep -i "dragon" dragon.txt
- cat dragon.txt
after_script:
- echo "Executed at the end, can be used for cleaning/removing content"
While this works, embedding multiple commands can quickly clutter your CI file.
Best Practice
Extract repetitive or lengthy command sequences into versioned scripts to keep your pipeline definitions clean and reusable.
2. Create a Dedicated Shell Script
- Open the GitLab Web IDE.
- Add a file named
ascii-script.shat your repository root:
#!/bin/sh
echo "Generating ASCII Artwork using COWSAY Program"
cowsay -f dragon "Run for cover, I am a DRAGON....RAWR" >> dragon.txt
grep -i "dragon" dragon.txt
cat dragon.txt
ls -ltr
Save and commit ascii-script.sh so it’s tracked by Git.
3. Update Your CI Configuration
Modify .gitlab-ci.yml to invoke the script instead of inline commands:
workflow:
name: Generate ASCII Artwork
ascii_job:
before_script:
- gem install cowsay
script:
- ./ascii-script.sh
after_script:
- echo "Executed at the end, can be used for cleaning/removing content"
Commit and push your changes. The pipeline will now call the external script.
4. Monitor Pipeline Status
Navigate to CI/CD > Pipelines in the GitLab UI to view your job status in real time.
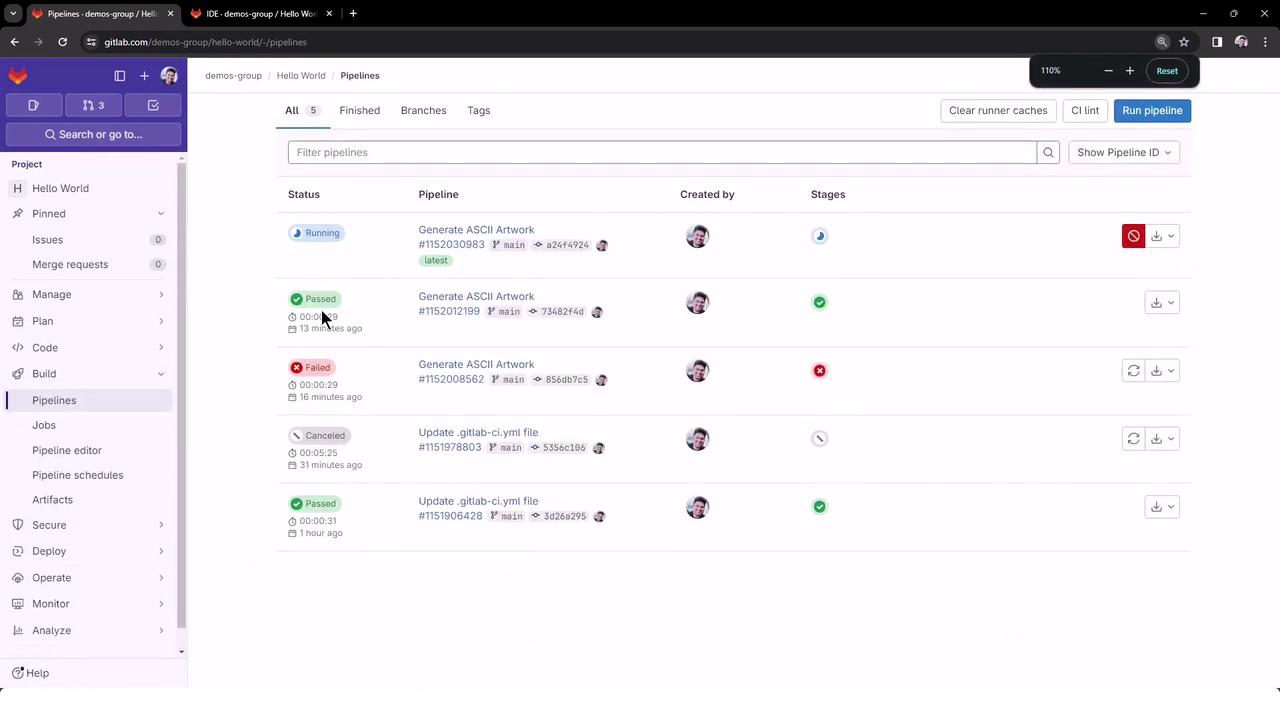
You should see the ascii_job running under the “Generate ASCII Artwork” pipeline.
5. Handling Permission Errors
If your script isn’t executable, GitLab will report a permission denied error:
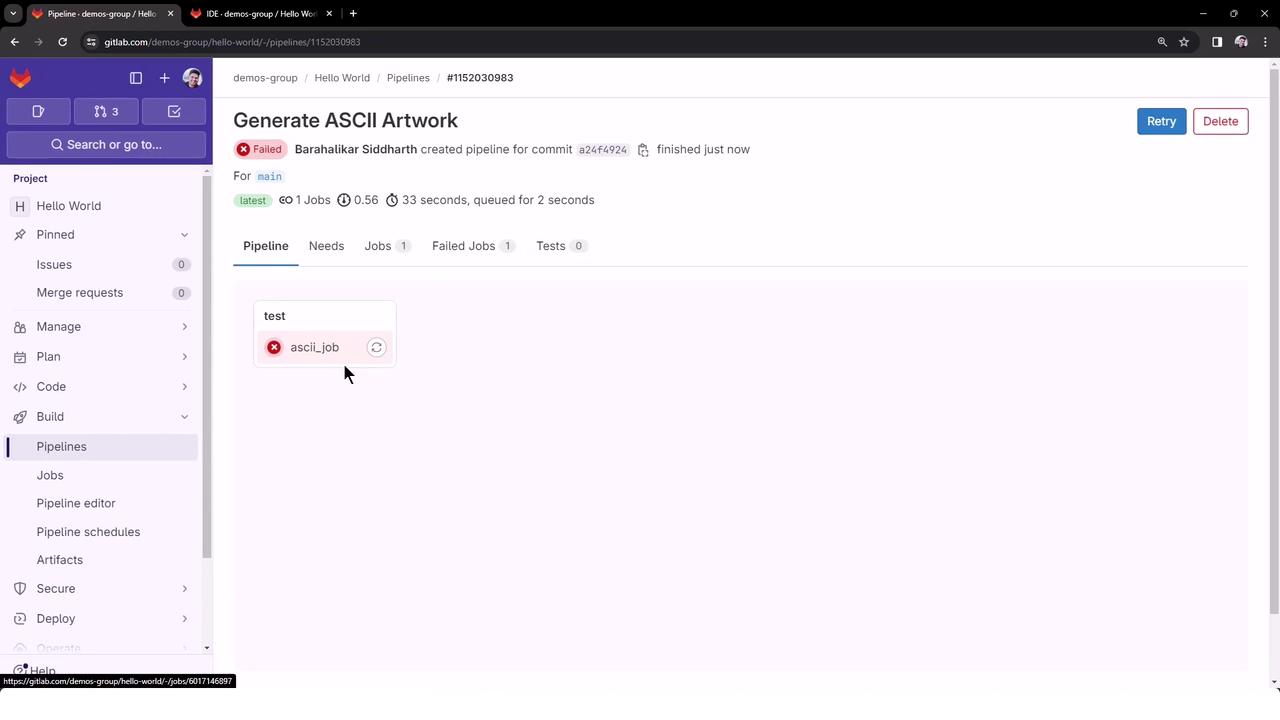
$ gem install cowsay
Successfully installed cowsay-0.3.0
1 gem installed
$ ./ascii-script.sh
/usr/bin/bash: ./ascii-script.sh: Permission denied
ERROR: Job failed: exit code 1
Permission Denied
Always ensure your shell scripts have execute permissions. Without chmod +x, GitLab runners cannot run them.
6. Grant Execute Permissions
Add a chmod step in before_script to make the script executable:
workflow:
name: Generate ASCII Artwork
ascii_job:
before_script:
- gem install cowsay
- chmod +x ascii-script.sh
script:
- ./ascii-script.sh
after_script:
- echo "Executed at the end, can be used for cleaning/removing content"
Commit and push. The next pipeline run will apply the new permissions automatically.
7. Confirm Successful Execution
Once fixed, your job logs should show:
$ chmod +x ascii-script.sh
$ ./ascii-script.sh
Generating ASCII Artwork using COWSAY Program
| Run for cover, I am a DRAGON....RAWR |
total 32
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 185 Jan 25 19:32 ascii-script.sh
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 6181 Jan 25 19:32 README.md
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 270 Jan 25 19:32 .gitlab-ci.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 948 Jan 25 19:32 dragon.txt
Running after_script
Job succeeded
With this pattern, your .gitlab-ci.yml stays concise, and complex logic lives in maintainable, version-controlled scripts.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content