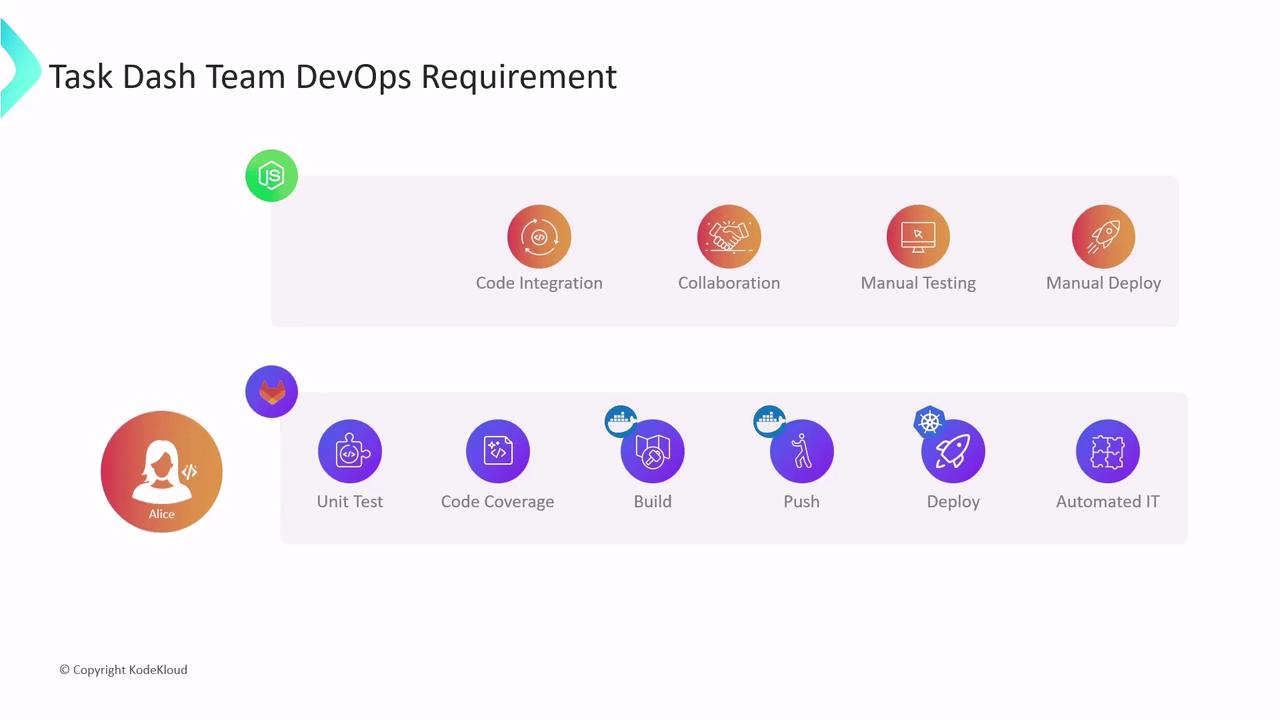
- No version control or branch management
- Manual code integration and testing
- Slow, unreliable test runs with low coverage
- Infrequent merges that elevate release risk
- Manual deployments to development, staging, and production
- Version control and collaboration on GitLab
- Automated unit tests with code coverage
- Docker image builds and registry pushes
- Deployment to Kubernetes clusters
- Automated integration tests before production rollout
Evaluating CI/CD Tools
The team evaluated several popular CI/CD platforms:| Tool | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | Highly extensible, large plugin ecosystem | Complex setup, infrastructure management |
| GitLab CI/CD | Integrated with GitLab, auto-scaling runners | Fewer community plugins compared to Jenkins |
| Travis CI | Simple YAML-based configuration | Limited concurrency, slower enterprise tier |
| CircleCI | Fast container performance, Docker support | Usage limits on free tier |
| GitHub Actions | Native to GitHub, rich marketplace | Requires GitHub ecosystem |
| Spinnaker | Advanced deployment strategies | Steep learning curve |
| Bamboo | Tight Atlassian integration | Licensing costs, less community-driven |
- Provision virtual machines with sufficient CPU, memory, and disk
- Install Java JDK, Jenkins, and required plugins
- Configure firewall rules and security groups
- Install and manage multiple Node.js versions and npm
- Install Docker for container builds
- Add Kubernetes tooling:
kubectl, Helm - Integrate external testing/reporting CLIs
- Java: Maven or Gradle
- Python: virtualenv, pip
- Cloud CLIs: AWS CLI, Azure CLI
- DevSecOps: vulnerability scanners like Trivy and KubeSec
Managing your own CI/CD infrastructure means spending more time on setup and maintenance rather than on writing pipelines.
- Require minimal infrastructure setup
- Let the team focus on pipeline authoring
- Provide built-in scalability and security

- Version control and merge request workflows
- Automated testing and code coverage
- Docker image creation and registry hosting
- Kubernetes deployments and rollbacks
- Integration testing and monitoring