GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Continuous Integration with GitLab
Invalidate Cache
In this guide, you'll learn how to force cache invalidation in GitLab CI/CD whenever your project dependencies change. We’ll cover:
- Restoring an existing cache
- Updating dependencies locally
- Detecting a cache miss in the pipeline
- Rebuilding and saving a new cache
- Manually clearing the cache via the GitLab UI
This ensures your runners always use up-to-date artifacts, improving build reliability and performance.
1. Restoring the Existing Cache
When you run your pipeline without modifying dependencies, GitLab CI restores the cache using a key derived from the SHA of package-lock.json.
$ gitlab-runner --version
Running with gitlab-runner 16.6.0~beta.105.gd263193 (d263193)
…
Restoring cache
Checking cache for node_modules-eb6511c24d2374382b3f5272690bfa2122-non_protected…
Downloading cache from https://storage.googleapis.com/.../node_modules-eb6511c24d2374382b3f5272690bfa2122-non_protected
Successfully extracted cache
…
$ npm install
up to date, audited 365 packages in 1s
31 packages are looking for funding
…
$ npm test
This confirms that the existing cache was restored and used for the npm install step.
Note
GitLab CI uses the contents of package-lock.json to generate a unique cache key. Any modification to this file produces a new key.
2. Updating Dependencies Locally
To demonstrate cache invalidation, we’ll add nodemon as a dev dependency. Nodemon automatically restarts your Node.js server on file changes.
Switch to your feature branch
$ cd solar-system $ git checkout feature/setting-up-gitlab-ci Switched to branch 'feature/setting-up-gitlab-ci'Install
nodemonand update lockfiles$ npm install nodemon --save-dev added 384 packages, and audited 385 packages in 9s 45 packages are looking for fundingVerify changes in
package.json{ "dependencies": { "cors": "^2.8.5", "express": "^4.18.2", "mongoose": "^5.13.20", "nyc": "^15.1.0" }, "devDependencies": { "nodemon": "^3.0.3", "chai": "*" } }Commit and push
$ git add package.json package-lock.json $ git commit -m "chore: add nodemon as devDependency" $ git push origin feature/setting-up-gitlab-ci
3. Observing Cache Invalidation in the Pipeline
After pushing, the pipeline’s unit testing job will attempt to restore the cache with a newly generated key. Because package-lock.json changed, GitLab cannot find the old cache.
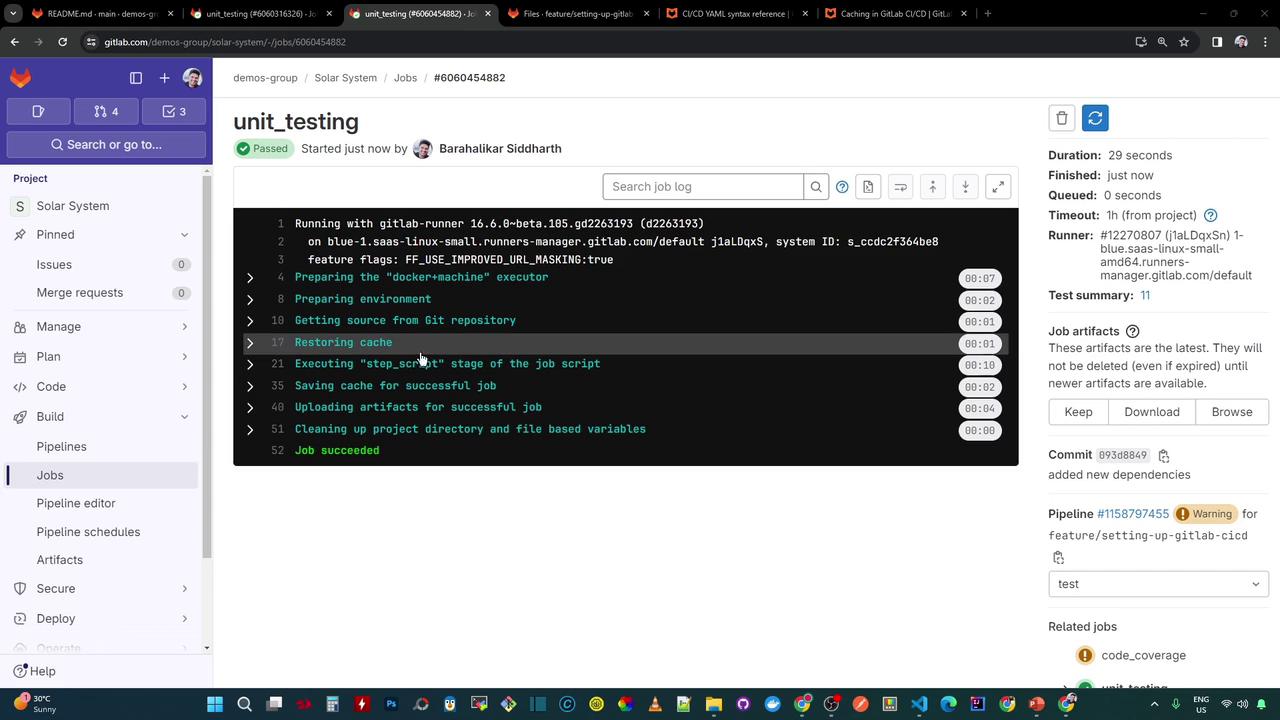
Restoring cache
Checking cache for node_modules-89184f59d584d146040c768c579d223d8bc7ab-non_protected…
WARNING: file does not exist
Failed to extract cache
…
Saving cache for successful job
Uploading artifacts for successful job
Job succeeded
| Phase | Cache Key (SHA) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Before dependency change | eb6511c24d2374382b3f5272690bfa2122 | Hit |
After adding nodemon | 89184f59d584d146040c768c579d223d8bc7ab | Miss |
Because the key changed, GitLab reports a cache miss and proceeds to install dependencies from scratch.
4. Rebuilding and Saving the New Cache
On cache miss, the job runs npm install again:
$ npm install
added 364 packages, and audited 385 packages in 7s
…
$ npm test
> Solar [email protected] test
> mocha app-test.js --timeout 10000 --reporter mocha-junit-reporter --exit
Server successfully running on port - 3000
After tests pass, GitLab saves a new cache under the updated key:
Saving cache for successful job
Creating cache node_modules-89184f59d584d146040c768c579d223d8bc7ab-non_protected…
node_modules: found 6041 matching artifact files and directories
Uploading cache.zip to https://storage.googleapis.com/.../node_modules-89184f59d584d146040c768c579d223d8bc7ab-non_protected
Created cache
Notice the increase in cached files (from ~5700 to ~6040) after adding nodemon.
5. Manually Clearing the Cache
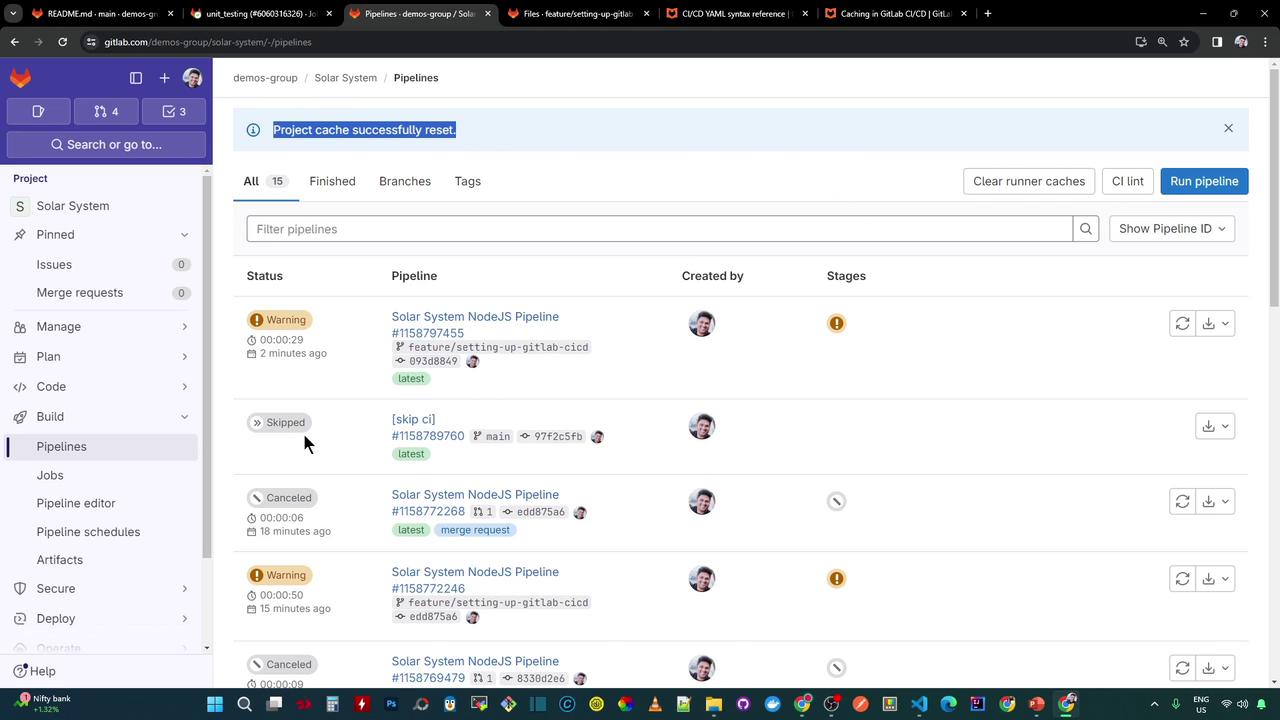
You can also clear all runner caches for your project via the GitLab UI:
- Go to CI/CD > Pipelines
- Click Clear runner caches
- Confirm the action
Warning
Clearing caches will remove all stored artifacts, potentially increasing build times until caches are rebuilt.
Links and References
By following this approach, you ensure GitLab CI invalidates and regenerates caches whenever your dependency lockfiles change, keeping your pipelines fast and reliable.
Watch Video
Watch video content