GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Continuous Integration with GitLab
Exploring Reports through Merge Request
In this guide, we’ll dive into GitLab CI’s reports keyword to display both test and coverage reports directly in a Merge Request (MR). Instead of merely storing artifacts, you’ll provide reviewers with immediate feedback—failing tests, coverage metrics, and line-by-line highlights.
Configuring JUnit and Coverage Reports
Add JUnit and Cobertura reporting to your .gitlab-ci.yml:
variables:
MONGO_URI: 'mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData'
MONGO_USERNAME: superuser
MONGO_PASSWORD: $M_DB_PASSWORD
stages:
- test
unit_testing:
stage: test
image: node:17-alpine3.14
before_script:
- npm install
script:
- npm test
artifacts:
when: always
expire_in: 3 days
name: Moca-Test-Result
paths:
- test-results.xml
reports:
junit: test-results.xml
code_coverage:
stage: test
image: node:17-alpine3.14
before_script:
- npm install
script:
- npm run coverage
artifacts:
name: Code-Coverage-Result
when: always
expire_in: 3 days
reports:
coverage_report:
coverage_format: cobertura
path: coverage/ci_cobertura-coverage.xml
Note
Setting expire_in: 3 days keeps recent results accessible without long-term storage costs.
Editing Multiple Files in the Web IDE
- Open the project in GitLab’s Web IDE.
- Switch to your feature branch.
- Remove any placeholder jobs.
- Copy in the CI definitions above.
Introducing a Test Failure
In app-test.js, force a test to fail by expecting "Planet-Mercury" instead of "Mercury":
let chaiHttp = require("chai-http");
chai.should();
chai.use(chaiHttp);
describe('Planets API Suite', () => {
describe('Fetching Planet Details', () => {
it('it should fetch a planet named Mercury', (done) => {
let payload = { id: 1 };
chai.request(server)
.post('/planet')
.send(payload)
.end((err, res) => {
res.should.have.status(200);
res.body.should.have.property('id').eql(1);
// Expect mismatch to simulate failure
res.body.should.have.property('name').eql('Planet-Mercury');
done();
});
});
it('it should fetch a planet named Venus', (done) => {
let payload = { id: 2 };
// additional test code here
});
});
});
Creating a Coverage Gap
Introduce an untested line in app.js:
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
user: process.env.MONGO_USERNAME,
pass: process.env.MONGO_PASSWORD,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, function(err) {
if (err) {
console.log("error!! " + err);
console.log("DB Connection error!! " + err);
} else {
// console.log("MongoDB Connection Successful")
}
});
Running the Pipeline
Commit and push your changes. A new pipeline will start automatically:
sample-job:
stage: test
needs:
- code_coverage
image: node:17-alpine3.14
script:
- echo testing sample job
Warning
Align your coverage thresholds with team guidelines to avoid unexpected failures.
Other Report Types
GitLab supports multiple report formats:
| Report Type | Format | CI Keyword | Example Path |
|---|---|---|---|
| JUnit | JUnit XML | reports:junit | test-results.xml |
| Coverage | Cobertura XML | reports:coverage_report | coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml |
| RSpec JUnit | RspecJunitFormatter XML | reports:junit | rspec.xml |
rspec:
stage: test
script:
- bundle install
- rspec --format RspecJunitFormatter --out rspec.xml
artifacts:
reports:
junit: rspec.xml
artifacts:
reports:
coverage_report:
coverage_format: cobertura
path: coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml
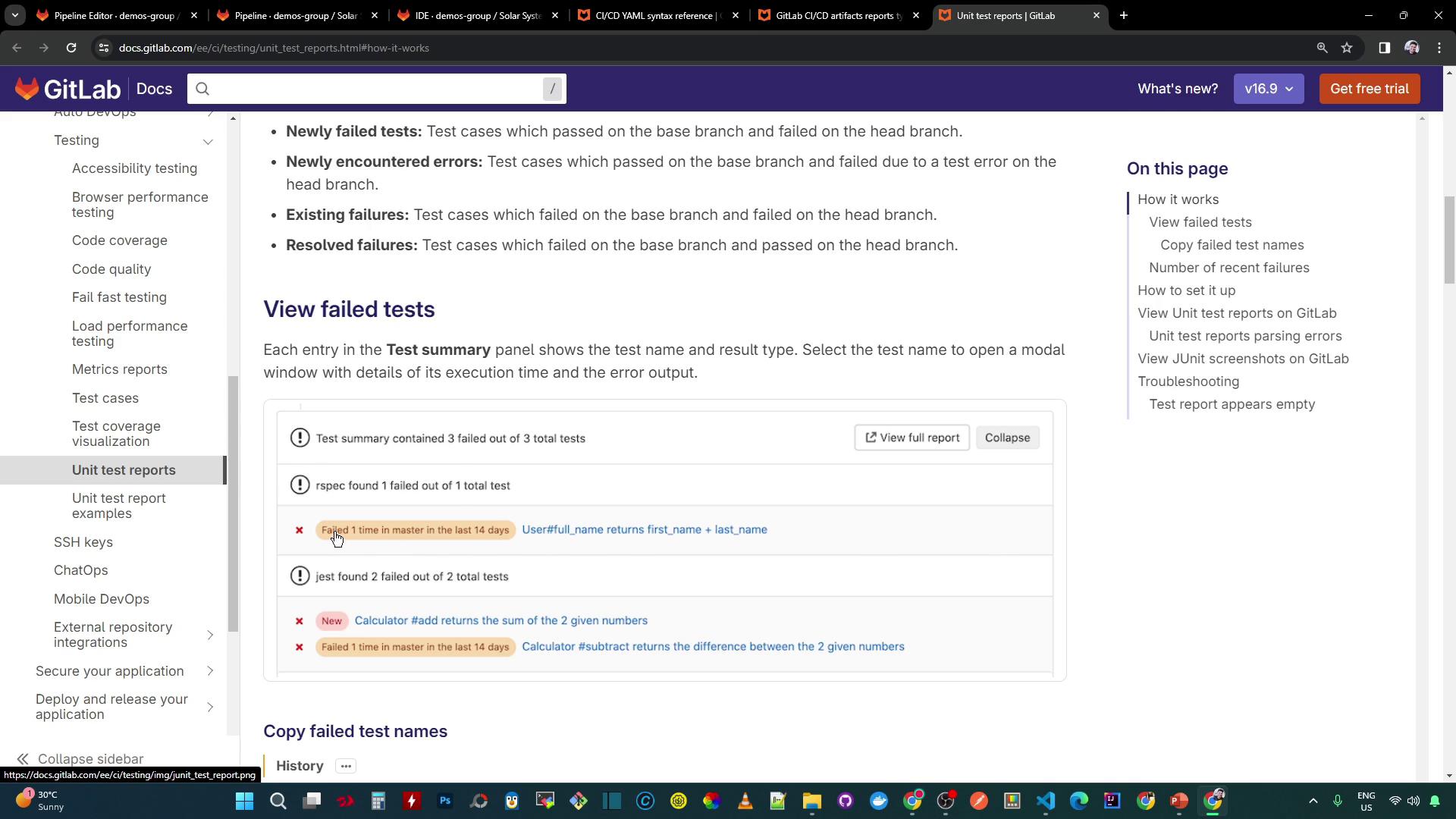
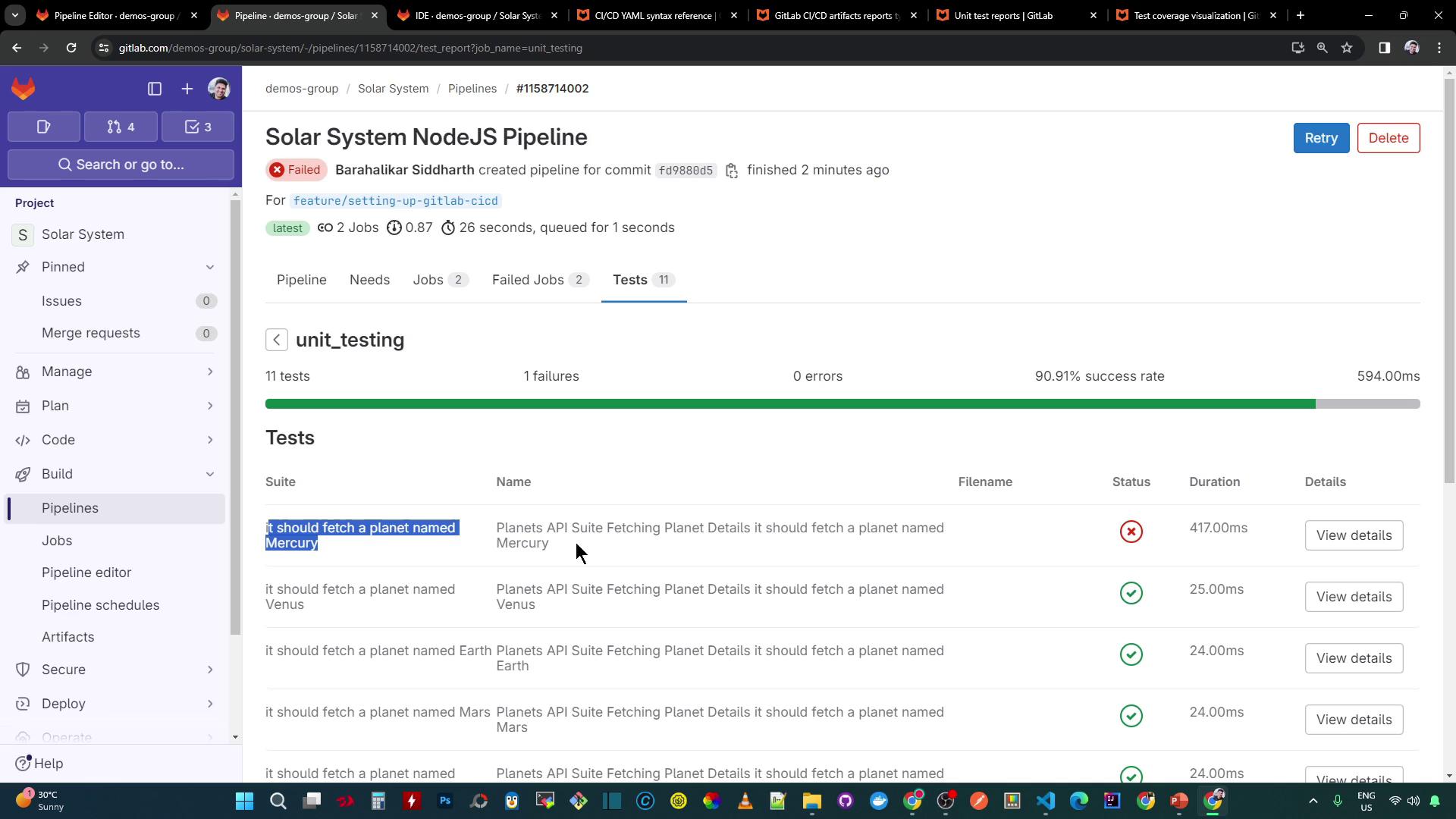
Viewing Test Failures in the Job Log
After the pipeline runs, review the job log for failures and coverage warnings:
ERROR: Coverage for lines (86.48%) does not meet global threshold (90%)
...
ERROR: Job failed: exit code 1
Exploring Reports in a Merge Request
Push your feature branch and open an MR titled Exploring GitLab CI/CD:
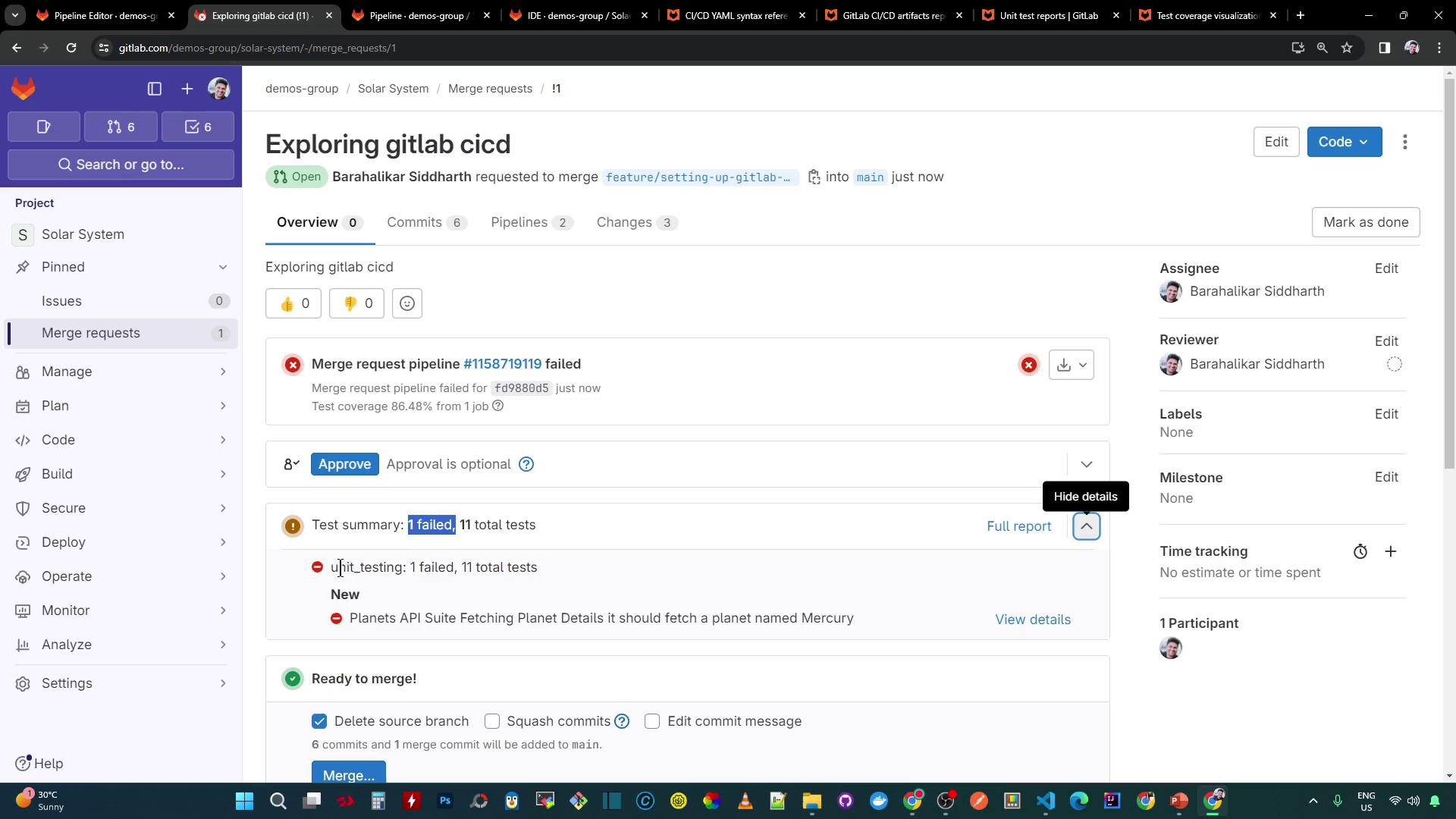
The MR pipeline runs via these workflow rules:
workflow: name: Solar System NodeJS Pipeline rules: - if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main" || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH =~ /^feature/' when: always - if: '$CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME =~ /^feature/ && $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"' when: alwaysCheck the MR sidebar for:
- A test summary (e.g., 1/11 failed)
- Coverage percentage
- Detailed assertion errors
In the Changes tab, you’ll see diffs highlighting:
- Modified test expectations
- New console logs in
app.js - Coverage gaps (orange) and covered lines (green)
Conclusion
By using GitLab CI’s reports keyword, you surface test results and coverage details directly within Merge Requests. This streamlines code reviews, enabling teams to catch failures and coverage gaps before merging.
Links and References
- GitLab CI/CD Reports Documentation
- JUnit Format Specification
- Cobertura Coverage Format
- GitLab Web IDE
- Chai HTTP
Watch Video
Watch video content