GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Continuous Integration with GitLab
Run and Test NodeJS App on Local Machine
Learn how to run and test the Solar System Node.js application locally before integrating it into a GitLab CI/CD pipeline. The source code is hosted on GitLab.
Prerequisites
- Node.js and npm
- A running MongoDB instance or Atlas cluster
- Git installed on your machine
To verify Node.js and npm:
node --version # e.g., v18.x.x
npm --version # e.g., 9.x.x
Clone the Repository
git clone https://gitlab.com/sidd-harth/solar-system.git
cd solar-system
Project Structure and Key Files
This repository includes:
- package.json: Defines metadata, scripts, dependencies, and coverage thresholds
- app.js: Backend Express.js server
- client.js: Frontend script to fetch planet data
- Dockerfile: Build instructions for a Docker image
- deployment.yaml & service.yaml: Kubernetes manifests
package.json
{
"name": "Solar System",
"version": "6.7.6",
"author": "Siddharth Barahalikar",
"license": "MIT",
"scripts": {
"start": "node app.js",
"test": "mocha app-test.js --timeout 10000 --reporter mocha-junit-reporter --exit",
"coverage": "nyc --reporter cobertura --reporter lcov --reporter text --reporter json-summary mocha app-test.js"
},
"nyc": {
"check-coverage": true,
"lines": 90
},
...
}
| Script | Description | Command |
|---|---|---|
| start | Launch the Express server | npm start |
| test | Run tests with Mocha and JUnit reporter | npm test |
| coverage | Generate coverage reports (cobertura, lcov) | npm run coverage |
Application Backend (app.js)
const path = require('path');
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cors = require('cors');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, '/')));
app.use(cors());
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
user: process.env.MONGO_USERNAME,
pass: process.env.MONGO_PASSWORD,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error("Connection error:", err);
} else {
console.log("Connected to MongoDB");
}
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server running on port 3000");
});
Note
Ensure you add your REST API route handlers in app.js (for example, a GET /os endpoint) before testing.
Frontend Controller (client.js)
console.log('Client script loaded');
window.onload = () => {
console.log("Requesting all planets");
fetch("/os", { method: "GET" })
.then(res => res.ok ? res.json() : Promise.reject("Fetch error"))
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
};
Dockerfile
FROM node:18-alpine3.17
WORKDIR /usr/app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
ENV MONGO_URI=uriPlaceholder
ENV MONGO_USERNAME=usernamePlaceholder
ENV MONGO_PASSWORD=passwordPlaceholder
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["npm", "start"]
Kubernetes Manifests
# deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: solar-system
labels:
app: solar-system
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: solar-system
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: solar-system
spec:
containers:
- name: solar-system
image: your-repo/solar-system:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
# service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: solar-system
labels:
app: solar-system
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: solar-system
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
| Resource Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Manages pods and rolling updates | Defined in deployment.yaml |
| Service | Exposes pods on the network | Defined in service.yaml |
Install Dependencies
npm install
You may see notices:
44 packages are looking for funding
Run `npm fund` for details
1 high severity vulnerability
To address all issues, run:
npm audit fix
Running the Server Locally
After dependencies are installed:
npm start
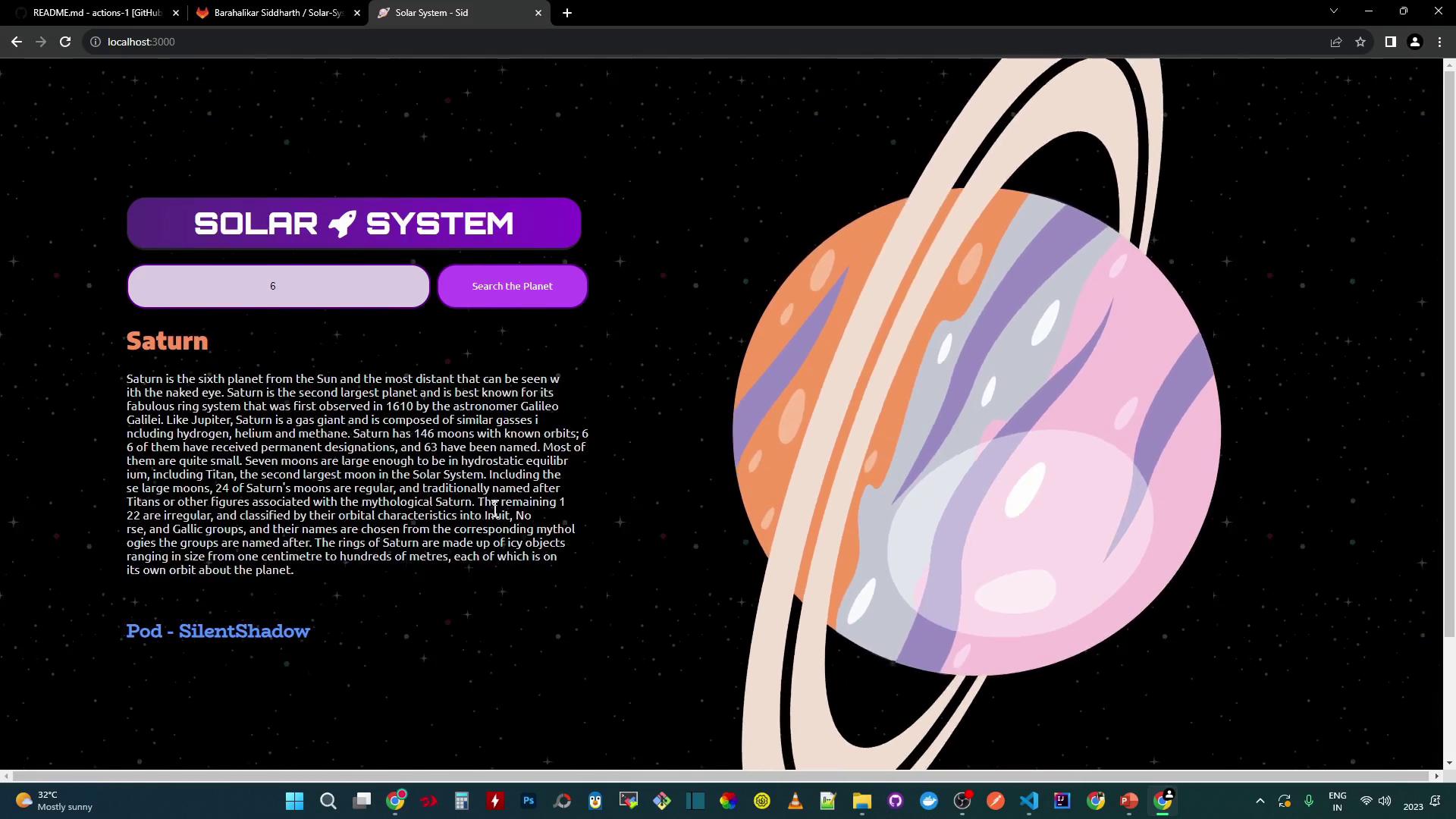
Open http://localhost:3000 in your browser:
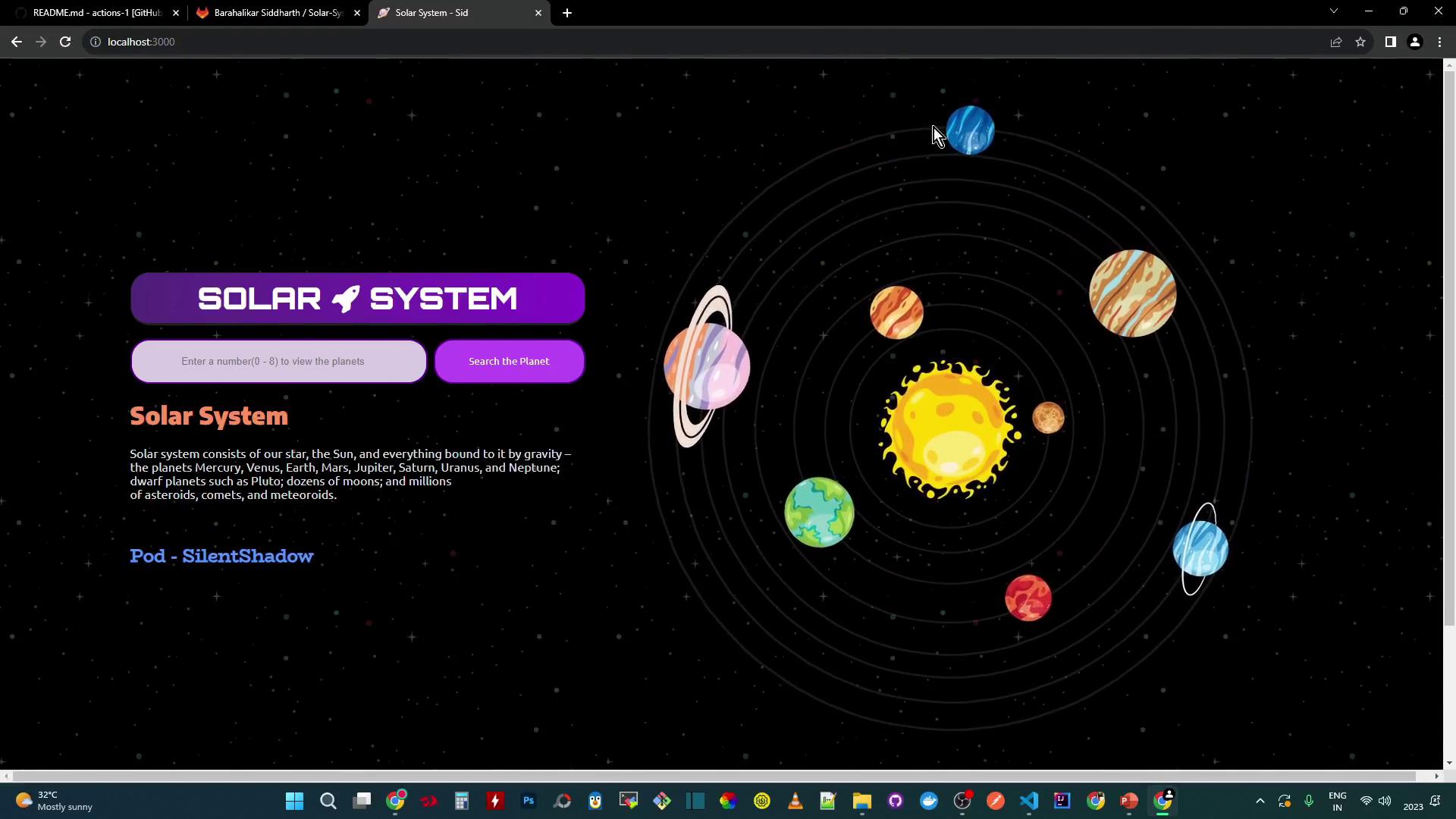
You can search by ID (e.g., 3 for Earth, 6 for Saturn). Data is fetched from your MongoDB.
Testing the Application
Run the test suite:
npm test
If environment variables are missing, you will see:
MongooseError: The `uri` parameter to `openUri()` must be a string, got `undefined`.
Warning
Tests will fail without MONGO_URI, MONGO_USERNAME, and MONGO_PASSWORD. Set these before running npm test.
Temporary Local Credentials
For a quick local demo, hard-code your MongoDB URI in app.js:
mongoose.connect('mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData', {
user: 'superuser',
pass: 'SuperPassword',
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, (err) => {
if (err) console.error("Connection error:", err);
});
Re-run tests:
npm test
echo $? # 0 means success
A test_results.xml file is generated for CI/CD:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<testsuites name="Mocha Tests" time="3.953" tests="11" failures="0">
<testsuite name="Planets API Suite" tests="8" time="3.953">
<testcase name="Fetching Planet Details - Mercury" time="2.350" />
<testcase name="Fetching Planet Details - Venus" time="0.224" />
<!-- more testcases -->
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
Coverage Report
Generate coverage:
npm run coverage
11 passing (4s)
ERROR: Coverage for lines (88.88%) does not meet global threshold (90%)
A non-zero exit code will signal coverage failures in CI pipelines.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content